
Eight-vertex model
Encyclopedia
In statistical mechanics
, the eight-vertex model is a generalisation of the ice-type (six-vertex) models
; it was discussed by Sutherland, and Fan & Wu, and solved by Baxter in the zero-field case.
, where each state is a configuration of arrows at a vertex. The allowed vertices have an even number of arrows pointing towards the vertex; these include the six inherited from the ice-type model
(1-6), and sinks and sources (7, 8).
We consider a lattice, with
lattice, with 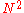 vertices and
vertices and 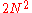 edges. Imposing periodic boundary conditions requires that the states 7 and 8 occur equally often, as do states 5 and 6, and thus can be taken to have the same energy. For the zero-field case the same is true for the two other pairs of states. Each vertex
edges. Imposing periodic boundary conditions requires that the states 7 and 8 occur equally often, as do states 5 and 6, and thus can be taken to have the same energy. For the zero-field case the same is true for the two other pairs of states. Each vertex 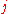 has an associated energy
has an associated energy  and Boltzmann weight
and Boltzmann weight
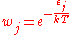 , giving the partition function
, giving the partition function
over the lattice as
where the summation is over all allowed configurations of vertices in the lattice. In this general form the partition function remains unsolved.
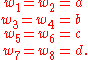
The solution is based on the observation that rows in transfer matrices commute, for a certain parametrisation of these four Boltzmann weights. This came about as a modification of an alternate solution for the six-vertex model; it makes use of elliptic theta functions.
 and
and  , for quantities
, for quantities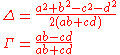
the transfer matrices and
and 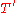 (associated with the weights
(associated with the weights  ,
, 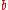 ,
,  ,
, 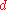 and
and  ,
,  ,
, 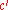 ,
,  ) commute. Using the star-triangle relation, Baxter reformulated this condition as equivalent to a parametrisation of the weights given as
) commute. Using the star-triangle relation, Baxter reformulated this condition as equivalent to a parametrisation of the weights given as
for fixed modulus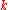 and
and  and variable
and variable  . Here snh is the hyperbolic analogue of sn, given by
. Here snh is the hyperbolic analogue of sn, given by
and and
and  are Jacobi elliptic functions of modulus
are Jacobi elliptic functions of modulus  . The associated transfer matrix
. The associated transfer matrix  thus is a function of
thus is a function of  alone; for all
alone; for all  ,
, 
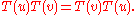
The matrix function
The other crucial part of the solution is the existence of a nonsingular matrix-valued function  , such that for all complex
, such that for all complex  the matrices
the matrices  commute with each other and the transfer matrices, and satisfy
commute with each other and the transfer matrices, and satisfy
where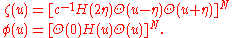
The existence and commutation relations of such a function are demonstrated by considering pair propagations through a vertex, and periodicity relations of the theta functions, in a similar way to the six-vertex model.
, and thus eigenvalues can be found. The partition function is calculated from the maximal eigenvalue, resulting in a free energy
per site of
for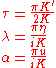
where and
and 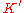 are the complete elliptic integrals of moduli
are the complete elliptic integrals of moduli 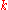 and
and 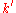 .
.
The eight vertex model was also solved in quasicrystals.
with 2-spin and 4-spin nearest neighbour interactions. The states of this model are spins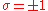 on faces of a square lattice. The analogue of 'edges' in the eight-vertex model are products of spins on adjacent faces:
on faces of a square lattice. The analogue of 'edges' in the eight-vertex model are products of spins on adjacent faces:
The most general form of the energy for this model is
where ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 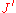 describe the horizontal, vertical and two diagonal 2-spin interactions, and
describe the horizontal, vertical and two diagonal 2-spin interactions, and  describes the 4-spin interaction between four faces at a vertex; the sum is over the whole lattice.
describes the 4-spin interaction between four faces at a vertex; the sum is over the whole lattice.
We denote horizontal and vertical spins (arrows on edges) in the eight-vertex model ,
,  respectively, and define up and right as positive directions. The restriction on vertex states is that the product of four edges at a vertex is 1; this automatically holds for Ising 'edges'. Each
respectively, and define up and right as positive directions. The restriction on vertex states is that the product of four edges at a vertex is 1; this automatically holds for Ising 'edges'. Each  configuration then corresponds to a unique
configuration then corresponds to a unique 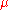 ,
,  configuration, whereas each
configuration, whereas each 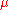 ,
,  configuration gives two choices of
configuration gives two choices of  configurations.
configurations.
