Georgian National Communications Commission
Encyclopedia
The Georgian National Communications Commission (GNCC) was established in 2000 as an independent regulatory body to license and oversee the operations of telecommunication and broadcasting companies within the national territory
. The GNCC consists of 5 members, appointed by the President of Georgia
and approved by Parliament. The Commission is fully independent and not subordinated to any state authorities.The budget is entirely funded through regulation fees paid by companies and telecom operators using the Georgian radiofrequency spectrum. The GNCC does not receive any funding from the state budget
.
The establishment of the GNCC was deemed as an important step forward in strengthening the transparency and competition of the Georgian telecommunications sector, aimed at the protection of consumer interests and the provision of a fair, equitable, and predictable regulatory environment for market players.
The GNCC is the only authority in Georgia to issue and suspend licenses in electronic communications and broadcasting on the basis of the fair competition and auctions. The Commission monitors activities of licensees and their compliance with the terms of license. As a part of its monitoring functions, GNCC maintains and processes data on the operations of license holders. The GNCC monitors the compliance of the license holders with Georgia’s laws “On Broadcasting”, “on Copyright”, “on Protection of Minors From Harmful Influence”, “on Advertising” and “On State Secret”.
The GNCC is tasked with the definition and allocation of Georgia’s national radio frequency
spectrum, certification of electronic communications and broadcasting facilities, standardization, provision of metrological services, etc. The GNCC controls and restricts unauthorized and unlicensed access and use of the radio frequencies and means of electronic communications in Georgia. In the event of unauthorized use of frequencies or communication facilities, the GNCC is responsible for the application and enforcement of penalties envisaged by the laws of Georgia.
s, institutions and unions such as the EBRD, CE, USAID
, etc. In 2001, the GNCC became an Associate Member of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). In 2007, in accordance with the ETSI rules of procedure, the GNCC became a full Administration Member of ETSI. In February, 2005, Georgia joined the ICANN/GAC and became the 100th member of Governmental Advisory Committee of Internet Corporation of Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN/GAC). According to the decision of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Georgia GNCC represents the interests of Georgia in this Committee. In 2007, the group became a full member of European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations
(CEPT). GNCC closely collaborates with CEPT as the regulatory authority for telecommunications and broadcasting in Georgia.
The GNCC is a fully transparent public authority
, whose operations information, management, and administrative procedures are open to public review.
of illegal, unlicensed business operations
within Georgia’s national territory, as well as participation in the Russian military’s invasion of the country in August, 2008. In a press release
, the GNCC has compared MegaFon’s operations in Georgia to “economic annexation.”*
The GNCC claims that the Mobile Communications Company registered in the Russian Federation
, “MegaFon”, started its illegal operations back in 2005 in the conflict zones of Georgia, in particular–South Ossetia region. Using the Georgian radiofrequency bandwidth, the Russian company provided coverage mostly in the areas of dislocation of the Russian military
forces (participating in the UNOMIG
mission). The rest of the area was mostly covered by the Georgian Communication Companies “Geocell” Ltd. and “Magticom". In the spring of 2008, the GNCC received complaints from Georgian mobile phone
carriers alleging destruction of their communication facilities and antennas in the region and installation of MefaFon antennas.
On June 5, 2008, the GNCC conducted a monitoring survey of the spectrum use in Zemo Nikozi, in the Tskhinvali region of South Ossetia
. Representatives of the Monitoring Department of the Commission conducted tests to identify the users of GSM-900 spectrum radio frequencies. The technical results show that MegaFon is maintaining unlicensed network coverage in the area. Since 2005, MegaFon has conducted retail sales
of SIM cards for consumer use within Georgia, as confirmed by the explanatory letters of local citizens using MegaFon services. Notably MegaFon never sought or received an authorization or license from the GNCC to operate in any part of Georgia.
On the basis of Administrative legislation of Georgia GNCC imposed two fines on MegaFon, the first–in the amount of 5000 GEL ($3,750.00 USD) in July 2008, and the second, for the recurrence of violation in the amount of 500,000 GEL (approx. $350,000.00 USD) in September 2008. GNCC transferred the files on violations, committed by MegaFon to the General Prosecutor of Georgia for initiating criminal proceedings against the key officials of MegaFon.
In August, 2008, during the Russian military intervention in Georgia, the company expanded the coverage area beyond the conflict zone. Namely, the coverage area now included the territory of the former Autonomous Province
of South Ossetia and Gori and Kareli districts of Georgia. On September 16, due to the findings of the second monitoring mission of GNCC and establishing its extended coverage
, “MegaFon” was fined with 500,000 GEL.On October 2 2008 Tbilisi City Court upheld the decision of GNCC and dismissed the claim of MegaFon, which was held liable for providing unlicensed telecommunication services in Georgia.
