Economic sector
Encyclopedia
- The ancient economyTraditional economyTraditional economy is a catching-all term normally used to describe economic systems that pertain in societies with extensive subsistence agriculture. The term may also be used for any economy that falls outside of popular notions of market and command economies...
was mainly based on subsistence farmingSubsistence agricultureSubsistence agriculture is self-sufficiency farming in which the farmers focus on growing enough food to feed their families. The typical subsistence farm has a range of crops and animals needed by the family to eat and clothe themselves during the year. Planting decisions are made with an eye...
.
- The industrial revolutionIndustrial RevolutionThe Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
lessened the role of subsistence farming, converting it to more extensiveExtensive farmingExtensive farming or Extensive agriculture is an agricultural production system that uses small inputs of labour, fertilizers, and capital, relative to the land area being farmed....
and monoculturalMonocultureMonoculture is the agricultural practice of producing or growing one single crop over a wide area. It is also known as a way of farming practice of growing large stands of a single species. It is widely used in modern industrial agriculture and its implementation has allowed for large harvests from...
forms of agriculture in the last three centuries. Economic growth took place mostly in mining, construction and manufacturing industries.
- In the economies of modern consumer societies, services, finance, and technology — the knowledge economyKnowledge economyThe knowledge economy is a term that refers either to an economy of knowledge focused on the production and management of knowledge in the frame of economic constraints, or to a knowledge-based economy. In the second meaning, more frequently used, it refers to the use of knowledge technologies to...
— play an increasingly significant role.
According to those who separate the tertiary sector into two distinct entities, modern economies are characterized as having four main sectors of activity:
- Primary sector of the economy: Involves the retrieval and production of raw materials, such as corn, coal, wood and iron. (A coal miner and a fisherman would be workers in the primary sector.)
- Secondary sector of the economy: Involves the transformation of raw or intermediate materials into goods e.g. manufacturing steel into cars, or textiles into clothing. (A builder and a dressmaker would be workers in the secondary sector.)
- Tertiary sector of the economy: Involves the supplying of services to consumers and businesses, such as baby-sitting, cinema and banking. (A shopkeeper and an accountant would be workers in the tertiary sector.)
- Quaternary sector of the economy: Involves the research and development needed to produce products from natural resources. (A logging company might research ways to use partially burnt wood to be processed so that the undamaged portions of it can be made into pulp for paper.) Note that education is sometimes included in this sector.
Other sectors include the
- Public sectorPublic sectorThe public sector, sometimes referred to as the state sector, is a part of the state that deals with either the production, delivery and allocation of goods and services by and for the government or its citizens, whether national, regional or local/municipal.Examples of public sector activity range...
or state sector - Private sectorPrivate sectorIn economics, the private sector is that part of the economy, sometimes referred to as the citizen sector, which is run by private individuals or groups, usually as a means of enterprise for profit, and is not controlled by the state...
or privately-run businesses - Social sectorSocial sectorSocial sector is one of several terms created as alternatives to nonprofit sector and nongovernmental sector. The latter are seen as putting an emphasis on what this sector is not, rather than calling attention to its focus on a social mission..Other terms that have been proposed are voluntary...
or Voluntary sectorVoluntary sectorThe voluntary sector or community sector is the sphere of social activity undertaken by organizations that are for non-profit and non-governmental. This sector is also called the third sector, in reference to the public sector and the private sector...
Based on stage in production chain
More details about the various phases of economic developmentEconomic development
Economic development generally refers to the sustained, concerted actions of policymakers and communities that promote the standard of living and economic health of a specific area...
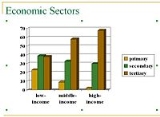
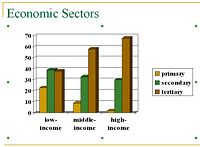
follow. As this process was far from being homogeneous geographically, the balance between these sectors differs widely among the various regions of the world.
See also
- North American Industry Classification System - a sample application of sector-oriented analysis

