
Full frame digital SLR
Encyclopedia
Digital single-lens reflex camera
Most digital single-lens reflex cameras are digital cameras that use a mechanical mirror system and pentaprism to direct light from the lens to an optical viewfinder on the back of the camera....
(DSLR) fitted with an image sensor
Image sensor
An image sensor is a device that converts an optical image into an electronic signal. It is used mostly in digital cameras and other imaging devices...
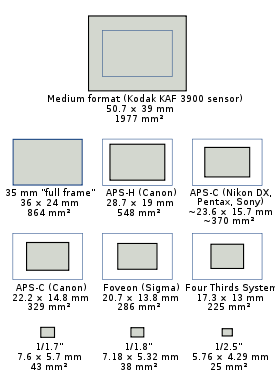
that is the same size as a 35 mm
135 film
The term 135 was introduced by Kodak in 1934 as a designation for cartridge film wide, specifically for still photography. It quickly grew in popularity, surpassing 120 film by the late 1960s to become the most popular photographic film format...
(36×24 mm) film frame.
This is in contrast to cameras with smaller sensors, typically of a size equivalent to APS-C
APS-C
Advanced Photo System type-C is an image sensor format approximately equivalent in size to the Advanced Photo System "classic" size negatives...
-size film, much smaller than a full 35 mm frame. Currently, the majority of digital cameras, both compact and SLR models, use a smaller-than-35 mm frame, as it is easier and cheaper to manufacture imaging sensors at a smaller size. Historically, the earliest digital SLR models, such as the Nikon NASA F4
Nikon NASA F4
The Nikon NASA F4 Electronic Still Camera was one of the first and rarest fully digital cameras ever. Constructed for NASA, it was first flown in September 1991 on board the Space Shuttle Discovery, mission STS-48...
or Kodak DCS 100, also used a smaller sensor.
Use of 35 mm film-camera lenses
If the lens mounts are compatible, many lenses, including manual-focus models, designed for 35 mm cameras can be mounted on the latest DSLR cameras. When a lens designed for a full-frame camera, whether film or digital, is mounted on a DSLR with a smaller sensor size, only the center of the lens's image circleImage circle
The image circle, or circle of illumination, of a lens is the circular area in the image plane formed by the cone of light transmitted by the lens . Within this circle is the smaller circle for which image definition is acceptable, the circle of good definition ; however, some authors make no...
is captured. The edges are cropped off, which is equivalent to zooming in on the center section of the imaging area. The ratio of the size of the full-frame 35 mm format to the size of the smaller format is known as the "crop factor
Crop factor
In digital photography, a crop factor is related to the ratio of the dimensions of a camera's imaging area compared to a reference format; most often, this term is applied to digital cameras, relative to 35 mm film format as a reference. In the case of digital cameras, the imaging device would be a...
" or "focal-length multiplier", and is typically in the range 1.3–2.0 for non-full-frame digital SLRs.
Advantages and disadvantages of full-frame digital SLRs

Angle of view
In photography, angle of view describes the angular extent of a given scene that is imaged by a camera. It is used interchangeably with the more general term field of view....
. On smaller-sensor DSLRs, wide-angle lenses have smaller angles of view equivalent to those of longer-focal-length lenses on 35 mm film cameras. For example, a 24 mm lens on a camera with a crop factor
Crop factor
In digital photography, a crop factor is related to the ratio of the dimensions of a camera's imaging area compared to a reference format; most often, this term is applied to digital cameras, relative to 35 mm film format as a reference. In the case of digital cameras, the imaging device would be a...
of 1.5 has a 62° diagonal angle of view, the same as that of a 36 mm lens on a 35 mm film camera. On a full-frame digital camera, the 24 mm lens has the same 84° angle of view as it would on a 35 mm film camera.
If the same lens is used on both full-frame and cropped formats, and the subject distance is adjusted to have the same field of view (i.e., the same framing of the subject) in each format, depth of field
Depth of field
In optics, particularly as it relates to film and photography, depth of field is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image...
