
Exponential dispersion model
Encyclopedia
Exponential dispersion models are statistical model
s in which the probability distribution is of a special form. This class of models represents a generalisation of the exponential family
of models which themselves play an important role in statistical theory
because they have a special structure which enables deductions to be made about appropriate statistical inference
.
: these have a probability density function
which, for a multivariate model, can be written as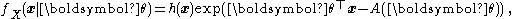
where the parameter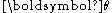 has the same dimension as the observation variable
has the same dimension as the observation variable 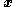 . The generalisation includes an extra scalar "index parameter",
. The generalisation includes an extra scalar "index parameter", 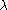 , and has density function of the form
, and has density function of the form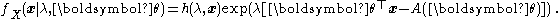
The terminology "dispersion parameter" is used for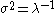 , while
, while 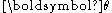 is the "natural parameter" (also known as "canonical parameter").
is the "natural parameter" (also known as "canonical parameter").
Statistical model
A statistical model is a formalization of relationships between variables in the form of mathematical equations. A statistical model describes how one or more random variables are related to one or more random variables. The model is statistical as the variables are not deterministically but...
s in which the probability distribution is of a special form. This class of models represents a generalisation of the exponential family
Exponential family
In probability and statistics, an exponential family is an important class of probability distributions sharing a certain form, specified below. This special form is chosen for mathematical convenience, on account of some useful algebraic properties, as well as for generality, as exponential...
of models which themselves play an important role in statistical theory
Statistical theory
The theory of statistics provides a basis for the whole range of techniques, in both study design and data analysis, that are used within applications of statistics. The theory covers approaches to statistical-decision problems and to statistical inference, and the actions and deductions that...
because they have a special structure which enables deductions to be made about appropriate statistical inference
Statistical inference
In statistics, statistical inference is the process of drawing conclusions from data that are subject to random variation, for example, observational errors or sampling variation...
.
Definition
Exponential dispersion models are a generalisation of the natural exponential familyNatural exponential family
In probability and statistics, the natural exponential family is a class of probability distributions that is a special case of an exponential family...
: these have a probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
which, for a multivariate model, can be written as
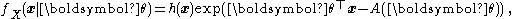
where the parameter
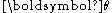 has the same dimension as the observation variable
has the same dimension as the observation variable 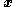 . The generalisation includes an extra scalar "index parameter",
. The generalisation includes an extra scalar "index parameter", 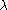 , and has density function of the form
, and has density function of the form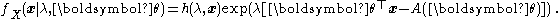
The terminology "dispersion parameter" is used for
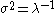 , while
, while 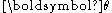 is the "natural parameter" (also known as "canonical parameter").
is the "natural parameter" (also known as "canonical parameter").

