
Ejection fraction
Encyclopedia
In cardiovascular physiology
, ejection fraction (Ef) is the fraction of Blood
pumped out of the Right Ventricle
of the heart to the Pulmonary Circulation
(lungs) and Left Ventricle
of the heart to the Systemic Circulation
(brain and body) with each Heart beat
or Cardiac cycle
. The term ejection fraction thus applies to forward performance of both the right and left ventricles.
Imaging of the physiology of the four chambered mammalian heart is the art that allowed meaningful mathematical terms that define Ef. Cardiac imaging has applied a means to study cardiac performance noninvasively, reproducibly and inexpensively. Simplified, Ejection fraction is a mathematical product allowed by cardiac imaging. As a mathematical term, Ejection Fraction is an intuitive extension of the work of Adolph Fick in Cardiac Output
. Technology such as Echocardiography
and MUGA
scanning have definitively allowed clinically relevant mathematics regarding Heart Failure.
RVEF and LVEF may vary widely from one another incumbent upon physiologic state. Ventricular Dyssynchrony represents theoretical pathology in which the LVEF and RVEF combined may be less than 100%. Without a qualifier, the term ejection fraction refers specifically to that of the left ventricle.
. Similarly, the volume of blood left in a ventricle at the end of contraction is end-systolic volume
. The difference between end-diastolic volume (EDV) and end-systolic volumes (ESV) is the stroke volume
, the volume of blood ejected with each beat. Ejection fraction (Ef) is the fraction of the end-diastolic volume that is ejected with each beat; that is, it is stroke volume (SV) divided by end-diastolic volume (EDV):
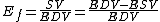
Right ventricular volumes being roughly equal to those of the left ventricle, the ejection fraction of the right ventricle is normally equal to that of the left ventricle within narrow limits.
Healthy individuals typically have ejection fractions between 50% and 65%. However, normal values depend upon the modality being used to calculate the ejection fraction, and some sources consider an ejection fraction of 55-75% to be normal. Damage to the muscle of the heart (myocardium), such as that sustained during myocardial infarction
or in cardiomyopathy
, impairs the heart's ability to eject blood and therefore reduces ejection fraction. This reduction in the ejection fraction can manifest itself clinically as heart failure.
The ejection fraction is one of the most important predictors of prognosis
; those with significantly reduced ejection fractions typically have poorer prognoses. However, recent studies have indicated that a preserved ejection fraction does not mean freedom from risk.
The QT interval
as recorded on a standard Electrocardiogram
is generally agreed to be an exemplary display of depolarization of the ventricles. Widening of the QT interval is a reliable and inexpensive method in determination of mismatched flow states between the RV and LV.
, in which the volumes of the heart's chambers are measured during the cardiac cycle
. Ejection fraction can then be obtained by dividing stroke volume by end-diastolic volume as described above.
Accurate volumetric measurement of performance of the right and left ventricles of the heart is inexpensively and routinely echocardiographically interpreted worldwide as a ratio of Dimension
between the ventricles in Systole
and Diastole
. For example, a ventricle in greatest dimension could measure 6cm while in least dimension 4cm. Measured and easily reproduced beat to beat for ten or more cycles, this ratio may represent a physiologically normal EF of 60%. Mathematical expression of this ratio can then be interpreted as the greater half as Cardiac Output
and the lesser half as Cardiac input
.
Other methods of measuring ejection fraction include cardiac MRI, fast scan cardiac computed axial tomography (CT) imaging, ventriculography, Gated SPECT
, and the MUGA scan
. A MUGA scan involves the injection of a radioisotope into the blood and detecting its flow through the left ventricle. The historical gold standard
for the measurement of ejection fraction is ventriculography.
Circulatory system
The circulatory system is an organ system that passes nutrients , gases, hormones, blood cells, etc...
, ejection fraction (Ef) is the fraction of Blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
pumped out of the Right Ventricle
Right ventricle
The right ventricle is one of four chambers in the human heart. It receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium via the tricuspid valve, and pumps it into the pulmonary artery via the pulmonary valve and pulmonary trunk....
of the heart to the Pulmonary Circulation
Pulmonary circulation
Pulmonary circulation is the half portion of the cardiovascular system which carries Oxygen-depleted Blood away from the heart, to the Lungs, and returns oxygenated blood back to the heart. Encyclopedic description and discovery of the pulmonary circulation is widely attributed to Doctor Ibn...
