
Evection
Encyclopedia
Evection in astronomy
, is the largest inequality produced by the action of the Sun
in the month
ly revolution of the Moon
around the Earth
. The evection, formerly called the moon's second anomaly, was approximately known in ancient times, and its discovery is attributed to Ptolemy
. (The current name itself dates much more recently, from the 17th century: it was coined by Bullialdus
in connection with his own (unsuccessful) theory of the Moon's motion.)
Evection causes the Moon's ecliptic longitude to vary by approximately ± 1.274° (degrees
), with a period of about 31.8 days. The evection in longitude is given by the expression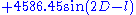 , where
, where  is the (mean) elongation, i.e. mean angular distance of the Moon from the Sun, and
is the (mean) elongation, i.e. mean angular distance of the Moon from the Sun, and 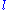 is the moon's mean anomaly, i.e. mean angular distance of the moon from its perigee.
is the moon's mean anomaly, i.e. mean angular distance of the moon from its perigee.
It can be considered as arising from an approximately 6-monthly periodic variation of the eccentricity of the Moon's orbit and a libration of similar period in the position of the Moon's perigee
, caused by the action of the Sun.
The evection can be considered as opposing the Moon's equation of the center
at the new and full moons, and augmenting the equation of the center at the Moon's quarters. This can be seen from the combination of the principal term of the equation of the center with the evection: .
.
At new and full moons, D=0° or 180°, 2D is effectively zero in either case, and the combined expression reduces to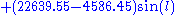 .
.
At the quarters, D=90° or 270°, 2D is effectively 180° in either case, changing the sign of the expression for the evection, so that the combined expression reduces now to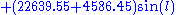 .
.
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, is the largest inequality produced by the action of the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
in the month
Month
A month is a unit of time, used with calendars, which was first used and invented in Mesopotamia, as a natural period related to the motion of the Moon; month and Moon are cognates. The traditional concept arose with the cycle of moon phases; such months are synodic months and last approximately...
ly revolution of the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
around the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
. The evection, formerly called the moon's second anomaly, was approximately known in ancient times, and its discovery is attributed to Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
. (The current name itself dates much more recently, from the 17th century: it was coined by Bullialdus
Ismaël Bullialdus
Ismaël Bullialdus was a French astronomer.Bullialdus was born Ismaël Boulliau in Loudun, Vienne, France, the first surviving son to Calvinists Susanna Motet and Ismaël Boulliau, a notary by profession and amateur astronomer. At age twenty-one he converted to Catholicism, and by twenty-six was...
in connection with his own (unsuccessful) theory of the Moon's motion.)
Evection causes the Moon's ecliptic longitude to vary by approximately ± 1.274° (degrees
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
), with a period of about 31.8 days. The evection in longitude is given by the expression
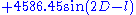 , where
, where  is the (mean) elongation, i.e. mean angular distance of the Moon from the Sun, and
is the (mean) elongation, i.e. mean angular distance of the Moon from the Sun, and 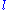 is the moon's mean anomaly, i.e. mean angular distance of the moon from its perigee.
is the moon's mean anomaly, i.e. mean angular distance of the moon from its perigee.It can be considered as arising from an approximately 6-monthly periodic variation of the eccentricity of the Moon's orbit and a libration of similar period in the position of the Moon's perigee
Perigee
Perigee is the point at which an object makes its closest approach to the Earth.. Often the term is used in a broader sense to define the point in an orbit where the orbiting body is closest to the body it orbits. The opposite is the apogee, the farthest or highest point.The Greek prefix "peri"...
, caused by the action of the Sun.
The evection can be considered as opposing the Moon's equation of the center
Equation of the center
For further closely related mathematical developments see also Two-body problem, also Gravitational two-body problem, also Kepler orbit, and Kepler problem...
at the new and full moons, and augmenting the equation of the center at the Moon's quarters. This can be seen from the combination of the principal term of the equation of the center with the evection:
 .
.At new and full moons, D=0° or 180°, 2D is effectively zero in either case, and the combined expression reduces to
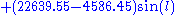 .
.At the quarters, D=90° or 270°, 2D is effectively 180° in either case, changing the sign of the expression for the evection, so that the combined expression reduces now to
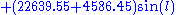 .
.