MegaFon’s appeal of the second administrative fine shall be discussed by Tbilisi City Court in November 2008.
The business news portal MediaGuide.ru reported that the Russian government
asked MegaFon on August 14 to send a number of "base stations" to the so called South Ossetia to connect with systems in neighboring North Ossetia, part of the Russian Federation. The government stated that the signal for one of two existing South Ossetian communication networks
, routed through Tbilisi, was "very weak" and had no "guaranteed stability." Once the stations were in place, MegaFon’s signal could be picked up as well in the neighboring Georgian town of Gori. GNCC declares that no Russian mobile communication company have been rooting any signal via Tbilisi, moreover, the separatist region does not have any “existing” communication networks. Therefore, the talks of expanded MegaFon coverage rather attempt to justify its illegal economic invasion in Georgia, whereas MegaFon itself has been and persisted to deny its operations in Georgia even in September. Numerous articles in Russian media, including Moscow Times
publish declarations by the separatist leaders, in particular Aduard Kokoity on the long-awaited expansion of the MegaFon network and multiplying the number of customers to 36,000.
National territory
"National Territory" is translated from "Territorio nacional", a term used for territories in Argentina. The last national territory was the Tierra del Fuego Province, which was given the status of a province in 1990....
. The GNCC consists of 5 members, appointed by the President of Georgia
President of Georgia
The President of Georgia is the head of state, supreme commander-in-chief and holder of the highest office within the Government of Georgia. Executive power is split between the President and the Prime Minister, who is the head of government...
and approved by Parliament. The Commission is fully independent and not subordinated to any state authorities.The budget is entirely funded through regulation fees paid by companies and telecom operators using the Georgian radiofrequency spectrum. The GNCC does not receive any funding from the state budget
Budget
A budget is a financial plan and a list of all planned expenses and revenues. It is a plan for saving, borrowing and spending. A budget is an important concept in microeconomics, which uses a budget line to illustrate the trade-offs between two or more goods...
.
Core mandate and functions of the GNCC
- Ensuring fair competition in the communications and broadcasting sector;
- Issuing and revoking authorizations for communication and broadcasting companies, seeking to operate in Georgia;
- Issuing licenses for communication and broadcasting companies to operate in Georgia;
- Overseeing public auctions of Georgia’s frequency bandwidth to competing operators;
- Mediating disputes between the communication and broadcasting companies in Georgia;
The establishment of the GNCC was deemed as an important step forward in strengthening the transparency and competition of the Georgian telecommunications sector, aimed at the protection of consumer interests and the provision of a fair, equitable, and predictable regulatory environment for market players.
The GNCC is the only authority in Georgia to issue and suspend licenses in electronic communications and broadcasting on the basis of the fair competition and auctions. The Commission monitors activities of licensees and their compliance with the terms of license. As a part of its monitoring functions, GNCC maintains and processes data on the operations of license holders. The GNCC monitors the compliance of the license holders with Georgia’s laws “On Broadcasting”, “on Copyright”, “on Protection of Minors From Harmful Influence”, “on Advertising” and “On State Secret”.
The GNCC is tasked with the definition and allocation of Georgia’s national radio frequency
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
spectrum, certification of electronic communications and broadcasting facilities, standardization, provision of metrological services, etc. The GNCC controls and restricts unauthorized and unlicensed access and use of the radio frequencies and means of electronic communications in Georgia. In the event of unauthorized use of frequencies or communication facilities, the GNCC is responsible for the application and enforcement of penalties envisaged by the laws of Georgia.
Collaboration with international organizations
To ensure compliance with its core mandate and goals, the GNCC closely collaborates with international organizationInternational organization
An intergovernmental organization, sometimes rendered as an international governmental organization and both abbreviated as IGO, is an organization composed primarily of sovereign states , or of other intergovernmental organizations...
s, institutions and unions such as the EBRD, CE, USAID
United States Agency for International Development
The United States Agency for International Development is the United States federal government agency primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid. President John F. Kennedy created USAID in 1961 by executive order to implement development assistance programs in the areas...
, etc. In 2001, the GNCC became an Associate Member of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). In 2007, in accordance with the ETSI rules of procedure, the GNCC became a full Administration Member of ETSI. In February, 2005, Georgia joined the ICANN/GAC and became the 100th member of Governmental Advisory Committee of Internet Corporation of Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN/GAC). According to the decision of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Georgia GNCC represents the interests of Georgia in this Committee. In 2007, the group became a full member of European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations
European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations
The European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations was established on June 26, 1959, as a coordinating body for European state telecommunications and postal organizations...