(DoF) is in inverse proportion to the format sizes, so for the same f-number, the full-frame format will have less DoF. Equivalently, for the same DoF, the full-frame format will require a larger f-number. This relationship is approximate and holds for moderate subject distances, breaking down as the distance with the smaller format approaches the hyperfocal distance, and as the magnification with the larger format approaches the macro range.
There are optical quality implications as well—not only because the image from the lens is effectively cropped—but because many lens designs are now optimized for sensors smaller than . The rear element of any SLR lens must have clearance for the camera's reflex mirror to move up when the shutter is released; with a wide-angle lens, this requires a retrofocus
Angenieux retrofocus
The Angénieux retrofocus photographic lens is a wide-angle lens design that uses an inverted telephoto configuration. The popularity of this lens design made the name retrofocus synonymous with this type of lens...
design, which is generally of inferior optical quality. Because a cropped-format sensor can have a smaller mirror, less clearance is needed, and some lenses, such as the EF-S
Canon EF-S lens mount
The EF-S lens mount is a derivative of the EF lens mount created for a subset of Canon digital single-lens reflex cameras with APS-C sized image sensors. It was released in 2003. Cameras supporting the EF-S mount are backward-compatible with the EF lens mount and, as such, have a flange focal...
lenses for the Canon APS-C
APS-C
Advanced Photo System type-C is an image sensor format approximately equivalent in size to the Advanced Photo System "classic" size negatives...
sized bodies, are designed with a shorter back-focus distance; however, they cannot be used on bodies with larger sensors.
In addition to wide-angle photography, another major advantage of full-frame cameras is pixel size. For a given number of pixels, the larger sensor allows for larger pixels or photosites that provide wider dynamic range and lower noise at high ISO levels.
As a consequence, full-frame DSLRs may produce better quality images in certain high contrast or low light situations.
The full-frame sensor can also be useful with wide-angle perspective control or tilt/shift lenses; in particular, the wider angle of view is often more suitable for architectural photography
Architectural photography
Architectural photography is the practice of photographing buildings and similar structures, both inside and out. Architectural photographs are usually produced by Architectural photographers, who are skilled in the use of specialized techniques and equipment...
.
While full-frame DSLRs offer advantages for wide-angle photography, smaller-sensor DSLRs offer some advantages for telephoto photography because the smaller angle of view of small-sensor DSLRs enhances the telephoto effect of the lenses. For example, a 200 mm lens on a camera with a crop factor of 1.5 has the same angle of view as a 300 mm lens on a full-frame camera. The extra "reach", for a given number of pixels, can be helpful in specific areas of photography such as wildlife or sports.
Production costs for a full-frame sensor can exceed twenty times the costs for an APS-C sensor. Only 20 full-frame sensors will fit on an 8 inches (203.2 mm) silicon wafer, and yield is comparatively low because the sensor's large area makes it very vulnerable to contaminants—20 evenly distributed defects could theoretically ruin an entire wafer. Additionally, the full-frame sensor requires three separate exposures during the photolithography
Photolithography
Photolithography is a process used in microfabrication to selectively remove parts of a thin film or the bulk of a substrate. It uses light to transfer a geometric pattern from a photomask to a light-sensitive chemical "photoresist", or simply "resist," on the substrate...
stage, tripling the number of masks and exposure processes.
Some full-frame DSLRs intended mainly for professional use include more features than typical consumer-grade DSLRs, so some of their larger dimensions and increased mass result from more rugged construction and additional features as opposed to this being an inherent consequence of the full-frame sensor.
CCD image sensor architectures
The term full-frame is also used to refer to a type of charge-coupled deviceCharge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time...
sensor technology in which the sensor elements occupy the entire sensor surface rather than sharing space with associated pixel storage sites.
The use of full-frame CCDs is typically restricted to digital SLRs since they require the use of a mechanical shutter and do not output a continuous image. The two uses of the term full-frame are not otherwise related.
135 film cameras
In 35 mm (135 film135 film
The term 135 was introduced by Kodak in 1934 as a designation for cartridge film wide, specifically for still photography. It quickly grew in popularity, surpassing 120 film by the late 1960s to become the most popular photographic film format...
