
Enthalpy-entropy chart
Encyclopedia

Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
of a thermodynamic system
Thermodynamic system
A thermodynamic system is a precisely defined macroscopic region of the universe, often called a physical system, that is studied using the principles of thermodynamics....
. A typical chart covers a pressure range of 0.01 - 1000 bar
Bar (unit)
The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
, and temperatures up to 800 degrees Celsius
Celsius
Celsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
. It shows enthalpy
 in terms of internal energy
in terms of internal energyInternal energy
In thermodynamics, the internal energy is the total energy contained by a thermodynamic system. It is the energy needed to create the system, but excludes the energy to displace the system's surroundings, any energy associated with a move as a whole, or due to external force fields. Internal...
 , pressure
, pressure 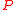 and volume
and volume  using the relationship
using the relationship  .
.History
The diagram was created in 1904, when Richard MollierRichard Mollier
Richard Mollier was a German professor of Applied Physics and Mechanics in Göttingen and Dresden, a pioneer of experimental research in thermodynamics, particularly for water, steam, and moist air....
plotted the total heat against entropy. At the 1923 Thermodynamics Conference held in Los Angeles it was decided to name, in his honor, as a “Mollier diagram” any thermodynamic diagram using the Enthalpy h as one of its axes.
Details
On the diagram, lines of constant pressure, constant temperature and volume are plotted, so in a two-phase region, the lines of constant pressure and temperature coincide. Thus, coordinates on the diagram represent entropyEntropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
and heat
Heat
In physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between...
.
The work done on vapor cycles is represented by length, so it can be measured directly, whereas in a T–s diagram it is shown as an area.
In an isobaric process
Isobaric process
An isobaric process is a thermodynamic process in which the pressure stays constant. The term derives from the Greek isos, , and barus,...
, the pressure remains constant, so the heat interaction is the change in enthalpy.
In an isenthalpic process
Isenthalpic process
An isenthalpic process or isoenthalpic process is a process that proceeds without any change in enthalpy, H; or specific enthalpy, h....
, the enthalpy is constant.
A vertical line in the h–s chart means an isentropic process and an horizontal line means an isenthalpic process. The process 3-4 in a rankine cycle
Rankine cycle
The Rankine cycle is a cycle that converts heat into work. The heat is supplied externally to a closed loop, which usually uses water. This cycle generates about 90% of all electric power used throughout the world, including virtually all solar thermal, biomass, coal and nuclear power plants. It is...
is isentropic when the steam turbine
Steam turbine
A steam turbine is a mechanical device that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam, and converts it into rotary motion. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Parsons in 1884....
is said to be an ideal one. So the expansion process in a turbine can be easily calculated using the h–s chart when the process is considered to be ideal (which is the case normally when calculating enthalpies, entropies, etc. Later the deviations from the ideal values can be calculated considering the isentropic efficiency of the steam turbine used.)
In a throttling process, the Joule–Thomson effect
Joule–Thomson effect
In thermodynamics, the Joule–Thomson effect or Joule–Kelvin effect or Kelvin–Joule effect describes the temperature change of a gas or liquid when it is forced through a valve or porous plug while kept insulated so that no heat is exchanged with the environment. This procedure is called a...
means that an adiabatic device uses energy equal to the decrease in the enthalpy of the fluid flowing through the device.
Lines of constant dryness fraction (x), sometimes called the quality of the steam, are drawn in the wet region and lines of constant temperature are drawn in the superheated region. X gives the fraction (by mass) of gaseous water in the wet region, the remainder being colloid
Colloid
A colloid is a substance microscopically dispersed evenly throughout another substance.A colloidal system consists of two separate phases: a dispersed phase and a continuous phase . A colloidal system may be solid, liquid, or gaseous.Many familiar substances are colloids, as shown in the chart below...
al liquid droplets. Above the heavy line, the temperature is above the boiling point, and the dry (superheated) steam consists of gas only.
In general such charts do not show the values of specific volume
Specific volume
In thermodynamics, the specific volume of a substance is the ratio of the substance's volume to its mass. It is the reciprocal of density:In thermodynamics, the specific volume of a substance is the ratio of the substance's volume to its mass...
s, nor do they show the enthalpies of saturated water at pressures which are of the order of those experienced in condensers in a thermal power station
Thermal power station
A thermal power station is a power plant in which the prime mover is steam driven. Water is heated, turns into steam and spins a steam turbine which drives an electrical generator. After it passes through the turbine, the steam is condensed in a condenser and recycled to where it was heated; this...
. Hence the chart is only useful for enthalpy changes in the expansion process of the steam cycle.
Applications and Usage
It can be used in practical applications such as maltMalt
Malt is germinated cereal grains that have been dried in a process known as "malting". The grains are made to germinate by soaking in water, and are then halted from germinating further by drying with hot air...
ing, to represent the grain-air-moisture system.
The underlying property data for the Mollier diagram is identical to a psychrometric chart. At first inspection, there may appear little resemblance between the charts, but if the user rotates a chart ninety degrees and looks at it in a mirror, the resemblance is apparent. The Mollier diagram coordinates are enthalpy h and humidity ratio x. The enthalpy coordinate is skewed and the constant enthalpy lines are parallel and evenly spaced.
The Mollier diagram is preferred by many users in Scandinavia, Eastern Europe, and Russia.

