
Exchange symmetry
Encyclopedia
Exchange symmetry is derived from a fundamental postulate of quantum statistics, which states that no observable physical quantity
should change after exchanging two identical particles
. It states that because all observables are proportional to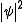 for a system of identical particles
for a system of identical particles
, the wave function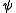 must either remain the same or change sign upon such an exchange.
must either remain the same or change sign upon such an exchange.
Because the exchange of two identical particles is mathematically equivalent to the rotation
of each particle by 180 degrees (and so to the rotation of one particle's frame by 360 degrees) , the symmetric nature of the wave function depends on the particle's spin
after the rotation operator is applied to it. Integer spin particles do not change the sign of their wave function upon a 360 degree rotation—therefore the sign of the wave function of the entire system does not change. Semi-integer spin particles change the sign of their wave function upon a 360 degree rotation (see more in spin-statistics theorem
).
Particles for which the wave function does not change sign upon exchange are called bosons, or particles with a symmetric wave function. The particles for which the wave function of the system changes sign are called fermion
s, or particles with an antisymmetric
wave function.
Fermions therefore obey different statistics (called Fermi-Dirac statistics
) than bosons (which obey Bose-Einstein statistics). One of the consequences of Fermi-Dirac statistics is the exclusion principle
for fermions—no two fermions can share the same quantum state (in other words, the wave function of two fermions in the same state is zero). This in turn results in degeneracy pressure for fermions—the strong resistance of fermions to compression into smaller volume. This resistance gives rise to the “stiffness” or “rigidity” of ordinary atomic matter (as atoms contain electrons which are fermions).
Physical quantity
A physical quantity is a physical property of a phenomenon, body, or substance, that can be quantified by measurement.-Definition of a physical quantity:Formally, the International Vocabulary of Metrology, 3rd edition defines quantity as:...
should change after exchanging two identical particles
Identical particles
Identical particles, or indistinguishable particles, are particles that cannot be distinguished from one another, even in principle. Species of identical particles include elementary particles such as electrons, and, with some clauses, composite particles such as atoms and molecules.There are two...
. It states that because all observables are proportional to
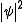 for a system of identical particles
for a system of identical particlesIdentical particles
Identical particles, or indistinguishable particles, are particles that cannot be distinguished from one another, even in principle. Species of identical particles include elementary particles such as electrons, and, with some clauses, composite particles such as atoms and molecules.There are two...
, the wave function
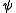 must either remain the same or change sign upon such an exchange.
must either remain the same or change sign upon such an exchange.Because the exchange of two identical particles is mathematically equivalent to the rotation
Rotation
A rotation is a circular movement of an object around a center of rotation. A three-dimensional object rotates always around an imaginary line called a rotation axis. If the axis is within the body, and passes through its center of mass the body is said to rotate upon itself, or spin. A rotation...
of each particle by 180 degrees (and so to the rotation of one particle's frame by 360 degrees) , the symmetric nature of the wave function depends on the particle's spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
after the rotation operator is applied to it. Integer spin particles do not change the sign of their wave function upon a 360 degree rotation—therefore the sign of the wave function of the entire system does not change. Semi-integer spin particles change the sign of their wave function upon a 360 degree rotation (see more in spin-statistics theorem
Spin-statistics theorem
In quantum mechanics, the spin-statistics theorem relates the spin of a particle to the particle statistics it obeys. The spin of a particle is its intrinsic angular momentum...
).
Particles for which the wave function does not change sign upon exchange are called bosons, or particles with a symmetric wave function. The particles for which the wave function of the system changes sign are called fermion
Fermion
In particle physics, a fermion is any particle which obeys the Fermi–Dirac statistics . Fermions contrast with bosons which obey Bose–Einstein statistics....
s, or particles with an antisymmetric
Antisymmetric
The word antisymmetric refers to a change to an opposite quantity when another quantity is symmetrically changed. This concept is related to that of Symmetry and Asymmetry. The difference between these three concepts can be simply illustrated with Latin letters. The character "A" is symmetric about...
wave function.
Fermions therefore obey different statistics (called Fermi-Dirac statistics
Fermi-Dirac statistics
Fermi–Dirac statistics is a part of the science of physics that describes the energies of single particles in a system comprising many identical particles that obey the Pauli Exclusion Principle...
) than bosons (which obey Bose-Einstein statistics). One of the consequences of Fermi-Dirac statistics is the exclusion principle
Pauli exclusion principle
The Pauli exclusion principle is the quantum mechanical principle that no two identical fermions may occupy the same quantum state simultaneously. A more rigorous statement is that the total wave function for two identical fermions is anti-symmetric with respect to exchange of the particles...
for fermions—no two fermions can share the same quantum state (in other words, the wave function of two fermions in the same state is zero). This in turn results in degeneracy pressure for fermions—the strong resistance of fermions to compression into smaller volume. This resistance gives rise to the “stiffness” or “rigidity” of ordinary atomic matter (as atoms contain electrons which are fermions).
See also
- Exchange interactionExchange interactionIn physics, the exchange interaction is a quantum mechanical effect without classical analog which increases or decreases the expectation value of the energy or distance between two or more identical particles when their wave functions overlap...
- Identical particlesIdentical particlesIdentical particles, or indistinguishable particles, are particles that cannot be distinguished from one another, even in principle. Species of identical particles include elementary particles such as electrons, and, with some clauses, composite particles such as atoms and molecules.There are two...
- Holstein–Herring method

