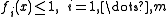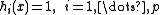Geometric programming
Encyclopedia
A geometric program is an optimization
problem of the form
In the context of geometric programming (unlike all other disciplines), a monomial is defined as a function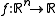 with
with 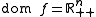 defined as
defined as
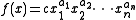
where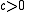 and
and 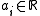 .
.
GPs have numerous application, such as components sizing in IC
design and parameter estimation via logistic regression in statistics. The maximum likelihood
estimator in logistic regression
is a GP.
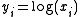 , the monomial
, the monomial 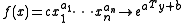 , where
, where 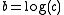 .
.
Similarly, if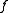 is the posynomial
is the posynomial
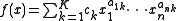
then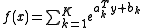 , where
, where 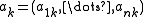 and
and 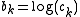 . After the change of variables, a posynomial becomes a sum of exponentials of affine functions.
. After the change of variables, a posynomial becomes a sum of exponentials of affine functions.
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
problem of the form
- Minimize
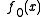 subject to
subject to
-
- where
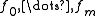 are posynomials and
are posynomials and 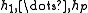 are monomials.
are monomials.
In the context of geometric programming (unlike all other disciplines), a monomial is defined as a function
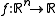 with
with 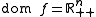 defined as
defined as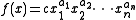
where
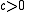 and
and 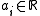 .
.GPs have numerous application, such as components sizing in IC
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
design and parameter estimation via logistic regression in statistics. The maximum likelihood
Maximum likelihood
In statistics, maximum-likelihood estimation is a method of estimating the parameters of a statistical model. When applied to a data set and given a statistical model, maximum-likelihood estimation provides estimates for the model's parameters....
estimator in logistic regression
Logistic regression
In statistics, logistic regression is used for prediction of the probability of occurrence of an event by fitting data to a logit function logistic curve. It is a generalized linear model used for binomial regression...
is a GP.
Convex form
Geometric programs are not (in general) convex optimization problems, but they can be transformed to convex problems by a change of variables and a transformation of the objective and constraint functions. In particular, defining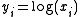 , the monomial
, the monomial 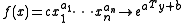 , where
, where 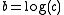 .
.Similarly, if
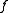 is the posynomial
is the posynomial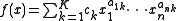
then
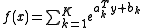 , where
, where 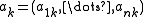 and
and 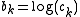 . After the change of variables, a posynomial becomes a sum of exponentials of affine functions.
. After the change of variables, a posynomial becomes a sum of exponentials of affine functions.External links
- S. Boyd, S. J. Kim, L. Vandenberghe, and A. Hassibi, A Tutorial on Geometric Programming
- S. Boyd, S. J. Kim, D. Patil, and M. Horowitz Digital Circuit Optimization via Geometric Programming