
Frame and panel
Encyclopedia
Woodworking
Woodworking is the process of building, making or carving something using wood.-History:Along with stone, mud, and animal parts, wood was one of the first materials worked by early humans. Microwear analysis of the Mousterian stone tools used by the Neanderthals show that many were used to work wood...
technique often used in the making of door
Door
A door is a movable structure used to open and close off an entrance, typically consisting of a panel that swings on hinges or that slides or rotates inside of a space....
s, wainscoting
Panelling
Panelling is a wall covering constructed from rigid or semi-rigid components. These are traditionally interlocking wood, but could be plastic or other materials....
, and other decorative features for cabinet
Cabinet making
Cabinet making is the practice of using various woodworking skills to create cabinets, shelving and furniture.Cabinet making involves techniques such as creating appropriate joints, dados, bevels, chamfers and shelving systems, the use of finishing tools such as routers to create decorative...
s, furniture
Furniture
Furniture is the mass noun for the movable objects intended to support various human activities such as seating and sleeping in beds, to hold objects at a convenient height for work using horizontal surfaces above the ground, or to store things...
, and homes. The basic idea is to capture a 'floating' panel within a sturdy frame, as opposed to techniques used in making a slab solid wood cabinet door or drawer front, the door is constructed of several solid wood pieces running in a vertical or horizontal direction with exposed endgrains. Usually, the panel is not glued to the frame but is left to 'float' within it so that seasonal movement of the wood comprising the panel does not distort the frame.
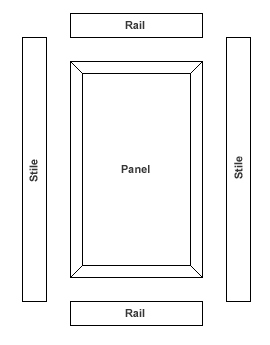
Frame and panel construction at its most basic consists of five members: the panel and the four members which make up the frame. The vertical members of the frame are called stiles while the horizontal members are known as rails. A basic frame and panel item consists of a top rail, a bottom rail, two stiles, and a panel. This is a common method of constructing cabinet doors and these are often referred to as a five piece door.
In larger panels it is common to divide the panel into one or more sections. To house the extra panels, dividing pieces known as mid rails and mid stiles or muntin
Muntin
Muntin or Muntin bar is a strip of wood or metal separating and holding panes of glass in a window. Muntins are also called "glazing bars", "muntin bars", or "sash bars". Muntins can be found in doors, windows and furniture, typically in western styles of architecture...
s are added to the frame.
Panels
Groove (joinery)
In joinery, a groove is a slot or trench cut into a member which runs parallel to the grain. A groove is thus differentiated from a dado, which runs across the grain....
made in the inside edge of the frame members or housed in an edge rabbet
Rabbet
A rabbet is a recess or groove cut into the edge of a piece of machineable material, usually wood. When viewed in cross-section, a rabbet is two-sided and open to the edge or end of the surface into which it is cut....
made in the rear inside edge. Panels are made slightly smaller than the available space within the frame to provide room for movement. Wood will expand and contract across the grain, and a wide panel made of solid wood could change width by a half of an inch, warping the door frame. By allowing the wood panel to float, it can expand and contract without damaging the door. A typical panel would be cut to allow 1/4" (5 mm) between itself and the bottom of the groove in the frame. It is common to place some sort of elastic material in the groove between the edge of the panel and the frame before assembly. These items center the panel in the frame and absorb seasonal movement. A popular item for this purpose is a small rubber ball, known as a spaceball (a trademarked product). Some cabinet makers will also use small pieces of cork
Cork (material)
Cork is an impermeable, buoyant material, a prime-subset of bark tissue that is harvested for commercial use primarily from Quercus suber , which is endemic to southwest Europe and northwest Africa...
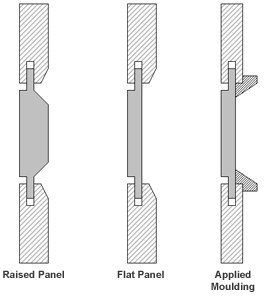
to allow for movement. The panels are usually either flat or raised.
