
First moment of area
Encyclopedia
The first moment of area, sometimes misnamed as the first moment of inertia, is based in the mathematical construct moments in metric spaces, stating that the moment of area equals the summation of area times distance to an axis [Σ(a x d)]. It is a measure of the distribution of the area of a shape in relationship to an axis.
First moment of area is commonly used in engineering applications to determine the centroid
of an object or the statical moment of area.
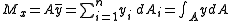
and .
.
The SI
unit for first moment of area is metre
to the third power (m3). In the American Engineering and Gravitational systems the unit is foot to the third power (ft3) or more commonly inch
3.
. By definition:
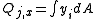 , where
, where
in a particular web section of the cross-section of a semi-monocoque structure is:
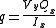
Shear stress
may now be calculated using the following equation:
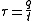
First moment of area is commonly used in engineering applications to determine the centroid
Centroid
In geometry, the centroid, geometric center, or barycenter of a plane figure or two-dimensional shape X is the intersection of all straight lines that divide X into two parts of equal moment about the line. Informally, it is the "average" of all points of X...
of an object or the statical moment of area.
Definition
Given an area, A, of any shape, and division of that area into n number of very small, elemental areas (dAi). Let xi and yi be the distances (coordinates) to each elemental area measured from a given x-y axis. Now, the first moment of area in the x and y directions are respectively given by: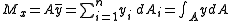
and
 .
.The SI
International System of Units
The International System of Units is the modern form of the metric system and is generally a system of units of measurement devised around seven base units and the convenience of the number ten. The older metric system included several groups of units...
unit for first moment of area is metre
Metre
The metre , symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units . Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole , its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology...
to the third power (m3). In the American Engineering and Gravitational systems the unit is foot to the third power (ft3) or more commonly inch
Inch
An inch is the name of a unit of length in a number of different systems, including Imperial units, and United States customary units. There are 36 inches in a yard and 12 inches in a foot...
3.
Statical moment of area
The static or statical moment of area, usually denoted by the symbol Q, is a property of a shape that is used to predict its resistance to shear stressShear stress
A shear stress, denoted \tau\, , is defined as the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. Shear stress arises from the force vector component parallel to the cross section...
. By definition:
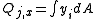 , where
, where- Qj,x - the first moment of area "j" about the neutral x axis of the entire body (not the neutral axis of the area "j");
- dA - an elemental area of area "j";
- y - the perpendicular distance to the element dA from the neutral axis x.
Shear Stress in a Semi-monocoque Structure
The equation for shear flowShear flow
The term shear flow is used in solid mechanics as well as in fluid dynamics. Loosely speaking, shear flow is defined as:* the gradient of a shear stress force through the body ;...
in a particular web section of the cross-section of a semi-monocoque structure is:
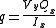
- q - the shear flow through a particular web section of the cross-section
- Vy - the shear force perpendicular to the neutral axis x through the entire cross-section
- Qx - the first moment of area about the neutral axis x for a particular web section of the cross-section
- Ix - the second moment of areaSecond moment of areaThe second moment of area, also known as the area moment of inertia, moment of inertia of plane area, or second moment of inertia is a property of a cross section that can be used to predict the resistance of beams to bending and deflection, around an axis that lies in the cross-sectional plane...
about the neutral axis x for the entire cross-section
Shear stress
Shear stress
A shear stress, denoted \tau\, , is defined as the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. Shear stress arises from the force vector component parallel to the cross section...
may now be calculated using the following equation:
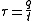
-
 - the shear stress through a particular web section of the cross-section
- the shear stress through a particular web section of the cross-section - q - the shear flow through a particular web section of the cross-section
- t - the (average) thickness of a particular web section of the cross-section

