Fibre Channel over Ethernet
Encyclopedia
Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is an encapsulation of Fibre Channel
frames over Ethernet
networks. This allows Fibre Channel to use 10 Gigabit Ethernet
networks (or higher speeds) while preserving the Fibre Channel protocol. The specification, supported by a large number of network and storage vendors, is part of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards T11 FC-BB-5 standard.
while being independent of the Ethernet forwarding scheme. The
FCoE protocol specification replaces the FC0 and FC1 layers of the Fibre Channel stack with Ethernet. By retaining the native Fibre Channel constructs, FCoE was meant to integrate with existing Fibre Channel networks and management software.
Many data centers use Ethernet for TCP/IP networks and Fibre Channel for storage area networks (SANs). With FCoE, Fibre Channel becomes another network protocol running on Ethernet, alongside traditional Internet Protocol (IP) traffic. FCoE operates directly above Ethernet in the network protocol stack, in contrast to iSCSI
which runs on top of TCP and IP. As a consequence, FCoE is not routable at the IP layer, and will not work across routed IP networks.
Since classical Ethernet had no priority-based flow control
, unlike Fibre Channel, FCoE requires enhancements to the Ethernet standard to support a priority-based flow control mechanism (this prevents frame loss). The IEEE standards body is working on this in the Data Center Bridging
Task Group.
Fibre Channel required three primary extensions to deliver the capabilities of Fibre Channel over Ethernet networks:
Computers connect to FCoE with Converged Network Adapter
s (CNAs), which contain both Fibre Channel Host Bus Adapter (HBA) and Ethernet Network Interface Card (NIC) functionality on the same adapter card. CNAs have one or more physical Ethernet ports. FCoE encapsulation can be done in software with a conventional Ethernet network interface card, however FCoE CNAs offload (from the CPU) the low level frame processing and SCSI protocol functions traditionally performed by Fibre Channel host bus adapters.
With FCoE, network (IP) and storage (SAN) data traffic can be consolidated using a single network. This consolidation can:
, 0x8906. A single 4-bit field (version) satisfies the IEEE sub-type requirements. The SOF (start of frame) and EOF (end of frame) are encoded as specified in RFC 3643. Reserved bits are present to guarantee that the FCoE frame meets the minimum length requirement of Ethernet. Inside the encapsulated Fibre Channel frame, the frame header is retained so as to allow connecting to a storage network by passing on the Fibre Channel frame directly after de-encapsulation.
The FIP (FCoE Initialization Protocol) is an integral part of FCoE. Its main goal is to discover and initialize FCoE capable entities connected to an Ethernet cloud. FIP uses a dedicated Ethertype of 0x8914.
The FCoE standardization activity started in April 2007.
The FCoE technology was defined as part of the INCITS T11 FC-BB-5 standard that was forwarded to ANSI for publication in June 2009.
The FC-BB-5 standard was published in May 2010 as ANSI/INCITS 462-2010.
An early implementor was Nuova Systems, a subsidiary of Cisco Systems
, which announced a switch in April 2008.
Brocade Communications Systems
also announced support in 2008.
After the Late-2000s financial crisis
, however, any new technology had a hard time getting established.
Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel, or FC, is a gigabit-speed network technology primarily used for storage networking. Fibre Channel is standardized in the T11 Technical Committee of the InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards , an American National Standards Institute –accredited standards...
frames over Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
networks. This allows Fibre Channel to use 10 Gigabit Ethernet
10 Gigabit Ethernet
The 10 gigabit Ethernet computer networking standard was first published in 2002. It defines a version of Ethernet with a nominal data rate of 10 Gbit/s , ten times faster than gigabit Ethernet.10 gigabit Ethernet defines only full duplex point to point links which are generally connected by...
networks (or higher speeds) while preserving the Fibre Channel protocol. The specification, supported by a large number of network and storage vendors, is part of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards T11 FC-BB-5 standard.
Functionality
FCoE maps Fibre Channel directly over EthernetEthernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
while being independent of the Ethernet forwarding scheme. The
FCoE protocol specification replaces the FC0 and FC1 layers of the Fibre Channel stack with Ethernet. By retaining the native Fibre Channel constructs, FCoE was meant to integrate with existing Fibre Channel networks and management software.
Many data centers use Ethernet for TCP/IP networks and Fibre Channel for storage area networks (SANs). With FCoE, Fibre Channel becomes another network protocol running on Ethernet, alongside traditional Internet Protocol (IP) traffic. FCoE operates directly above Ethernet in the network protocol stack, in contrast to iSCSI
ISCSI
In computing, iSCSI , is an abbreviation of Internet Small Computer System Interface, an Internet Protocol -based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. By carrying SCSI commands over IP networks, iSCSI is used to facilitate data transfers over intranets and to manage...
which runs on top of TCP and IP. As a consequence, FCoE is not routable at the IP layer, and will not work across routed IP networks.
Since classical Ethernet had no priority-based flow control
Ethernet flow control
Ethernet flow control is a mechanism for temporarily stopping the transmission of data on Ethernet family computer networks.-Description:Ethernet is a popular family of computer network protocols. Flow control can be implemented at the data link layer...
, unlike Fibre Channel, FCoE requires enhancements to the Ethernet standard to support a priority-based flow control mechanism (this prevents frame loss). The IEEE standards body is working on this in the Data Center Bridging
Data center bridging
Data center bridging refers to a set of enhancements to Ethernet local area networks for use in data center environments. Specifically, DCB goals are, for selected traffic, to eliminate loss due to queue overflow and to be able to allocate bandwidth on links. Essentially, DCB enables, to some...
Task Group.
