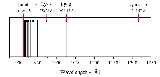
Lyman series
Overview
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, the Lyman series is the series of transitions and resulting ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
emission lines of the hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
as an electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
goes from n ≥ 2 to n = 1 (where n is the principal quantum number
Principal quantum number
In atomic physics, the principal quantum symbolized as n is the firstof a set of quantum numbers of an atomic orbital. The principal quantum number can only have positive integer values...
referring to the energy level of the electron). The transitions are named sequentially by Greek letters: from n = 2 to n = 1 is called Lyman-alpha
Lyman-alpha line
In physics, the Lyman-alpha line, sometimes written as Ly-\alpha line, is a spectral line of hydrogen, or more generally of one-electron ions, in the Lyman series, emitted when the electron falls from the n = 2 orbital to the n = 1 orbital, where n is the principal quantum number...
, 3 to 1 is Lyman-beta, 4 to 1 is Lyman-gamma, etc.