Equating general forms of Boltzmann weights for each vertex , the following relations between the
, the following relations between the  and
and  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 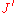 ,
, 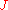 define the correspondence between the lattice models:
define the correspondence between the lattice models: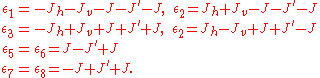
It follows that in the zero-field case of the eight-vertex model, the horizontal and vertical interactions in the corresponding Ising model vanish.
These relations gives the equivalence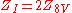 between the partition functions of the eight-vertex model, and the 2,4-spin Ising model. Consequently a solution in either model would lead immediately to a solution in the other.
between the partition functions of the eight-vertex model, and the 2,4-spin Ising model. Consequently a solution in either model would lead immediately to a solution in the other.
Statistical mechanics
Statistical mechanics or statistical thermodynamicsThe terms statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics are used interchangeably...
, the eight-vertex model is a generalisation of the ice-type (six-vertex) models
Ice-type model
In statistical mechanics, the ice-type models or six-vertex models are a family of vertex models for crystal lattices with hydrogen bonds. The first such model was introduced by Linus Pauling in 1935 to account for the residual entropy of water ice. Variants have been proposed as models of certain...
; it was discussed by Sutherland, and Fan & Wu, and solved by Baxter in the zero-field case.
Description
As with the ice-type models, the eight-vertex model is a square lattice modelLattice (group)
In mathematics, especially in geometry and group theory, a lattice in Rn is a discrete subgroup of Rn which spans the real vector space Rn. Every lattice in Rn can be generated from a basis for the vector space by forming all linear combinations with integer coefficients...
, where each state is a configuration of arrows at a vertex. The allowed vertices have an even number of arrows pointing towards the vertex; these include the six inherited from the ice-type model
Ice-type model
In statistical mechanics, the ice-type models or six-vertex models are a family of vertex models for crystal lattices with hydrogen bonds. The first such model was introduced by Linus Pauling in 1935 to account for the residual entropy of water ice. Variants have been proposed as models of certain...
(1-6), and sinks and sources (7, 8).
We consider a
 lattice, with
lattice, with 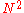 vertices and
vertices and 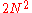 edges. Imposing periodic boundary conditions requires that the states 7 and 8 occur equally often, as do states 5 and 6, and thus can be taken to have the same energy. For the zero-field case the same is true for the two other pairs of states. Each vertex
edges. Imposing periodic boundary conditions requires that the states 7 and 8 occur equally often, as do states 5 and 6, and thus can be taken to have the same energy. For the zero-field case the same is true for the two other pairs of states. Each vertex 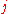 has an associated energy
has an associated energy  and Boltzmann weight
and Boltzmann weightBoltzmann factor
In physics, the Boltzmann factor is a weighting factor that determines the relative probability of a particle to be in a state i in a multi-state system in thermodynamic equilibrium at temperature T...
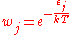 , giving the partition function
, giving the partition functionPartition function (statistical mechanics)
Partition functions describe the statistical properties of a system in thermodynamic equilibrium. It is a function of temperature and other parameters, such as the volume enclosing a gas...
over the lattice as

where the summation is over all allowed configurations of vertices in the lattice. In this general form the partition function remains unsolved.
Solution in the zero-field case
The zero-field case of the model corresponds physically to the absence of external electric fields. Hence, the model remains unchanged under the reversal of all arrows; the states 1 and 2, and 3 and 4, consequently must occur as pairs. The vertices can be assigned arbitrary weights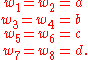
The solution is based on the observation that rows in transfer matrices commute, for a certain parametrisation of these four Boltzmann weights. This came about as a modification of an alternate solution for the six-vertex model; it makes use of elliptic theta functions.