(lungs) and Left Ventricle
Left ventricle
The left ventricle is one of four chambers in the human heart. It receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium via the mitral valve, and pumps it into the aorta via the aortic valve.-Shape:...
of the heart to the Systemic Circulation
Systemic circulation
Systemic circulation is the part of the cardiovascular system which carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart. This physiologic theory of circulation was first described by William Harvey...
(brain and body) with each Heart beat
Heart Beat
Heart Beat is a 1980 film written and directed by John Byrum, based on the autobiography by Carolyn Cassady. The film is about seminal figures in the Beat Generation...
or Cardiac cycle
Cardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is a term referring to all or any of the events related to the flow or blood pressure that occurs from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. The frequency of the cardiac cycle is described by the heart rate. Each beat of the heart involves five major stages...
. The term ejection fraction thus applies to forward performance of both the right and left ventricles.
Imaging of the physiology of the four chambered mammalian heart is the art that allowed meaningful mathematical terms that define Ef. Cardiac imaging has applied a means to study cardiac performance noninvasively, reproducibly and inexpensively. Simplified, Ejection fraction is a mathematical product allowed by cardiac imaging. As a mathematical term, Ejection Fraction is an intuitive extension of the work of Adolph Fick in Cardiac Output
Cardiac output
Cardiac output is the volume of blood being pumped by the heart, in particular by a left or right ventricle in the time interval of one minute. CO may be measured in many ways, for example dm3/min...
. Technology such as Echocardiography
Echocardiography
An echocardiogram, often referred to in the medical community as a cardiac ECHO or simply an ECHO, is a sonogram of the heart . Also known as a cardiac ultrasound, it uses standard ultrasound techniques to image two-dimensional slices of the heart...
and MUGA
Muga
The Muga is a river in Catalonia which rises in the Alberes mountains of the eastern Pyrenees and enters the sea at the Gulf of Roses.The river is 58 km long with its source below the summit of Montnegre...
scanning have definitively allowed clinically relevant mathematics regarding Heart Failure.
RVEF and LVEF may vary widely from one another incumbent upon physiologic state. Ventricular Dyssynchrony represents theoretical pathology in which the LVEF and RVEF combined may be less than 100%. Without a qualifier, the term ejection fraction refers specifically to that of the left ventricle.
Overview
By definition, the volume of blood within a ventricle immediately before a contraction is known as the end-diastolic volumeEnd-diastolic volume
In cardiovascular physiology, end-diastolic volume is the volume of blood in the right and/or left ventricle at end Load or filling in . Because greater EDVs cause greater distention of the ventricle, EDV is often used synonymously with preload, which refers to the length of the sarcomeres in...
. Similarly, the volume of blood left in a ventricle at the end of contraction is end-systolic volume
End-systolic volume
End-systolic volume is the volume of blood in a ventricle at the end of contraction, or systole, and the beginning of filling, or diastole.ESV is the lowest volume of blood in the ventricle at any point in the cardiac cycle....
. The difference between end-diastolic volume (EDV) and end-systolic volumes (ESV) is the stroke volume
Stroke volume
In cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume is the volume of blood pumped from one ventricle of the heart with each beat. SV is calculated using measurements of ventricle volumes from an echocardiogram and subtracting the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of a beat from the volume...
, the volume of blood ejected with each beat. Ejection fraction (Ef) is the fraction of the end-diastolic volume that is ejected with each beat; that is, it is stroke volume (SV) divided by end-diastolic volume (EDV):
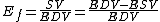
Normal values
In a healthy 70-kg (154-lb) man, the SV is approximately 70 ml and the left ventricular EDV is 120 ml, giving an ejection fraction of 70/120, or 0.58 (58%).Right ventricular volumes being roughly equal to those of the left ventricle, the ejection fraction of the right ventricle is normally equal to that of the left ventricle within narrow limits.
Healthy individuals typically have ejection fractions between 50% and 65%. However, normal values depend upon the modality being used to calculate the ejection fraction, and some sources consider an ejection fraction of 55-75% to be normal. Damage to the muscle of the heart (myocardium), such as that sustained during myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction or acute myocardial infarction , commonly known as a heart attack, results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, causing heart cells to die...
or in cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. People with cardiomyopathy are often at risk of arrhythmia or sudden cardiac death or both. Cardiomyopathy can often go undetected, making it especially dangerous to...
