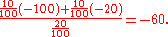Expected shortfall
Encyclopedia
Expected shortfall is a risk measure
, a concept used in finance (and more specifically in the field of financial risk measurement) to evaluate the market risk
or credit risk
of a portfolio. It is an alternative to value at risk
that is more sensitive to the shape of the loss distribution in the tail of the distribution. The "expected shortfall at q% level" is the expected return on the portfolio in the worst % of the cases.
% of the cases.
Expected shortfall is also called conditional value at risk (CVaR), average value at risk (AVaR), and expected tail loss (ETL).
ES evaluates the value (or risk) of an investment in a conservative way, focusing on the less profitable outcomes. For high values of it ignores the most profitable but unlikely possibilities, for small values of
it ignores the most profitable but unlikely possibilities, for small values of  it focuses on the worst losses. On the other hand, unlike the discounted maximum loss
it focuses on the worst losses. On the other hand, unlike the discounted maximum loss
even for lower values of expected shortfall does not consider only the single most catastrophic outcome. A value of
expected shortfall does not consider only the single most catastrophic outcome. A value of  often used in practice is 5%.
often used in practice is 5%.
Expected shortfall is a coherent
, and moreover a spectral
, measure
of financial portfolio risk. It requires a quantile
-level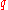 , and is defined to be the expected loss of portfolio
, and is defined to be the expected loss of portfolio
value given that a loss is occurring at or below the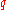 -quantile.
-quantile.
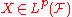 is the payoff of a portfolio at some future time and
is the payoff of a portfolio at some future time and 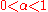 then we define the expected shortfall as
then we define the expected shortfall as 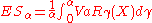 where
where 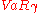 is the Value at risk
is the Value at risk
. This can be equivalently written as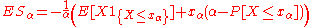 where
where  is the lower
is the lower  -quantile
-quantile
. The dual representation is
where is the set of probability measure
is the set of probability measure
s which are absolutely continuous to the physical measure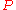 such that
such that 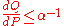 almost surely
almost surely
. Note that is the Radon–Nikodym derivative of
is the Radon–Nikodym derivative of  with respect to
with respect to  .
.
If the underlying distribution for is a continuous distribution then the expected shortfall is equivalent to the tail conditional expectation defined by
is a continuous distribution then the expected shortfall is equivalent to the tail conditional expectation defined by  .
.
Informally, and non rigorously, this equation amounts to saying "in case of losses so severe that they occur only alpha percent of the time, what is our average loss".
Example 2. Consider a portfolio that will have the following possible values at the end of the period:
Notice that, for convenience, the outcomes have been ordered from worst (first row) to best (last row). Also, the probabilities add up to 100% by construction.
Now assume that we paid 100 at the beginning of the period for this portfolio. Then the profit in each case is (ending value-initial investment) or:
From this table let us calculate the expected shortfall for a few (arbitrarily chosen) values of
for a few (arbitrarily chosen) values of  :
:
To see how these values were calculated, consider the calculation of , the expectation in the worst 5 out of 100 cases. These cases belong to (are a subset of) row 1 in the profit table, which have a profit of -100 (total loss of the 100 invested). The expected profit for these cases is -100.
, the expectation in the worst 5 out of 100 cases. These cases belong to (are a subset of) row 1 in the profit table, which have a profit of -100 (total loss of the 100 invested). The expected profit for these cases is -100.
Now consider the calculation of , the expectation in the worst 20 out of 100 cases. These cases are as follows: 10 cases from row one, and 10 cases from row two (note that 10+10 equals the desired 20 cases). For row 1 there is a profit of -100, while for row 2 a profit of -20. Using the expected value formula we get
, the expectation in the worst 20 out of 100 cases. These cases are as follows: 10 cases from row one, and 10 cases from row two (note that 10+10 equals the desired 20 cases). For row 1 there is a profit of -100, while for row 2 a profit of -20. Using the expected value formula we get
Similarly for any value of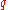 . We select as many rows starting from the top as are necessary to give a cumulative probability of
. We select as many rows starting from the top as are necessary to give a cumulative probability of  and then calculate an expectation over those cases. In general the last row selected may not be fully used (for example in calculating
and then calculate an expectation over those cases. In general the last row selected may not be fully used (for example in calculating 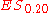 we used only 10 of the 30 cases per 100 provided by row 2).
we used only 10 of the 30 cases per 100 provided by row 2).
As a final example, calculate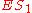 . This is the expectation over all cases, or
. This is the expectation over all cases, or
 increases as
increases as  increases.
increases.
The 100%-quantile expected shortfall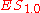 equals the Expected value
equals the Expected value
of the portfolio. (Note that this is a special case; expected shortfall and expected value are not equal in general).