) cameras, the terms full-frame and half-frame were used to distinguish the 24 × 36 mm and 18 × 24 mm film format
Film format
A film format is a technical definition of a set of standard characteristics regarding image capture on photographic film, for either stills or movies. It can also apply to projected film, either slides or movies. The primary characteristic of a film format is its size and shape.In the case of...
s; the half-frame 35 mm film format is also known as single-frame in movie film, and as a result, full-frame film cameras were sometimes known as double-frame.
SLRs

- Contax N DigitalContax N DigitalThe Contax N Digital was a six-megapixel digital SLR camera produced by Contax in Japan. The camera was announced in late 2000, and began to be sold in spring 2002, after several delays...
(2002) - Canon EOS-1DsCanon EOS-1DsThe EOS-1Ds is a full-frame 11.4 megapixel digital SLR camera body formerly made by Canon, released in the spring of 2003. Its dimensions are 156 mm in width, 157.6 mm in height, and 79.9 mm in depth. Its mass is 1,265 g.-Functions:...
(2002) - Kodak DCS Pro 14nKodak DCS Pro 14nThe Kodak Professional DCS Pro 14n is a professional Nikon F80 based F-mount digital SLR produced by Eastman Kodak. It was announced at the photographic trade show Photokina in Germany during September 2002; production examples became available in May 2003....
(2003) - Kodak DCS Pro SLR/nKodak DCS Pro SLR/nThe Kodak Professional DCS Pro SLR/n is a 13.5 megapixel full-frame 35mm digital SLR produced as a collaboration between Nikon Corporation and Eastman Kodak. It was an improved version of the Kodak Professional DCS Pro 14n series, and was based on a modified N80 film SLR and thus compatible with...
(2004) - Kodak DCS Pro SLR/cKodak DCS Pro SLR/cThe Kodak Professional DCS Pro SLR/c is a 13.5 megapixel digital SLR camera produced by Eastman Kodak. Unlike most DSLRs, it is full frame—it uses an image sensor that is the full size of a 35 mm frame. It is compatible with Canon EOS lenses...
(2004) - Canon EOS-1Ds Mark IICanon EOS-1Ds Mark IIThe EOS-1Ds Mark II is a digital SLR camera body by Canon Inc. of Japan. It was the top model in the Canon EOS line of digital cameras until April 2007, with a full-frame 16.7 megapixel CMOS sensor. The EOS-1Ds Mark II had the highest pixel count available in a 35mm format digital SLR at the time...
(2004) - Canon EOS 5DCanon EOS 5DThe EOS 5D is a 12.8 megapixel digital single-lens reflex camera body produced by Canon. The EOS 5D was announced by Canon on August 22, 2005, and at the time was priced above the EOS 20D but below the EOS-1D Mark II and EOS-1Ds Mark II in Canon's EOS digital SLR series...
(2005) - Nikon D3Nikon D3The Nikon D3 is a 12.1 megapixel professional grade full frame digital single lens reflex camera announced by the Nikon Corporation on 23 August 2007 along with the Nikon D300 DX format camera. The D3, along with the Nikon D3X, was a flagship model in Nikon's line of DSLRs, superseding the D2Hs...
(2007) - Canon EOS-1Ds Mark IIICanon EOS-1Ds Mark IIIThe EOS-1Ds Mark III is a digital SLR camera body by Canon designed for professional photographers. The Canon EOS 1Ds Mark III is successor to the EOS-1Ds Mark II and was announced in August 2007. The camera features a full-frame 21.1 megapixel CMOS sensor with 14 bit A/D converters for a total...
(2007) - Nikon D700Nikon D700The Nikon D700 is a professional grade full-frame digital single-lens reflex camera introduced by the Nikon Corporation in July 2008 and manufactured in Japan. It uses the same 12.1 megapixel "FX" CMOS image sensor as the Nikon D3, and is Nikon's second full-frame digital SLR camera...