, impairs the heart's ability to eject blood and therefore reduces ejection fraction. This reduction in the ejection fraction can manifest itself clinically as heart failure.
The ejection fraction is one of the most important predictors of prognosis
Prognosis
Prognosis is a medical term to describe the likely outcome of an illness.When applied to large statistical populations, prognostic estimates can be very accurate: for example the statement "45% of patients with severe septic shock will die within 28 days" can be made with some confidence, because...
; those with significantly reduced ejection fractions typically have poorer prognoses. However, recent studies have indicated that a preserved ejection fraction does not mean freedom from risk.
The QT interval
QT interval
In cardiology, the QT interval is a measure of the time between the start of the Q wave and the end of the T wave in the heart's electrical cycle. In general, the QT interval represents electrical depolarization and repolarization of the left and right ventricles...
as recorded on a standard Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiography is a transthoracic interpretation of the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time, as detected by electrodes attached to the outer surface of the skin and recorded by a device external to the body...
is generally agreed to be an exemplary display of depolarization of the ventricles. Widening of the QT interval is a reliable and inexpensive method in determination of mismatched flow states between the RV and LV.
Measurement
Ejection fraction is commonly measured by echocardiographyEchocardiography
An echocardiogram, often referred to in the medical community as a cardiac ECHO or simply an ECHO, is a sonogram of the heart . Also known as a cardiac ultrasound, it uses standard ultrasound techniques to image two-dimensional slices of the heart...
, in which the volumes of the heart's chambers are measured during the cardiac cycle
Cardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is a term referring to all or any of the events related to the flow or blood pressure that occurs from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. The frequency of the cardiac cycle is described by the heart rate. Each beat of the heart involves five major stages...
. Ejection fraction can then be obtained by dividing stroke volume by end-diastolic volume as described above.
Accurate volumetric measurement of performance of the right and left ventricles of the heart is inexpensively and routinely echocardiographically interpreted worldwide as a ratio of Dimension
Dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a space or object is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus a line has a dimension of one because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on it...
between the ventricles in Systole
Systole
Systole may refer to:*Systole , a term describing the contraction of the heart*Systolic array, a term used in computer architecture*Systolic geometry, a term used in mathematics...
and Diastole
Diastole
Diastole is the period of time when the heart fills with blood after systole . Ventricular diastole is the period during which the ventricles are relaxing, while atrial diastole is the period during which the atria are relaxing...
. For example, a ventricle in greatest dimension could measure 6cm while in least dimension 4cm. Measured and easily reproduced beat to beat for ten or more cycles, this ratio may represent a physiologically normal EF of 60%. Mathematical expression of this ratio can then be interpreted as the greater half as Cardiac Output
Cardiac output
Cardiac output is the volume of blood being pumped by the heart, in particular by a left or right ventricle in the time interval of one minute. CO may be measured in many ways, for example dm3/min...
and the lesser half as Cardiac input
Cardiac input
Cardiac input is the inverse operation of cardiac output .Cardiac output implies ejection fraction.Ejection fraction is an easily understood and inexpensively imaged mathematical model of systole....
.
Other methods of measuring ejection fraction include cardiac MRI, fast scan cardiac computed axial tomography (CT) imaging, ventriculography, Gated SPECT
Gated SPECT
Gated SPECT - A nuclear medicine imaging SPECT procedure where the ECG guides the acquisition so that the resulting set of SPECT images shows the heart as it contracts over the interval from one R wave to the next.The acquisition computer defines the number of time bins or frames to divide the R...
, and the MUGA scan
MUGA scan
A MUGA scan is a time-proven yet dated nuclear medicine test designed to evaluate the function of the right and left ventricles of the heart, thus allowing informed diagnostic intervention in heart failure. It is also called radionuclide angiography, as well as gated blood pool imaging...
. A MUGA scan involves the injection of a radioisotope into the blood and detecting its flow through the left ventricle. The historical gold standard
Gold standard (test)
In medicine and statistics, gold standard test refers to a diagnostic test or benchmark that is the best available under reasonable conditions. It does not have to be necessarily the best possible test for the condition in absolute terms...
for the measurement of ejection fraction is ventriculography.