For a given portfolio the expected shortfall is worse than (or equal) to the Value at Risk
is worse than (or equal) to the Value at Risk 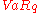 at the same
at the same  level.
level.

where .
.
This is not a time-consistent risk measure. The time-consistent version is given by
such that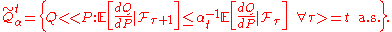
Methods of statistical estimation of VaR and ES can be found in
Embrechts et al. and Novak .
Risk measure
A Risk measure is used to determine the amount of an asset or set of assets to be kept in reserve. The purpose of this reserve is to make the risks taken by financial institutions, such as banks and insurance companies, acceptable to the regulator...
, a concept used in finance (and more specifically in the field of financial risk measurement) to evaluate the market risk
Market risk
Market risk is the risk that the value of a portfolio, either an investment portfolio or a trading portfolio, will decrease due to the change in value of the market risk factors. The four standard market risk factors are stock prices, interest rates, foreign exchange rates, and commodity prices...
or credit risk
Credit risk
Credit risk is an investor's risk of loss arising from a borrower who does not make payments as promised. Such an event is called a default. Other terms for credit risk are default risk and counterparty risk....
of a portfolio. It is an alternative to value at risk
Value at risk
In financial mathematics and financial risk management, Value at Risk is a widely used risk measure of the risk of loss on a specific portfolio of financial assets...
that is more sensitive to the shape of the loss distribution in the tail of the distribution. The "expected shortfall at q% level" is the expected return on the portfolio in the worst
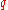 % of the cases.
% of the cases.Expected shortfall is also called conditional value at risk (CVaR), average value at risk (AVaR), and expected tail loss (ETL).
ES evaluates the value (or risk) of an investment in a conservative way, focusing on the less profitable outcomes. For high values of
 it ignores the most profitable but unlikely possibilities, for small values of
it ignores the most profitable but unlikely possibilities, for small values of 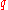 it focuses on the worst losses. On the other hand, unlike the discounted maximum loss
it focuses on the worst losses. On the other hand, unlike the discounted maximum lossDiscounted maximum loss
Discounted maximum loss is the present value of the worst case scenario for a financial portfolio.An investor must consider all possible alternatives for the value of his investment. How he weights the different alternatives is a matter of preference. One might require a pension fund never to go...
even for lower values of
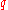 expected shortfall does not consider only the single most catastrophic outcome. A value of
expected shortfall does not consider only the single most catastrophic outcome. A value of  often used in practice is 5%.
often used in practice is 5%.Expected shortfall is a coherent
Coherent risk measure
In the field of financial economics there are a number of ways that risk can be defined; to clarify the concept theoreticians have described a number of properties that a risk measure might or might not have...
, and moreover a spectral
Spectral risk measure
A Spectral risk measure is a risk measure given as a weighted average of outcomes where bad outcomes are, typically, included with larger weights. A spectral risk measure is a function of portfolio returns and outputs the amount of the numeraire to be kept in reserve. A spectral risk measure is...
, measure
Risk measure
A Risk measure is used to determine the amount of an asset or set of assets to be kept in reserve. The purpose of this reserve is to make the risks taken by financial institutions, such as banks and insurance companies, acceptable to the regulator...
of financial portfolio risk. It requires a quantile
Quantile
Quantiles are points taken at regular intervals from the cumulative distribution function of a random variable. Dividing ordered data into q essentially equal-sized data subsets is the motivation for q-quantiles; the quantiles are the data values marking the boundaries between consecutive subsets...
-level
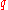 , and is defined to be the expected loss of portfolio
, and is defined to be the expected loss of portfolioPortfolio (finance)
Portfolio is a financial term denoting a collection of investments held by an investment company, hedge fund, financial institution or individual.-Definition:The term portfolio refers to any collection of financial assets such as stocks, bonds and cash...
value given that a loss is occurring at or below the
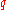 -quantile.
-quantile.Formal definition
If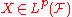 is the payoff of a portfolio at some future time and
is the payoff of a portfolio at some future time and 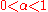 then we define the expected shortfall as
then we define the expected shortfall as 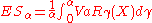 where
where 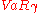 is the Value at risk
is the Value at riskValue at risk
In financial mathematics and financial risk management, Value at Risk is a widely used risk measure of the risk of loss on a specific portfolio of financial assets...
. This can be equivalently written as
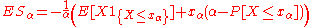 where
where  is the lower
is the lower  -quantile
-quantileQuantile
Quantiles are points taken at regular intervals from the cumulative distribution function of a random variable. Dividing ordered data into q essentially equal-sized data subsets is the motivation for q-quantiles; the quantiles are the data values marking the boundaries between consecutive subsets...