(CEPT). GNCC closely collaborates with CEPT as the regulatory authority for telecommunications and broadcasting in Georgia.
The GNCC is a fully transparent public authority
Public benefit corporation
A public-benefit corporation is a public corporation chartered by a state designed to perform some public benefit.A public authority is a type of public-benefit corporation that takes on a more bureaucratic role, such as the maintenance of public infrastructure, that often has broad powers to...
, whose operations information, management, and administrative procedures are open to public review.
Georgian National Communications Commission vs Megafon
In a recent notable case, the GNCC has accused the Russian mobile telecommunications provider MegaFonMegaFon
MegaFon ,previously known as North-West GSM, is the second largest mobile phone operator in Russia. It works in the GSM and UMTS standard. Its main competitors are Bee Line GSM and Mobile TeleSystems ....
of illegal, unlicensed business operations
Business operations
Business operations are those ongoing recurring activities involved in the running of a business for the purpose of producing value for the stakeholders...
within Georgia’s national territory, as well as participation in the Russian military’s invasion of the country in August, 2008. In a press release
News release
A press release, news release, media release, press statement or video release is a written or recorded communication directed at members of the news media for the purpose of announcing something ostensibly newsworthy...
, the GNCC has compared MegaFon’s operations in Georgia to “economic annexation.”*
The GNCC claims that the Mobile Communications Company registered in the Russian Federation
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, “MegaFon”, started its illegal operations back in 2005 in the conflict zones of Georgia, in particular–South Ossetia region. Using the Georgian radiofrequency bandwidth, the Russian company provided coverage mostly in the areas of dislocation of the Russian military
Armed Forces of the Russian Federation
The Armed Forces of the Russian Federation are the military services of Russia, established after the break-up of the Soviet Union. On 7 May 1992 Boris Yeltsin signed a decree establishing the Russian Ministry of Defence and placing all Soviet Armed Forces troops on the territory of the RSFSR...
forces (participating in the UNOMIG
United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia
The United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia was established by United Nations Security Council Resolution 858 in August 1993 to verify compliance with a 27 July 1993 ceasefire agreement between the Republic of Georgia and forces in Abkhazia with special attention given to the situation in the...
mission). The rest of the area was mostly covered by the Georgian Communication Companies “Geocell” Ltd. and “Magticom". In the spring of 2008, the GNCC received complaints from Georgian mobile phone
Mobile phone
A mobile phone is a device which can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile network operator...
carriers alleging destruction of their communication facilities and antennas in the region and installation of MefaFon antennas.
On June 5, 2008, the GNCC conducted a monitoring survey of the spectrum use in Zemo Nikozi, in the Tskhinvali region of South Ossetia
South Ossetia
South Ossetia or Tskhinvali Region is a disputed region and partly recognized state in the South Caucasus, located in the territory of the South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast within the former Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic....
. Representatives of the Monitoring Department of the Commission conducted tests to identify the users of GSM-900 spectrum radio frequencies. The technical results show that MegaFon is maintaining unlicensed network coverage in the area. Since 2005, MegaFon has conducted retail sales
Retailing
Retail consists of the sale of physical goods or merchandise from a fixed location, such as a department store, boutique or kiosk, or by mail, in small or individual lots for direct consumption by the purchaser. Retailing may include subordinated services, such as delivery. Purchasers may be...
of SIM cards for consumer use within Georgia, as confirmed by the explanatory letters of local citizens using MegaFon services. Notably MegaFon never sought or received an authorization or license from the GNCC to operate in any part of Georgia.
On the basis of Administrative legislation of Georgia GNCC imposed two fines on MegaFon, the first–in the amount of 5000 GEL ($3,750.00 USD) in July 2008, and the second, for the recurrence of violation in the amount of 500,000 GEL (approx. $350,000.00 USD) in September 2008. GNCC transferred the files on violations, committed by MegaFon to the General Prosecutor of Georgia for initiating criminal proceedings against the key officials of MegaFon.