Fibre Channel required three primary extensions to deliver the capabilities of Fibre Channel over Ethernet networks:
- Encapsulation of native Fibre Channel frames into Ethernet Frames.
- Extensions to the Ethernet protocol itself to enable an Ethernet fabric in which frames are not routinely lost during periods of congestion.
- Mapping between Fibre Channel N_port IDs (aka FCIDs) and Ethernet MAC addresses.
Computers connect to FCoE with Converged Network Adapter
Converged Network Adapter
A converged network adapter , also called a converged network interface controller , is a computer input/output device that combines the functionality of a Host Bus Adaptor to a storage area network with a network interface controller for a general-purpose computer network.-Support :Some products...
s (CNAs), which contain both Fibre Channel Host Bus Adapter (HBA) and Ethernet Network Interface Card (NIC) functionality on the same adapter card. CNAs have one or more physical Ethernet ports. FCoE encapsulation can be done in software with a conventional Ethernet network interface card, however FCoE CNAs offload (from the CPU) the low level frame processing and SCSI protocol functions traditionally performed by Fibre Channel host bus adapters.
Application
The main application of FCoE is in data center storage area networks (SANs). FCoE has particular application in data centers due to the cabling reduction it makes possible, as well as in server virtualization applications, which often require many physical I/O connections per server.With FCoE, network (IP) and storage (SAN) data traffic can be consolidated using a single network. This consolidation can:
- reduce the number of network interface cards required to connect to disparate storage and IP networks
- reduce the number of cables and switches
- reduce power and cooling costs
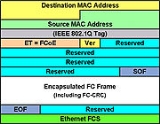
Frame Format
FCoE is encapsulated over Ethernet with the use of a dedicated EthertypeEtherType
EtherType is a two-octet field in an Ethernet frame. It is used to indicate which protocol is encapsulated in the PayLoad of an Ethernet Frame. This field was first defined by the Ethernet II framing networking standard, and later adapted for the IEEE 802.3 Ethernet networking standard.EtherType...
, 0x8906. A single 4-bit field (version) satisfies the IEEE sub-type requirements. The SOF (start of frame) and EOF (end of frame) are encoded as specified in RFC 3643. Reserved bits are present to guarantee that the FCoE frame meets the minimum length requirement of Ethernet. Inside the encapsulated Fibre Channel frame, the frame header is retained so as to allow connecting to a storage network by passing on the Fibre Channel frame directly after de-encapsulation.
The FIP (FCoE Initialization Protocol) is an integral part of FCoE. Its main goal is to discover and initialize FCoE capable entities connected to an Ethernet cloud. FIP uses a dedicated Ethertype of 0x8914.
Timeline
Azule Technology developed early implementation and applied for a patent in October 2003.The FCoE standardization activity started in April 2007.
The FCoE technology was defined as part of the INCITS T11 FC-BB-5 standard that was forwarded to ANSI for publication in June 2009.
The FC-BB-5 standard was published in May 2010 as ANSI/INCITS 462-2010.
An early implementor was Nuova Systems, a subsidiary of Cisco Systems
Cisco Systems
Cisco Systems, Inc. is an American multinational corporation headquartered in San Jose, California, United States, that designs and sells consumer electronics, networking, voice, and communications technology and services. Cisco has more than 70,000 employees and annual revenue of US$...
, which announced a switch in April 2008.
Brocade Communications Systems
Brocade Communications Systems
Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. , based in Silicon Valley , is a vendor of storage area network hardware and software. The company also designs, manufactures, and sells networking products and management applications for local, metro, and wide area networks...
also announced support in 2008.
After the Late-2000s financial crisis
Late-2000s financial crisis
The late-2000s financial crisis is considered by many economists to be the worst financial crisis since the Great Depression of the 1930s...
, however, any new technology had a hard time getting established.
See also
- Converged Network AdapterConverged Network AdapterA converged network adapter , also called a converged network interface controller , is a computer input/output device that combines the functionality of a Host Bus Adaptor to a storage area network with a network interface controller for a general-purpose computer network.-Support :Some products...
- iSCSIISCSIIn computing, iSCSI , is an abbreviation of Internet Small Computer System Interface, an Internet Protocol -based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. By carrying SCSI commands over IP networks, iSCSI is used to facilitate data transfers over intranets and to manage...
- ATA over EthernetATA over EthernetATA over Ethernet is a network protocol developed by the Brantley Coile Company, designed for simple, high-performance access of SATA storage devices over Ethernet networks. It is used to build storage area networks with low-cost, standard technologies.- Protocol description :AoE runs on layer 2...
(AoE) - HyperSCSIHyperSCSIHyperSCSI was a computer network protocol for accessing storage by sending and receiving SCSI commands.It was developed by researchers at the Data Storage Institute in Singapore in 2000 to 2003....
External links
- LIO Unified Target (LinuxLinuxLinux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
standard, includes iSCSIISCSIIn computing, iSCSI , is an abbreviation of Internet Small Computer System Interface, an Internet Protocol -based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. By carrying SCSI commands over IP networks, iSCSI is used to facilitate data transfers over intranets and to manage...
, FCFibre ChannelFibre Channel, or FC, is a gigabit-speed network technology primarily used for storage networking. Fibre Channel is standardized in the T11 Technical Committee of the InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards , an American National Standards Institute –accredited standards...
, FCoE, IBInfiniBandInfiniBand is a switched fabric communications link used in high-performance computing and enterprise data centers. Its features include high throughput, low latency, quality of service and failover, and it is designed to be scalable...
) - Implementation for the Linux operating system
- Project's homepage
- Free Windows FCoE implementation
- A site that tracks FCoE development

