
Fermi acceleration
Encyclopedia
Fermi acceleration , sometimes referred to as diffusive shock acceleration (a subclass of Fermi acceleration), is the acceleration
that charged
particles
undergo when being repeatedly reflected, usually by a magnetic mirror
. This is thought to be the primary mechanism by which particles gain non thermal energies in astrophysical shock waves
. It plays a very important role in many astrophysical models, mainly of shocks including solar flares and supernova remnant
s. It is studied by using the Fermi-Ulam model.
There are two types of Fermi acceleration: First order Fermi acceleration (in shocks) and Second Order Fermi acceleration (in the environment of moving magnetized gas clouds). In both cases the environment has to be collisionless in order for the mechanism to be effective. This is because Fermi acceleration only applies to particles with energies exceeding the thermal energies, and frequent collisions with surrounding particles will cause severe energy loss and as a result no acceleration will occur.

where the spectral index depends, for non-relativistic shocks, only on the compression ratio of the shock.
depends, for non-relativistic shocks, only on the compression ratio of the shock.
The term "First order" comes from the fact that the energy gain per shock crossing is proportional to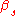 , the velocity of the shock divided by the speed of light.
, the velocity of the shock divided by the speed of light.
s". So, if the magnetic mirror is moving towards the particle, the particle will end up with increased energy upon reflection. The opposite holds if the mirror is receding. This notion was used by Fermi (1949) to explain the mode of formation of cosmic rays. In this case the magnetic mirror is a moving interstellar magnetized cloud. In a random motion environment, Fermi argued, the probability of a head-on collision is greater than a head-tail collision, so particles would, on average, be accelerated. This random process is now called second-order Fermi acceleration, because the mean energy gain per bounce depends on the mirror velocity squared, .
.
Surprisingly, the resulting energy spectrum anticipated from this physical setup is very similar to the one found for first order Fermi acceleration.
Acceleration
In physics, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time. In one dimension, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows down. However, since velocity is a vector, acceleration describes the rate of change of both the magnitude and the direction of velocity. ...
that charged
Charge (physics)
In physics, a charge may refer to one of many different quantities, such as the electric charge in electromagnetism or the color charge in quantum chromodynamics. Charges are associated with conserved quantum numbers.-Formal definition:...
particles
Subatomic particle
In physics or chemistry, subatomic particles are the smaller particles composing nucleons and atoms. There are two types of subatomic particles: elementary particles, which are not made of other particles, and composite particles...
undergo when being repeatedly reflected, usually by a magnetic mirror
Magnetic mirror
A magnetic mirror is a magnetic field configuration where the field strength changes when moving along a field line. The mirror effect results in a tendency for charged particles to bounce back from the high field region....
. This is thought to be the primary mechanism by which particles gain non thermal energies in astrophysical shock waves
Shock Waves
Shock Waves, , is a 1977 horror movie written and directed by Ken Wiederhorn...
. It plays a very important role in many astrophysical models, mainly of shocks including solar flares and supernova remnant
Supernova remnant
A supernova remnant is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar material it sweeps up and shocks along the way.There are two...
s. It is studied by using the Fermi-Ulam model.
There are two types of Fermi acceleration: First order Fermi acceleration (in shocks) and Second Order Fermi acceleration (in the environment of moving magnetized gas clouds). In both cases the environment has to be collisionless in order for the mechanism to be effective. This is because Fermi acceleration only applies to particles with energies exceeding the thermal energies, and frequent collisions with surrounding particles will cause severe energy loss and as a result no acceleration will occur.
First order Fermi acceleration
Shock waves typically have moving magnetic inhomogeneities both preceding and following them. Consider the case of a charged particle traveling through the shock wave (from upstream to downstream). If it encounters a moving change in the magnetic field, this can reflect it back through the shock (downstream to upstream) at increased velocity. If a similar process occurs upstream, the particle will again gain energy. These multiple reflections greatly increase its energy. The resulting energy spectrum of many particles undergoing this process (assuming that they do not influence the structure of the shock) turns out to be a power law:
where the spectral index
 depends, for non-relativistic shocks, only on the compression ratio of the shock.
depends, for non-relativistic shocks, only on the compression ratio of the shock. The term "First order" comes from the fact that the energy gain per shock crossing is proportional to
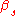 , the velocity of the shock divided by the speed of light.
, the velocity of the shock divided by the speed of light.The injection problem
A mystery of first order Fermi processes is the injection problem. In the environment of a shock, only particles with energies that exceed the thermal energy by much (a factor of a few at least) can cross the shock and 'enter the game' of acceleration. It is presently unclear what mechanism causes the particles to initially have energies sufficiently high to do so.Second order Fermi acceleration
Second order Fermi Acceleration relates to the amount of energy gained during the motion of a charged particle in the presence of randomly moving "magnetic mirrorMagnetic mirror
A magnetic mirror is a magnetic field configuration where the field strength changes when moving along a field line. The mirror effect results in a tendency for charged particles to bounce back from the high field region....
s". So, if the magnetic mirror is moving towards the particle, the particle will end up with increased energy upon reflection. The opposite holds if the mirror is receding. This notion was used by Fermi (1949) to explain the mode of formation of cosmic rays. In this case the magnetic mirror is a moving interstellar magnetized cloud. In a random motion environment, Fermi argued, the probability of a head-on collision is greater than a head-tail collision, so particles would, on average, be accelerated. This random process is now called second-order Fermi acceleration, because the mean energy gain per bounce depends on the mirror velocity squared,
 .
.Surprisingly, the resulting energy spectrum anticipated from this physical setup is very similar to the one found for first order Fermi acceleration.
External links
- David Darling's article on Fermi acceleration
- Rieger, Bosch-Ramon and Duffy: Fermi acceleration in astrophysical jets. Astrophys.Space Sci. 309:119-125 (2007)

