
Epidemiology of obesity
Encyclopedia
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
was rarely seen. It was not until the 20th century that it became common, so much so that in 1997 the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
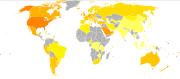
(WHO) formally recognized obesity as a global epidemic. As of 2005 the WHO estimates that at least 400 million adults (9.8%) are obese, with higher rates among women than men. As of 2008, The World Health Organization claimed that 1.5 billion adults, 20 and older, were overweight and of these over 200 million men and nearly 300 million women were obese. The rate of obesity also increases with age at least up to 50 or 60 years old. Once considered a problem only of high-income countries, obesity rates are rising worldwide. These increases have been felt most dramatically in urban settings. The only remaining region of the world where obesity is not common is sub-Saharan Africa.
Australia
In the 2005 National Health Survey, 53.6% of Australians reported being overweight (above a 25 BMIBody mass index
The body mass index , or Quetelet index, is a heuristic proxy for human body fat based on an individual's weight and height. BMI does not actually measure the percentage of body fat. It was invented between 1830 and 1850 by the Belgian polymath Adolphe Quetelet during the course of developing...
), with 18% falling into the "obese" category (above a 30 BMI).
Canada
The number of Canadians who are obese has risen dramatically in recent years. In 2004, direct measurements of height and weight found 23.1% of Canadians older than 18 had a BMI greater than 30. When broken down into degrees of obesity, 15.2% were class I (BMI 30–34.9), 5.1% were class II (BMI 35–39.9), and 2.7%, class III (BMI > 40). This is in contrast to self-reported data the previous year of 15.2% and in 1978/1979 of 13.8%. The greatest increases occurred among the more severe degrees of obesity; class III obesity increased from 0.9% to 2.7% from 1978/1979 to 2004. Obesity in Canada varies by ethnicity; people of Aboriginal origin have a significantly higher rate of obesity (37.6%) than the national average.In children obesity has substantially increased between 1989 and 2004 with rates in boys increasing from 2% to 10% and rates among girls increasing from 2% to 9%.
China
China is currently facing challenges of overnutrition. This is believed to be primarily due to the rapid declines in physical activity and changing dietary habits which has occurred between the 1980s and the 2000s. The decline in physical activity is attributed to increasing technology in the workplace and changing leisure activities. In 1989 65% of Chinese had jobs that required heavy labor. This decreased to 51% in the year 2000. Combined with this has been a change to a diet higher in meat and oil, and an increase in overall available calories. Available calories per person increased from 2330 kcal/day in 1980 to 2940 kcal/day in 2002. Rates of overweight and obese adults increased 12.9% in 1991 to 27.3% in 2004.Overall rates of obesity are below 5% in China as a whole but are greater than 20% in some cities.
Egypt
The peasants in Egypt believe that fatness is proper as the “envelope for conception;” therefore, there is enough room to bear and give warmth to the child.European Union
_1981-2006.jpg)
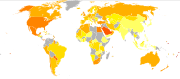
Most recent statistics show that, among the 19 EU Member States for which data are available, the proportion of obese people in the adult population varied in 2008/9 between 8,0 % (Romania) and 23,9 % (UK) for women and between 7,6 % (Romania) and 24,7 % (Malta) for men.
India
In India urbanization and modernization has been associated with obesity. In Northern India obesity was most prevalent in urban populations (male = 5.5%, female = 12.6%), followed by the urban slums (male = 1.9%, female = 7.2%). Obesity rates were the lowest in rural populations (male = 1.6%, female = 3.8%). Socioeconomic class also had an effect on the rate of obesity. Women of high socioeconomic class had rates of 10.4% as opposed to 0.9% in women of low socioeconomic class. With people moving into urban centers and wealth increasing, concerns about an obesity epidemic in India are growing.Iran
In Iran, as of 2008, 26.3% of the population is obese. Obesity was more among women (39.5%) than men (14.5%).Japan
Using the WHO criteria Japan has the lowest rate of obesity among the OECDOrganisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is an international economic organisation of 34 countries founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade...
member countries at 3.2%. However, as Asian populations are particularly susceptible to the health risks of excess adipose tissue the Japanese have redefined obesity as any BMI greater than 25. Using this cut off value the prevalence of obesity in Japan would be 20%, a threefold increase from 1962 to 2002. A 2008 report stated that 28.6% of men and 20.6% of women in Japan were considered to be obese.
Mexico
Mexico has the second-highest rate of obesity among OECD members, at 24.2% of the population.New Zealand
Obesity in New Zealand has become an important national health concern in recent years, with high numbers of people afflicted in every age and ethnic group. As of June 2008, 26.5% of New Zealanders are obese, a number only surpassed in the AnglosphereAnglosphere
Anglosphere is a neologism which refers to those nations with English as the most common language. The term can be used more specifically to refer to those nations which share certain characteristics within their cultures based on a linguistic heritage, through being former British colonies...
by the United States
Obesity in the United States
Obesity in the United States has been increasingly cited as a major health issue in recent decades. While many industrialized countries have experienced similar increases, obesity rates in the United States are among the highest in the world with 74.6% of Americans being overweight or obese...
.
Pakistan
Changing lifestyles, owing to urbanisation, as well as diet issues are the main reasons for obesity in Pakistan. According to a recent study, approximately one out of four Pakistani adults (or 22.2% of individuals) are classified as obese.South Pacific
Many of the island nations of the South Pacific have very high rates of obesity. NauruNauru
Nauru , officially the Republic of Nauru and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country in Micronesia in the South Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Kiribati, to the east. Nauru is the world's smallest republic, covering just...
has the highest rates of obesity in the world (80%) followed by Tonga
Tonga
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga , is a state and an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, comprising 176 islands scattered over of ocean in the South Pacific...
