Fondaparinux
Encyclopedia
Fondaparinux is an anticoagulant
medication chemically related to low molecular weight heparin
s. It is marketed by GlaxoSmithKline
.
(HS). Within heparin and heparan sulfate this monomeric sequence is thought to form the high affinity binding site for the anti-coagulant factor antithrombin III (ATIII). Binding of heparin/HS to ATIII has been shown to increase the anti-coagulant activity of antithrombin III 1000 fold. In contrast to heparin, fondaparinux does not inhibit thrombin
.
in patients who have had orthopedic surgery as well as for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
.
(HIT) is substantially lower. Furthermore, there have been case reports of fondaparinux being used to anticoagulate patients with established HIT as it has no affinity to PF-4. However, its renal excretion precludes its use in patients with renal dysfunction.
Unlike direct factor Xa inhibitor
s, it mediates its effects indirectly through antithrombin III, but unlike heparin
, it is selective for factor X
a.
in reducing the risk of ischemic events at nine days, but it substantially reduces major bleeding and improves long term mortality and morbidity.
It has been investigated for use in conjunction with streptokinase
.
Can be used as treatment against Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia
.
Anticoagulant
An anticoagulant is a substance that prevents coagulation of blood. A group of pharmaceuticals called anticoagulants can be used in vivo as a medication for thrombotic disorders. Some anticoagulants are used in medical equipment, such as test tubes, blood transfusion bags, and renal dialysis...
medication chemically related to low molecular weight heparin
Low molecular weight heparin
In medicine, low-molecular-weight heparin is a class of medication used as an anticoagulant in diseases that feature thrombosis, as well as for prophylaxis in situations that lead to a high risk of thrombosis....
s. It is marketed by GlaxoSmithKline
GlaxoSmithKline
GlaxoSmithKline plc is a global pharmaceutical, biologics, vaccines and consumer healthcare company headquartered in London, United Kingdom...
.
Structure and mechanism
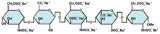
Fondaparinux is a synthetic pentasaccharide Factor Xa inhibitor. Apart from the O-methyl group at the reducing end of the molecule, the identity and sequence of the five monomeric sugar units contained in fondaparinux is identical to a sequence of five monomeric sugar units that can be isolated after either chemical or enzymatic cin]] and heparan sulfateHeparan sulfate
Heparan sulfate is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins...
(HS). Within heparin and heparan sulfate this monomeric sequence is thought to form the high affinity binding site for the anti-coagulant factor antithrombin III (ATIII). Binding of heparin/HS to ATIII has been shown to increase the anti-coagulant activity of antithrombin III 1000 fold. In contrast to heparin, fondaparinux does not inhibit thrombin
Thrombin
Thrombin is a "trypsin-like" serine protease protein that in humans is encoded by the F2 gene. Prothrombin is proteolytically cleaved to form thrombin in the first step of the coagulation cascade, which ultimately results in the stemming of blood loss...
.
Administration
Fondaparinux is given subcutaneously daily. Clinically, it is used for the prevention of deep vein thrombosisDeep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein. Deep vein thrombosis commonly affects the leg veins or the deep veins of the pelvis. Occasionally the veins of the arm are affected...
in patients who have had orthopedic surgery as well as for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage of the main artery of the lung or one of its branches by a substance that has travelled from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream . Usually this is due to embolism of a thrombus from the deep veins in the legs, a process termed venous thromboembolism...
.
Comparison to other agents
One potential advantage of fondaparinux over LMWH or unfractionated heparin is that the risk for heparin-induced thrombocytopeniaHeparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia is the development of thrombocytopenia , due to the administration of various forms of heparin, an anticoagulant...
(HIT) is substantially lower. Furthermore, there have been case reports of fondaparinux being used to anticoagulate patients with established HIT as it has no affinity to PF-4. However, its renal excretion precludes its use in patients with renal dysfunction.
Unlike direct factor Xa inhibitor
Direct factor Xa inhibitor
Direct factor Xa inhibitors are a class of anticoagulant drugs which act directly upon Factor X in the coagulation cascade, without using antithrombin as a mediator.-Clinical uses:Direct factor Xa inhibitors are being used clinically...
s, it mediates its effects indirectly through antithrombin III, but unlike heparin
Heparin
Heparin , also known as unfractionated heparin, a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan, is widely used as an injectable anticoagulant, and has the highest negative charge density of any known biological molecule...
, it is selective for factor X
Factor X
Factor X, also known by the eponym Stuart-Prower factor or as prothrombinase, is an enzyme of the coagulation cascade. It is a serine endopeptidase .-Physiology:...
a.
Uses
Fondaparinux is similar to enoxaparinEnoxaparin
Enoxaparin is a low molecular weight heparin marketed under the trade names Lovenox and Clexane, among others. It is an anticoagulant used to prevent and treat deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, and is given as a subcutaneous injection...
in reducing the risk of ischemic events at nine days, but it substantially reduces major bleeding and improves long term mortality and morbidity.
It has been investigated for use in conjunction with streptokinase
Streptokinase
Streptokinase , a protein secreted by several species of streptococci can bind and activate human plasminogen. SK is used as an effective and inexpensive thrombolysis medication in some cases of myocardial infarction and pulmonary embolism...
.
Can be used as treatment against Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a relative decrease of platelets in blood.A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. These limits are determined by the 2.5th lower and upper percentile, so values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease...
.
Abbreviations
- GlcNS(6S) = 2-deoxy-6-O-sulfo-2-(sulfoamino)-α-D-glucopyranoside
- GlcA = β-D-glucopyranuronosylGlucuronic acidGlucuronic acid is a carboxylic acid. Its structure is similar to that of glucose. However, glucuronic acid's sixth carbon is oxidized to a carboxylic acid...
- GlcNS(3S,6S) = 2-deoxy-3,6-di-O-sulfo-2-(sulfoamino)-α-D-glucopyranosyl
- IdoA(2S) = 2-O-sulfo-α-L-idopyranuronosylIduronic acidL-Iduronic acid is the major uronic acid component of the glycosaminoglycans dermatan sulfate, and heparin. It is also present in heparan sulfate although here in a minor amount relative to its carbon-5 epimer glucuronic acid....
- GlcNS(6S)OMe = methyl-O-2-deoxy-6-O-sulfo-2-(sulfoamino)-α-D-glucopyranoside

