Flow tracer
Encyclopedia
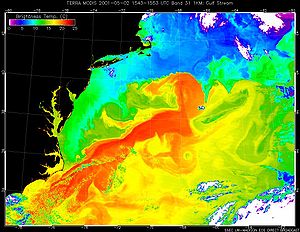

Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
are physical tracers. Tracers may be artificially introduced, like dye tracers, or they may be naturally occurring. Conservative
Conservation law
In physics, a conservation law states that a particular measurable property of an isolated physical system does not change as the system evolves....
tracers remain constant following fluid parcels, whereas reactive
Reactive
Reactive may refer to:*Generally, capable of having a reaction*Reactance , the imaginary component of AC impedance*Reactive mind*Reactive programming...
tracers (such as compounds undergoing a mutual chemical reaction) grow or decay with time.
Active tracers dynamically alter the flow of the fluid by changing fluid properties which appear in the equation of motion
Equation of motion
Equations of motion are equations that describe the behavior of a system in terms of its motion as a function of time...
such as density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
or viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
, while passive tracers have no influence on flow.
Tracers are used in oceanography
Oceanography
Oceanography , also called oceanology or marine science, is the branch of Earth science that studies the ocean...
to deduce flow patterns in the ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
. Common examples include potential temperature, salinity
Salinity
Salinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of a body of water. It is a general term used to describe the levels of different salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium and calcium sulfates, and bicarbonates...
, and concentration of CFCs, tritium
Tritium
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. The nucleus of tritium contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of protium contains one proton and no neutrons...
(introduced to the ocean surface by atomic bomb tests), oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, and many other compounds.
External links
- Plastic ducks and other bath toys, washed from a container shipContainer shipContainer ships are cargo ships that carry all of their load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. They form a common means of commercial intermodal freight transport.-History:...
into the Pacific OceanPacific OceanThe Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
in 1992, are used as a flow tracer for the calibrationCalibrationCalibration is a comparison between measurements – one of known magnitude or correctness made or set with one device and another measurement made in as similar a way as possible with a second device....
and verificationVerification and ValidationIn software project management, software testing, and software engineering, verification and validation is the process of checking that a software system meets specifications and that it fulfills its intended purpose...
of ocean currentOcean currentAn ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
models. - ctraj Library of advection codes, including passive tracer modelling.

