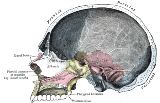
Ethmoid bone
Overview
The ethmoid bone is a bone
in the skull
that separates the nasal cavity
from the brain
. As such, it is located at the roof of the nose
, between the two orbit
s. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction. The ethmoid bone is one of the bones that makes up the orbit of the eye. The ethmoid has three parts: the cribriform plate, the ethmodial labyrinth, and the perpendicular plate
The ethmoid articulates with fifteen bones:
Fracture of the lamina papyracea, the lateral plate of the ethmoid labyrinth bone, permits communication between the nasal cavity and the ipsilateral orbit through the inferomedial orbital wall, resulting in orbital emphysema.
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
in the skull
Human skull
The human skull is a bony structure, skeleton, that is in the human head and which supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.In humans, the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones...
that separates the nasal cavity
Nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is a large air filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face.- Function :The nasal cavity conditions the air to be received by the other areas of the respiratory tract...
from the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
. As such, it is located at the roof of the nose
Human nose
The visible part of the human nose is the protruding part of the face that bears the nostrils. The shape of the nose is determined by the ethmoid bone and the nasal septum, which consists mostly of cartilage and which separates the nostrils...
, between the two orbit
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents...
s. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction. The ethmoid bone is one of the bones that makes up the orbit of the eye. The ethmoid has three parts: the cribriform plate, the ethmodial labyrinth, and the perpendicular plate
The ethmoid articulates with fifteen bones:
- four of the neurocranium—the frontalFrontal boneThe frontal bone is a bone in the human skull that resembles a cockleshell in form, and consists of two portions:* a vertical portion, the squama frontalis, corresponding with the region of the forehead....
, and the sphenoidSphenoid boneThe sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone situated at the base of the skull in front of the temporal bone and basilar part of the occipital bone.The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit...
(at the sphenoidal bodyBody of sphenoid boneThe body of the sphenoid bone, more or less cubical in shape, is hollowed out in its interior to form two large cavities, the sphenoidal air sinuses, which are separated from each other by a septum.- Superior surface :...
and at the sphenoidal conchaeSphenoidal conchaeThe sphenoidal conchae are two thin, curved plates, situated at the anterior and lower part of the body of the sphenoid...
). - eleven of the viscerocranium—, two Nasal bones, two maxillae, two lacrimals, two palatinesPalatine boneThe palatine bone is a bone in many species of the animal kingdom, commonly termed the palatum .-Human anatomy:...
, two inferior nasal conchaeInferior nasal conchaeThe inferior nasal concha is one of the turbinates in the nose. It extends horizontally along the lateral wall of the nasal cavity [Fig. 1] and consists of a lamina of spongy bone, curled upon itself like a scroll...
, and the vomerVomerThe vomer is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones.-Biology:...
Fracture of the lamina papyracea, the lateral plate of the ethmoid labyrinth bone, permits communication between the nasal cavity and the ipsilateral orbit through the inferomedial orbital wall, resulting in orbital emphysema.
Unanswered Questions