. The dual representation is

where
 is the set of probability measure
is the set of probability measureProbability measure
In mathematics, a probability measure is a real-valued function defined on a set of events in a probability space that satisfies measure properties such as countable additivity...
s which are absolutely continuous to the physical measure
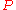 such that
such that 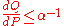 almost surely
almost surelyAlmost surely
In probability theory, one says that an event happens almost surely if it happens with probability one. The concept is analogous to the concept of "almost everywhere" in measure theory...
. Note that
 is the Radon–Nikodym derivative of
is the Radon–Nikodym derivative of  with respect to
with respect to  .
.If the underlying distribution for
 is a continuous distribution then the expected shortfall is equivalent to the tail conditional expectation defined by
is a continuous distribution then the expected shortfall is equivalent to the tail conditional expectation defined by  .
.Informally, and non rigorously, this equation amounts to saying "in case of losses so severe that they occur only alpha percent of the time, what is our average loss".
Examples
Example 1. If we believe our average loss on the worst 5% of the possible outcomes for our portfolio is EUR 1000, then we could say our expected shortfall is EUR 1000 for the 5% tail.Example 2. Consider a portfolio that will have the following possible values at the end of the period:
Notice that, for convenience, the outcomes have been ordered from worst (first row) to best (last row). Also, the probabilities add up to 100% by construction.
| probability | ending value |
|---|---|
| of event | of the portfolio |
| 10% | 0 |
| 30% | 80 |
| 40% | 100 |
| 20% | 150 |
Now assume that we paid 100 at the beginning of the period for this portfolio. Then the profit in each case is (ending value-initial investment) or:
| probability | |
|---|---|
| of event | profit |
| 10% | −100 |
| 30% | −20 |
| 40% | 0 |
| 20% | 50 |
From this table let us calculate the expected shortfall
 for a few (arbitrarily chosen) values of
for a few (arbitrarily chosen) values of  :
:  |
expected shortfall  |
|---|---|
| 5% | −100 |
| 10% | −100 |
| 20% | −60 |
| 40% | −40 |
| 100% | −6 |
To see how these values were calculated, consider the calculation of
 , the expectation in the worst 5 out of 100 cases. These cases belong to (are a subset of) row 1 in the profit table, which have a profit of -100 (total loss of the 100 invested). The expected profit for these cases is -100.
, the expectation in the worst 5 out of 100 cases. These cases belong to (are a subset of) row 1 in the profit table, which have a profit of -100 (total loss of the 100 invested). The expected profit for these cases is -100.Now consider the calculation of
 , the expectation in the worst 20 out of 100 cases. These cases are as follows: 10 cases from row one, and 10 cases from row two (note that 10+10 equals the desired 20 cases). For row 1 there is a profit of -100, while for row 2 a profit of -20. Using the expected value formula we get
, the expectation in the worst 20 out of 100 cases. These cases are as follows: 10 cases from row one, and 10 cases from row two (note that 10+10 equals the desired 20 cases). For row 1 there is a profit of -100, while for row 2 a profit of -20. Using the expected value formula we getSimilarly for any value of
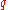 . We select as many rows starting from the top as are necessary to give a cumulative probability of
. We select as many rows starting from the top as are necessary to give a cumulative probability of  and then calculate an expectation over those cases. In general the last row selected may not be fully used (for example in calculating
and then calculate an expectation over those cases. In general the last row selected may not be fully used (for example in calculating  we used only 10 of the 30 cases per 100 provided by row 2).
we used only 10 of the 30 cases per 100 provided by row 2).As a final example, calculate
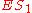 . This is the expectation over all cases, or
. This is the expectation over all cases, orProperties
The expected shortfall increases as
increases as  increases.
increases.The 100%-quantile expected shortfall
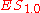 equals the Expected value
equals the Expected valueExpected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
of the portfolio. (Note that this is a special case; expected shortfall and expected value are not equal in general).
For a given portfolio the expected shortfall
 is worse than (or equal) to the Value at Risk
is worse than (or equal) to the Value at Risk 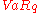 at the same
at the same  level.
level.Dynamic expected shortfall
The conditional version of the expected shortfall at the time t is defined by
where
 .
.This is not a time-consistent risk measure. The time-consistent version is given by

such that
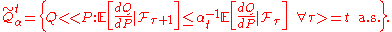
See also
- Coherent risk measureCoherent risk measureIn the field of financial economics there are a number of ways that risk can be defined; to clarify the concept theoreticians have described a number of properties that a risk measure might or might not have...
Methods of statistical estimation of VaR and ES can be found in
Embrechts et al. and Novak .