, the Federated States of Micronesia
Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia or FSM is an independent, sovereign island nation, made up of four states from west to east: Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosrae. It comprises approximately 607 islands with c...
, and the Cook Islands
Cook Islands
The Cook Islands is a self-governing parliamentary democracy in the South Pacific Ocean in free association with New Zealand...
. Being big has traditionally been associated with health, beauty, and status and many of these beliefs remain prevalent today.
Taiwan
In 2002, 15% of children range from 6 to 12 years of age were overweight, by gender, 15.5% of male and 14.4% of female were overweight. In the same age range, 12% of children were obese, by gender, 14.7% of male and 9.1% of female were categorized as obese. In 2005, 14.9% children range from 6 to 12 years of age were overweight, where by gender, 15.85% of male and 14.02% of female were overweight. 10.3% were categorized as obese, where by gender, 10.92% of male and 9.73% were categorized as obese.Base on these reports done, the trends were inconclusive, although with more than 10% of the age group being obese, the problem of overweight and obesity does appear to be a problem.
United Kingdom
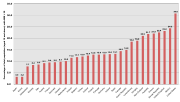
In the UK the rate of obesity has increased about fourfold over the last 30 years, reaching levels of 22-24% in 2008/9.| Year | Percent males obese | Percent females obese |
|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 6% | 8% |
| 1993 | 13% | 16% |
| 2000 | 21% | 21% |
| 2008/9 | 22% | 24% |
United States
The United States has the highest obesity rates in the developed world. This is a long-standing phenomenon: already by 1962, 45% of adult Americans were overweight, and 13% of adult Americans were obese; these numbers were already higher than obesity rates observed in most developed countries as late as 2001-02. From 1980 to 2002, obesity rates have doubled, reaching the current rate of 33% of the adult population. As of 2007, 33% of men and 36% of women are obese. Rates of obesity vary between social groups, with minorities and low-income individuals more likely to be overweight. The rates are as high as 50% among African American women. Geography is a major factor. The American South has been described alternatively as "Stroke belt", "Obesity belt", or "Diabetes belt", to reflect the fact that all residents of the region have high incidences of these three conditions, compared to people of the same race/ethnicity elsewhere in the country. The lowest obesity rates of major racial/ethnic groups across 50 states are thought to be among non-Hispanic white residents of ColoradoColorado
Colorado is a U.S. state that encompasses much of the Rocky Mountains as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the Great Plains...
and Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
, at around 16%. However, these numbers are based on self-reported height and weight data and likely to be underestimated (the bias is so large that, for example, estimates of obesity that rely on self-reported data arrive at the rate of 22% among non-Hispanic white females, whereas studies that involve direct measurement show that the rate is closer to 34%.)
The prevalence of class III obesity (BMI ≥40) has increased the most dramatically, from 1.3% in the late 1970s, to 2.9% in 1988-94, to 4.7% in 2000, to 5.7% in 2008. Among African American women, its prevalence is estimated to be as high as 14%.
The overall rate of obesity began to plateau in the '00s, but severe obesity and obesity in children continued to rise. In January 2010, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that the obesity rate for American women has remained constant over the last decade, with only small rises amongst men and children.
Obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
is one of the leading health issues in US society, resulting in about 300,000 deaths per year in the United States. About 65 percent of Americans are now considered either overweight or obese. According to National Health and Nutrition Examination Study collected between 1970s and 2004, overweight and obesity prevalence have increased steadily among all groups of Americans over the past three decades.
Vietnam
Socioeconomic changes have led to profound changes in individuals' lifestyles, including the adoption of unhealthy food consumption patterns, prevalent tobacco use, alcohol abuse and physical inactivity, especially in large cities like Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC).The Stepwise Approach to Surveillance of Non-communicable Disease Risk Factors survey was conducted to identify physical activity patterns and factors associated with 'insufficient' levels of physical activity for health in adults in HCMC.
Methods:
A cross-sectional survey was conducted in 2005 among 1906 adults aged 2564 years using a probability proportional to size cluster sampling method to estimate the prevalence of non-communicable disease risk factors including physical inactivity.
Data on socioeconomic status, health behaviours, and time spent in physical activity during work, commuting and leisure time were collected. Physical activity was measured using the validated Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ). Responders were classified as 'sufficiently active' or 'insufficiently active' using the GPAQ protocol. Correlates of insufficient physical activity were identified using multivariable logistic regression.
Results:
A high proportion of adults were physically inactive, with only 56.2% (95% CI = 52.160.4) aged 2564 years in HCMC achieving the minimum recommendation of 'doing 30 minutes moderate-intensity physical activity for at least 5 days per week'. The main contributors to total physical activity among adults were from working and active commuting. Leisure-time physical activity represented a very small proportion (9.4%) of individuals' total activity level. Some differences in the pattern of physical activity between men and women were noted, with insufficient activity levels decreasing with age among women, but not among men. Physical inactivity was positively associated with high income (OR = 1.77, 95% CI = 1.052.97) and high household wealth index (OR = 1.86, 95% CI = 1.292.66) amongst men. Conclusion: Public health policies and programs to preserve active commuting in HCMC and to promote time spent in recreational physical activity in both genders and across all age groups, but especially among young adults, will be critical in any comprehensive national plan to tackle inactivity. Clear and consistent national recommendations about how much physical activity Vietnamese people need for preventing and managing non-communicable diseases should also be part of this population-wide promotional effort.
Offical Papers