Commuting transfer matrices
The proof relies on the fact that when and
and  , for quantities
, for quantities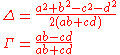
the transfer matrices
 and
and  (associated with the weights
(associated with the weights  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 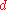 and
and  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ) commute. Using the star-triangle relation, Baxter reformulated this condition as equivalent to a parametrisation of the weights given as
) commute. Using the star-triangle relation, Baxter reformulated this condition as equivalent to a parametrisation of the weights given as
for fixed modulus
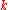 and
and  and variable
and variable  . Here snh is the hyperbolic analogue of sn, given by
. Here snh is the hyperbolic analogue of sn, given by
and
 and
and  are Jacobi elliptic functions of modulus
are Jacobi elliptic functions of modulus  . The associated transfer matrix
. The associated transfer matrix  thus is a function of
thus is a function of  alone; for all
alone; for all  ,
, 
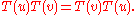
The matrix function 
The other crucial part of the solution is the existence of a nonsingular matrix-valued function  , such that for all complex
, such that for all complex  the matrices
the matrices  commute with each other and the transfer matrices, and satisfy
commute with each other and the transfer matrices, and satisfywhere
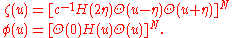
The existence and commutation relations of such a function are demonstrated by considering pair propagations through a vertex, and periodicity relations of the theta functions, in a similar way to the six-vertex model.
Explicit solution
The commutation of matrices in allow them to be diagonalisedDiagonalizable matrix
In linear algebra, a square matrix A is called diagonalizable if it is similar to a diagonal matrix, i.e., if there exists an invertible matrix P such that P −1AP is a diagonal matrix...
, and thus eigenvalues can be found. The partition function is calculated from the maximal eigenvalue, resulting in a free energy
Thermodynamic free energy
The thermodynamic free energy is the amount of work that a thermodynamic system can perform. The concept is useful in the thermodynamics of chemical or thermal processes in engineering and science. The free energy is the internal energy of a system less the amount of energy that cannot be used to...
per site of

for
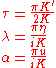
where
 and
and 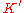 are the complete elliptic integrals of moduli
are the complete elliptic integrals of moduli 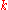 and
and 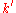 .
.The eight vertex model was also solved in quasicrystals.
Equivalence with an Ising model
There is a natural correspondence between the eight-vertex model, and the Ising modelIsing model
The Ising model is a mathematical model of ferromagnetism in statistical mechanics. The model consists of discrete variables called spins that can be in one of two states . The spins are arranged in a graph , and each spin interacts with its nearest neighbors...
with 2-spin and 4-spin nearest neighbour interactions. The states of this model are spins
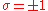 on faces of a square lattice. The analogue of 'edges' in the eight-vertex model are products of spins on adjacent faces:
on faces of a square lattice. The analogue of 'edges' in the eight-vertex model are products of spins on adjacent faces:
The most general form of the energy for this model is

where
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 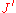 describe the horizontal, vertical and two diagonal 2-spin interactions, and
describe the horizontal, vertical and two diagonal 2-spin interactions, and  describes the 4-spin interaction between four faces at a vertex; the sum is over the whole lattice.
describes the 4-spin interaction between four faces at a vertex; the sum is over the whole lattice.We denote horizontal and vertical spins (arrows on edges) in the eight-vertex model
 ,
,  respectively, and define up and right as positive directions. The restriction on vertex states is that the product of four edges at a vertex is 1; this automatically holds for Ising 'edges'. Each
respectively, and define up and right as positive directions. The restriction on vertex states is that the product of four edges at a vertex is 1; this automatically holds for Ising 'edges'. Each  configuration then corresponds to a unique
configuration then corresponds to a unique  ,
,  configuration, whereas each
configuration, whereas each  ,
,  configuration gives two choices of
configuration gives two choices of  configurations.
configurations.Equating general forms of Boltzmann weights for each vertex
 , the following relations between the
, the following relations between the  and
and  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 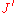 ,
, 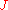 define the correspondence between the lattice models:
define the correspondence between the lattice models: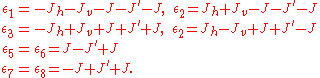
It follows that in the zero-field case of the eight-vertex model, the horizontal and vertical interactions in the corresponding Ising model vanish.
These relations gives the equivalence
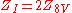 between the partition functions of the eight-vertex model, and the 2,4-spin Ising model. Consequently a solution in either model would lead immediately to a solution in the other.
between the partition functions of the eight-vertex model, and the 2,4-spin Ising model. Consequently a solution in either model would lead immediately to a solution in the other.