(2008) - Sony α DSLR-A900 (2008)
- Canon EOS 5D Mark IICanon EOS 5D Mark IIThe Canon EOS 5D Mark II is a 21.1-megapixel full-frame CMOS digital single-lens reflex camera made by Canon. It succeeds the EOS 5D and was announced on September 17, 2008.-Improvements compared to original EOS 5D:...
(2008) - Nikon D3XNikon D3XThe Nikon D3X is a 24.5 megapixel professional-grade full frame digital single-lens reflex camera announced by the Nikon Corporation on 1 December 2008. The D3X is the third camera in Nikon's line to offer a full frame sensor, following the D3 and D700...
(2008) - Sony α DSLR-A850 (2009)
- Nikon D3SNikon D3SThe Nikon D3S is a 12.1 megapixel professional-grade full frame digital single-lens reflex camera announced by Nikon Corporation on 14 October 2009. The D3S is the fourth camera in Nikon's line to feature a full frame sensor, following the D3, D700 and D3X. It is also Nikon's first full frame...
(2009) - Canon EOS-1D XCanon EOS-1D XThe Canon EOS-1D X is a future digital SLR camera body by Canon Inc. It will succeed the company's flagship Canon EOS-1Ds Mark III and the Canon EOS-1D Mark IV. It was announced on October 18, 2011 and is expected to reach dealers in March 2012...
(announced in 2011, to be released in March 2012)
The Nikon E2/E2s (1994), E2N/E2Ns (1996) and E3
Nikon E3
The Nikon E3 and Nikon E3s, co-developed with Fujifilm and marketed also as the Fujix DS-565, are autofocus 1.3 megapixel professional grade quasi-full frame digital single lens reflex cameras announced by the Nikon Corporation on 15 June 1998 and released in December 1999. The E3S is identical...
/E3s (1998) digital SLRs as well as the similar Fujifilm Fujix DS-505/DS-515, DS-505A/DS-515A and DS-560/DS-565 models used a reduction optical system (ROS) to compress a full-frame 35 mm field onto a smaller 2/3-inch
Image sensor format
In digital photography, the image sensor format is the shape and size of the image sensor.The image sensor format of a digital camera determines the angle of view of a particular lens when used with a particular camera...
(11 mm diagonal) CCD imager
Charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time...
. They were therefore not digital SLRs with full-frame sensors, however had an angle of view
Angle of view
In photography, angle of view describes the angular extent of a given scene that is imaged by a camera. It is used interchangeably with the more general term field of view....
equivalent to full-frame digital SLRs for a given lens; they had no crop factor with respect to angle of view, but did have a factor that changed the f-number
F-number
In optics, the f-number of an optical system expresses the diameter of the entrance pupil in terms of the focal length of the lens; in simpler terms, the f-number is the focal length divided by the "effective" aperture diameter...
of the lens by more than a factor of 2.
Nikon has designated its full frame cameras as FX format and its smaller sensor cameras as the DX format
Nikon DX format
The Nikon DX format is an alternative name used by Nikon corporation for APS-C image sensor format being approximately 24×16 mm. Its dimensions are about 2/3 those of the 35mm film format . The format was created by Nikon for its digital SLR cameras, many of which are equipped with DX-sized...
.
Prototype full-frame digital SLRs
- Pentax MZ-DPentax MZ-DThe Pentax MZ-D, also known by its internal code name of MR-52, was a prototype digital single-lens reflex camera from Pentax of Japan. It was announced at Photokina in September 2000 and was demonstrated to the press at the Photo Marketing Association show in January 2001...
"MR-52" (presented in 2000, based on Pentax MZ-SPentax MZ-SThe Pentax MZ-S is a 35mm single-lens reflex camera from Pentax of Japan. It was introduced in 2001and discontinued in February 2006.It is closely related to the prototype MZ-D Full-frame digital SLR, which never entered production....
, with the same sensor as Contax N, it never went into production) - Sony Alpha flagship model "CX62500" (presented at PMA 2007, early prototype of what one-and-a-half years later became the DSLR-A900 (aka "CX85100"), though with many detail differences)

