
Glycine reductase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a glycine reductase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
The 4 substrates
of this enzyme are acetyl phosphate, NH3
, thioredoxin disulfide, and H2O
, whereas its 3 products
are glycine
, phosphate
, and thioredoxin
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductase
s, to be specific, those acting on X-H and Y-H to form an X-Y bond with a disulfide as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is acetyl-phosphate ammonia:thioredoxin disulfide oxidoreductase (glycine-forming).
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- acetyl phosphate + NH3 + thioredoxin disulfide + H2O
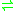 glycine + phosphate + thioredoxin
glycine + phosphate + thioredoxin
The 4 substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are acetyl phosphate, NH3
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
, thioredoxin disulfide, and H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, whereas its 3 products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are glycine
Glycine
Glycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
, phosphate
Phosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
, and thioredoxin
Thioredoxin
Thioredoxin is a class of small redox proteins known to be present in all organisms. It plays a role in many important biological processes. In humans, it is encoded by the TXN gene. Loss-of-function mutation of either of the two human thioredoxin genes is lethal at the four-cell stage of the...
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductase
Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another...
s, to be specific, those acting on X-H and Y-H to form an X-Y bond with a disulfide as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is acetyl-phosphate ammonia:thioredoxin disulfide oxidoreductase (glycine-forming).