A flat panel has its visible face flush with the front of the groove in the frame. This gives the panel an inset appearance. This style of panel is commonly made from man-made materials such as MDF
Medium-density fibreboard
Medium-density fiberboard is an engineered wood product formed by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into wood fibres, often in a defibrator, combining it with wax and a resin binder, and forming panels by applying high temperature and pressure...
or plywood
Plywood
Plywood is a type of manufactured timber made from thin sheets of wood veneer. It is one of the most widely used wood products. It is flexible, inexpensive, workable, re-usable, and can usually be locally manufactured...
but may also be made from solid wood or tongue and groove
Tongue and groove
A strong joint, the tongue and groove joint is widely used for re-entrant angles. The effect of wood shrinkage is concealed when the joint is beaded or otherwise moulded...
planks. Panels made from MDF will be painted to hide their appearance, but panels of hardwood-veneer plywood will be stained and finished to match the solid wood rails and stiles.
A raised panel has a profile cut into its edge so that the panel surface is flush with or proud of the frame. Some popular profiles are the ogee, chamfer, and scoop or cove. Panels may be raised by a number of methods - the two most common in modern cabinetry are by coving on the tablesaw or the use of a panel raising cutter in a wood router
Wood router
A router is a tool used to rout out an area in the face of a relatively hard workpiece, typically of wood or plastic. The main application of routers is in woodworking, especially cabinetry....
or spindle moulder.
Frame
The stiles and rails often have a profile cut into the inside edge of the outside face - usually a smaller version to match the profile of the panel. In some panel styles, a profile may also be cut on the outside edge of the outside face.Frame construction style falls into three categories: cope and stick
Cope and stick
Cope and stick construction is a frame and panel technique often used in the making of doors, wainscoting, and other decorative features for cabinets, furniture, and homes....
, mitred
Miter joint
A miter joint , sometimes shortened to miter, is a joint made by bevelling each of two parts to be joined, usually at a 45° angle, to form a corner, usually a 90° angle...
sticking and applied moulding. Cope and stick is the most common method, as it is more efficient to manufacture. In modern cabinetry, the cope and stick joinery is achieved with a set of special router cutters. These cut the profile on the edge of the frame parts and also cut a reverse version of the same profile in the ends of the rail so that they may be slipped over the ends of the stiles and glued in place.
If done correctly, the cope cut in the end of the rail will mate perfectly with the sticking profile. When glued together, the resulting joint will have sufficient strength for most cabinet door applications without further reinforcement. For extremely large and heavy doors, the cope and stick joint can be further reinforced with dowels, loose tenons
Mortise and tenon
The mortise and tenon joint has been used for thousands of years by woodworkers around the world to join pieces of wood, mainly when the adjoining pieces connect at an angle of 90°. In its basic form it is both simple and strong. Although there are many joint variations, the basic mortise and tenon...
, or by some other method.
In mitred sticking, the profile (known as the sticking) is applied to the edges of both the rail and stile and then a section of the sticking at the ends of each stile is removed leaving a mitred edge which aligns to a similar mitre cut on the ends of the sticking on each rail. This traditional method is more time consuming to complete, hence the popularity of cope and stick for manufactured items.
When applied moulding is to be used, the frame members are joined with mortise and tenon
Mortise and tenon
The mortise and tenon joint has been used for thousands of years by woodworkers around the world to join pieces of wood, mainly when the adjoining pieces connect at an angle of 90°. In its basic form it is both simple and strong. Although there are many joint variations, the basic mortise and tenon...
, reinforced butt joint
Butt joint
A butt joint is a joinery technique in which two members are joined by simply butting them together. The butt joint is the simplest joint to make since it merely involves cutting the members to the appropriate length and butting them together. It is also the weakest because unless some form of...
, or bridle joint
Bridle joint
A bridle joint is a woodworking joint, similar to a mortise and tenon, in that a tenon is cut on the end of one member and a mortise is cut into the other to accept it...
. Once the panel has been assembled, the moulding is applied to the inside edge of the outer face of the frame. An alternative method is to use a router to cut a sticking profile in the frame after assembly.
The process of making raised panel doors begins with gluing up panels, and then moves into cutting and preparing the frame parts. Next, the panels are cut to size and shaped. Parts and panel are sanded before construction. It is also common to apply a finish to panels prior to assembly so that raw wood is not visible if the panel shrinks. The joints are glued and set into clamps. If the frame and panel items are paint grade they are sometimes nailed at the frame joints on the reverse side. The door then moves on to finish sanding where it is brought to its final thickness, and the outside profile is added if required.