In August, 2008, during the Russian military intervention in Georgia, the company expanded the coverage area beyond the conflict zone. Namely, the coverage area now included the territory of the former Autonomous Province
Autonomous area
An autonomous area or autonomous entity is an area of a country that has a degree of autonomy, or freedom from an external authority. Typically it is either geographically distinct from the rest of the country or populated by a national minority. Countries that include autonomous areas are often...
of South Ossetia and Gori and Kareli districts of Georgia. On September 16, due to the findings of the second monitoring mission of GNCC and establishing its extended coverage
Extended coverage
Extended coverage is a term used in the property insurance business. All insurance policies have exclusions - specific causes of loss that are not covered by the insurance company. An Extended coverage endorsement was a common extension of property insurance beyond coverage for fire and lightning...
, “MegaFon” was fined with 500,000 GEL.On October 2 2008 Tbilisi City Court upheld the decision of GNCC and dismissed the claim of MegaFon, which was held liable for providing unlicensed telecommunication services in Georgia.
MegaFon’s appeal of the second administrative fine shall be discussed by Tbilisi City Court in November 2008.
| MegaFon coverage in Georgia before Russian invasion | MegaFon coverage in Georgia after Russian invasion |
|---|---|
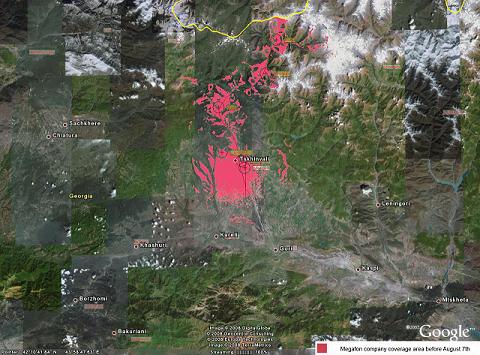 |
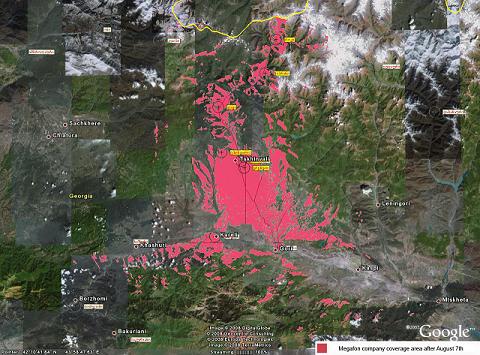 |
The business news portal MediaGuide.ru reported that the Russian government
Politics of Russia
The politics of Russia take place in a framework of a federal semi-presidential republic. According to the Constitution of Russia, the President of Russia is head of state, and of a multi-party system with executive power exercised by the government, headed by the Prime Minister, who is appointed...
asked MegaFon on August 14 to send a number of "base stations" to the so called South Ossetia to connect with systems in neighboring North Ossetia, part of the Russian Federation. The government stated that the signal for one of two existing South Ossetian communication networks
Telecommunications network
A telecommunications network is a collection of terminals, links and nodes which connect together to enable telecommunication between users of the terminals. Networks may use circuit switching or message switching. Each terminal in the network must have a unique address so messages or connections...
, routed through Tbilisi, was "very weak" and had no "guaranteed stability." Once the stations were in place, MegaFon’s signal could be picked up as well in the neighboring Georgian town of Gori. GNCC declares that no Russian mobile communication company have been rooting any signal via Tbilisi, moreover, the separatist region does not have any “existing” communication networks. Therefore, the talks of expanded MegaFon coverage rather attempt to justify its illegal economic invasion in Georgia, whereas MegaFon itself has been and persisted to deny its operations in Georgia even in September. Numerous articles in Russian media, including Moscow Times
The Moscow Times
The Moscow Times is an English-language daily newspaper published in Moscow, Russia since 1992. The circulation in 2008 stood at 35,000 copies and the newspaper is typically given out for free at places English-language "expats" attend, including hotels, cafés and restaurants, as well as by...
publish declarations by the separatist leaders, in particular Aduard Kokoity on the long-awaited expansion of the MegaFon network and multiplying the number of customers to 36,000.
External links
- Georgian National Communications Commission
- Reuters: Georgia's Communications Commission Fines Russia's Megafon; Decries 'Economic Annexation'
- Reuters:Georgia threatens to multiply Russia MegaFon fine
- Reuters: Georgia files charges against Russia's MegaFon
- Reuters: Megafon Goes to Court in Georgia over Disputed South Ossetia Operations
- EurasiaNet: THE FIGHT BETWEEN TBILISI AND MOSCOW OVER SOUTH OSSETIA GOES CELLULAR
- Reuters: Court Upholds Fine Against Megafon for Illegal Operations in Georgia
- Guardian: Dreams of empire strike back Q: What do Osama bin Laden and Vladimir Putin have in common? A: Worrying ambitions to reverse imperial decline

