
Equivalent width
Encyclopedia
The equivalent width of a spectral line
is a measure of the area of the line on a plot of intensity
versus wavelength
. It is found by forming a rectangle with a height equal to that of continuum emission, and finding the width such that the area of the rectangle is equal to the area in the spectral line. It is a measure of the strength of spectral features that is primarily used in astronomy
.
 .
.
Here,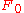 represents the continuum intensity on either side of the absorption
represents the continuum intensity on either side of the absorption
(or emission) feature, while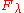 represents the intensity across the entire wavelength range of interest. Then
represents the intensity across the entire wavelength range of interest. Then 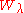 represents the width of a hypothetical line which drops to an intensity of zero and has the "same integrated flux deficit from the continuum as the true one." This equation can be applied to either emission or absorption, but when applied to emission, the value of
represents the width of a hypothetical line which drops to an intensity of zero and has the "same integrated flux deficit from the continuum as the true one." This equation can be applied to either emission or absorption, but when applied to emission, the value of  is negative, and so the absolute value is used.
is negative, and so the absolute value is used.
due to motions of the gas emitting the photons. The photons will be shifted away from the line center, thus rendering the height of the emission line a poor measure of its overall strength. The equivalent width, on the other hand, "measures the fraction of energy removed from the spectrum by the line," regardless of the broadening intrinsic to the line or a detector with poor resolution
. Thus the equivalent width can in many conditions yield the number of absorbing or emitting atoms.
For example, measurements of the equivalent width of the Balmer alpha
transition in T Tauri star
s are used in order to classify individual T Tauri stars as being classical or weak-lined. The equivalent width is also be used in studying star formation
in Lyman alpha
galaxies
, as the equivalent width of the Lyman alpha line is related to the star formation rate in the galaxy. The equivalent width is also used in many other situations where a quantitative comparison between line strengths is needed.
Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from a deficiency or excess of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies.- Types of line spectra :...
is a measure of the area of the line on a plot of intensity
Luminous intensity
In photometry, luminous intensity is a measure of the wavelength-weighted power emitted by a light source in a particular direction per unit solid angle, based on the luminosity function, a standardized model of the sensitivity of the human eye...
versus wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
. It is found by forming a rectangle with a height equal to that of continuum emission, and finding the width such that the area of the rectangle is equal to the area in the spectral line. It is a measure of the strength of spectral features that is primarily used in astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
.
Definition
Formally, the equivalent width is given by the equation .
.Here,
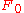 represents the continuum intensity on either side of the absorption
represents the continuum intensity on either side of the absorptionAbsorption (electromagnetic radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way by which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed to other forms of energy for example, to heat. The absorption of light during wave propagation is...
(or emission) feature, while
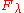 represents the intensity across the entire wavelength range of interest. Then
represents the intensity across the entire wavelength range of interest. Then 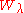 represents the width of a hypothetical line which drops to an intensity of zero and has the "same integrated flux deficit from the continuum as the true one." This equation can be applied to either emission or absorption, but when applied to emission, the value of
represents the width of a hypothetical line which drops to an intensity of zero and has the "same integrated flux deficit from the continuum as the true one." This equation can be applied to either emission or absorption, but when applied to emission, the value of  is negative, and so the absolute value is used.
is negative, and so the absolute value is used.Applications
The equivalent width is used as a quantitative measure of the strength of spectral features. The equivalent width is a convenient choice because the shapes of spectral features can vary depending upon the configuration of the system which is producing the lines. For instance, the line may experience Doppler broadeningDoppler broadening
In atomic physics, Doppler broadening is the broadening of spectral lines due to the Doppler effect caused by a distribution of velocities of atoms or molecules. Different velocities of the emitting particles result in different shifts, the cumulative effect of which is the line broadening.The...
due to motions of the gas emitting the photons. The photons will be shifted away from the line center, thus rendering the height of the emission line a poor measure of its overall strength. The equivalent width, on the other hand, "measures the fraction of energy removed from the spectrum by the line," regardless of the broadening intrinsic to the line or a detector with poor resolution
Spectral resolution
The spectral resolution of a spectrograph, or, more generally, of a frequency spectrum, is a measure of its ability to resolve features in the electromagnetic spectrum...
. Thus the equivalent width can in many conditions yield the number of absorbing or emitting atoms.
For example, measurements of the equivalent width of the Balmer alpha
Balmer series
The Balmer series or Balmer lines in atomic physics, is the designation of one of a set of six different named series describing the spectral line emissions of the hydrogen atom....
transition in T Tauri star
T Tauri star
T Tauri stars are a class of variable stars named after their prototype – T Tauri. They are found near molecular clouds and identified by their optical variability and strong chromospheric lines.-Characteristics:...
s are used in order to classify individual T Tauri stars as being classical or weak-lined. The equivalent width is also be used in studying star formation
Star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense parts of molecular clouds collapse into a ball of plasma to form a star. As a branch of astronomy star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium and giant molecular clouds as precursors to the star formation process and the study of young...
in Lyman alpha
Lyman series
In physics and chemistry, the Lyman series is the series of transitions and resulting ultraviolet emission lines of the hydrogen atom as an electron goes from n ≥ 2 to n = 1...
galaxies
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
, as the equivalent width of the Lyman alpha line is related to the star formation rate in the galaxy. The equivalent width is also used in many other situations where a quantitative comparison between line strengths is needed.

