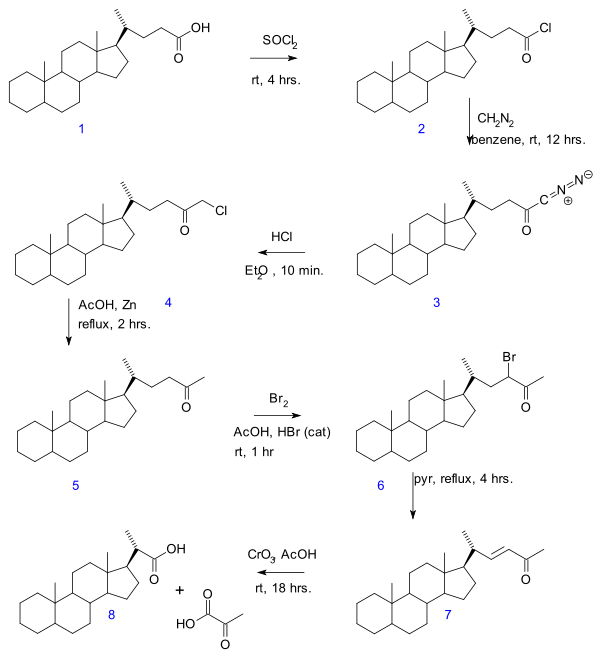
Gallagher-Hollander degradation
Encyclopedia
In the Gallagher-Hollander Degradation (1946) pyruvic acid
is removed from a linear aliphatic carboxylic acid
yielding a new acid with 2 carbon atoms less . The original publication concerns the conversion of bile acid
in a series of reactions: acid chloride (2) formation with thionyl chloride
, diazoketone formation (3) with diazomethane
, chloromethyl ketone formation (4) with hydrochloric acid
, organic reduction of chlorine to methylketone (5), ketone halogenation
to 6, elimination reaction
with pyridine
to enone
7 and finally oxidation with chromium trioxide
to bisnorcholanic acid 8.
Pyruvic acid
Pyruvic acid is an organic acid, a ketone, as well as the simplest of the alpha-keto acids. The carboxylate ion of pyruvic acid, CH3COCOO−, is known as pyruvate, and is a key intersection in several metabolic pathways....
is removed from a linear aliphatic carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
yielding a new acid with 2 carbon atoms less . The original publication concerns the conversion of bile acid
Bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals. Bile salts are bile acids compounded with a cation, usually sodium. In humans, the salts of taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid represent approximately eighty percent of all bile salts. The two major bile acids are cholic...
in a series of reactions: acid chloride (2) formation with thionyl chloride
Thionyl chloride
Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula SOCl2. It is a reactive chemical reagent used in chlorination reactions. It is a colorless, distillable liquid at room temperature and pressure that decomposes above 140 °C. Thionyl chloride is sometimes confused with sulfuryl...
, diazoketone formation (3) with diazomethane
Diazomethane
Diazomethane is the chemical compound CH2N2. It is the simplest of diazo compounds. In the pure form at room temperature, it is a extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas, thus it is almost universally used as a solution in diethyl ether...
, chloromethyl ketone formation (4) with hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid is a solution of hydrogen chloride in water, that is a highly corrosive, strong mineral acid with many industrial uses. It is found naturally in gastric acid....
, organic reduction of chlorine to methylketone (5), ketone halogenation
Ketone halogenation
In organic chemistry ketone halogenation is a special type of halogenation.The position alpha to the carbonyl group in a ketone is easily halogenated, due to the ability to form an enolate in basic solution, or an enol in acidic solution...
to 6, elimination reaction
Elimination reaction
An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one or two-step mechanism...
with pyridine
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
to enone
Enone
An enone is an unsaturated chemical compound or functional group consisting of a conjugated system of an alkene and a ketone. The simplest enone is methyl vinyl ketone or CH2=CHCOCH3....
7 and finally oxidation with chromium trioxide
Chromium trioxide
Chromium trioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula CrO3. It is the acidic anhydride of chromic acid, and is sometimes marketed under the same name.This compound is a dark-red/orange brown solid, which dissolves in water concomitant with hydrolysis...
to bisnorcholanic acid 8.