
Faraday's laws of electrolysis
Encyclopedia

Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday, FRS was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry....
in 1834.
Statements of the laws
Several versions of the laws can be found in textbooks and the scientific literature. The most-common statements resemble the following:- Faraday's 1st Law of Electrolysis - The mass of a substance altered at an electrodeElectrodeAn electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
during electrolysisElectrolysisIn chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a method of using a direct electric current to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction...
is directly proportional to the quantity of electricityQuantity of electricityIn physics the term quantity of electricity refers to the quantity of electric charge. It is designated by the letter Q and in the SI system is measured in derived units called Coulombs.- Pre-English origins :...
transferred at that electrode. Quantity of electricity refers to the quantity of electrical charge, typically measured in coulomb.
- Faraday's 2nd Law of Electrolysis - For a given quantity of electricity (electric charge), the mass of an elementalChemical elementA chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
material altered at an electrode is directly proportional to the element's equivalent weightEquivalent weightEquivalent weight is a term which has been used in several contexts in chemistry. In its most general usage, it is the mass of one equivalent, that is the mass of a given substance which will:...
. The equivalent weight of a substance is its molar massMolar massMolar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
divided by an integer that depends on the reaction undergone by the material.
Mathematical form
Faraday's laws can be summarized by
where:
- m is the mass of the substance liberated at an electrode in grams
- Q is the total electric charge passed through the substance
- F = 96,487 C mol−1 is the Faraday constant
- M is the molar mass of the substance
- z is the valency number of ionIonAn ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s of the substance (electrons transferred per ion).
Note that M/z is the same as the equivalent weight
Equivalent weight
Equivalent weight is a term which has been used in several contexts in chemistry. In its most general usage, it is the mass of one equivalent, that is the mass of a given substance which will:...
of the substance altered.
For Faraday's first law, M, F, and z are constants, so that the larger the value of Q the larger m will be.
For Faraday's second law, Q, F, and z are constants, so that the larger the value of M/z (equivalent weight) the larger m will be.
In the simple case of constant-current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
electrolysis,
 leading to
leading to
and then to
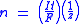
where:
- n is the amount of substanceAmount of substanceAmount of substance is a standards-defined quantity that measures the size of an ensemble of elementary entities, such as atoms, molecules, electrons, and other particles. It is sometimes referred to as chemical amount. The International System of Units defines the amount of substance to be...
("number of moles") liberated: n = m/M - t is the total time the constant current was applied.
In the more-complicated case of a variable electrical current, the total charge Q is the electric current I(
 ) integrated over time
) integrated over time  :
: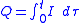
Here t is the total electrolysis time. Please note that tau is used as the current I is a function of tau.
See also
- ElectrolysisElectrolysisIn chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a method of using a direct electric current to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction...
- Michael FaradayMichael FaradayMichael Faraday, FRS was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry....
- Faraday constant
- Faraday's law of inductionFaraday's law of inductionFaraday's law of induction dates from the 1830s, and is a basic law of electromagnetism relating to the operating principles of transformers, inductors, and many types of electrical motors and generators...

