
Earnings growth
Encyclopedia
Earnings growth is the annual rate of growth
of earnings
from investment
s.
When the dividend payout ratio is the same, the dividend growth rate is equal to the earnings growth rate.
Earnings growth rate is a key value that is needed when the DCF
model, or the Gordon's model is used for stock valuation
.
The present value of stock is given by
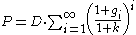 .
.
where P = the present value, k = discount rate
, D = current dividend and is the revenue growth rate for period i.
is the revenue growth rate for period i.
If the growth rate is constant for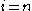 to
to 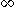 , then,
, then,
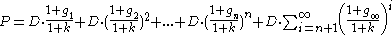
The last term corresponts to the terminal case.
When the growth rate is always the same for perpetuity, the Gordon's model results:
 .
.
As the Gordon's model suggests, the valuation is very sensitive to the value of g used.
Note that part of the earnings is paid out as dividends and part of it is retained to fund growth, as given by the payout ratio and the plowback ratio. Thus the growth rate is given by
 .
.
Note that for S&P500, the return on equity
has ranged between 10 to 15% during the 20th century, the plowback ratio has ranged from 10 to 67% (see payout ratio).
should be checked to ensure that earnings growth is not coming from special situations like sale of assets.
When the earnings acceleration (rate of change of earnings growth) is positive, it ensures that earnings growth is likely to continue.
The table below gives recent values of earnings growth for S&P 500.
The Federal Reserve responded to decline in earnings growth by cutting the Intended federal funds rate
(from 6.00 to 1.75% in 2001) and raising them when the growth rates are high(from 3.25 to 5.50 in 1994, 2.50 to 4.25 in 2005).
s generally command a higher P/E ratio because their future earnings are expected to be greater. In Stocks for the Long Run
, Jeremy Siegel examines the P/E ratios of growth and technology stocks. He examined Nifty Fifty
stocks for the duration December 1972 to Nov 2001. He found that
This suggests that the significantly P/E ratio for the Nifty Fifty as a group in 1972 was actually justified by the returns during the next three decades. However, he found that some individual stocks within the Nifty Fifty were overvalued while others were undervalued.
Compound annual growth rate
Compound annual growth rate is a business and investing specific term for the smoothed annualized gain of an investment over a given time period...
of earnings
Earnings
Earnings are the net benefits of a Corporation's operation. Earnings is also the amount on which corporate tax is due. For an analysis of specific aspects of corporate operations several more specific terms are used as EBIT -- earnings before interest and taxes, EBITDA - earnings before...
from investment
Investment
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. Finance investment is putting money into something with the expectation of gain, that upon thorough analysis, has a high degree of security for the principal amount, as well as security of return, within an expected period of time...
s.
Overview
Generally, the greater the earnings growth, the better.When the dividend payout ratio is the same, the dividend growth rate is equal to the earnings growth rate.
Earnings growth rate is a key value that is needed when the DCF
Discounted cash flow
In finance, discounted cash flow analysis is a method of valuing a project, company, or asset using the concepts of the time value of money...
model, or the Gordon's model is used for stock valuation
Stock valuation
In financial markets, stock valuation is the method of calculating theoretical values of companies and their stocks. The main use of these methods is to predict future market prices, or more generally potential market prices, and thus to profit from price movement – stocks that are judged...
.
The present value of stock is given by
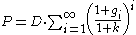 .
.where P = the present value, k = discount rate
Discount rate
The discount rate can mean*an interest rate a central bank charges depository institutions that borrow reserves from it, for example for the use of the Federal Reserve's discount window....
, D = current dividend and
 is the revenue growth rate for period i.
is the revenue growth rate for period i.If the growth rate is constant for
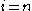 to
to 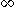 , then,
, then,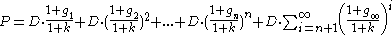
The last term corresponts to the terminal case.
When the growth rate is always the same for perpetuity, the Gordon's model results:
 .
.As the Gordon's model suggests, the valuation is very sensitive to the value of g used.
Note that part of the earnings is paid out as dividends and part of it is retained to fund growth, as given by the payout ratio and the plowback ratio. Thus the growth rate is given by
 .
.Note that for S&P500, the return on equity
Return on equity
Return on equity measures the rate of return on the ownership interest of the common stock owners. It measures a firm's efficiency at generating profits from every unit of shareholders' equity . ROE shows how well a company uses investment funds to generate earnings growth...
has ranged between 10 to 15% during the 20th century, the plowback ratio has ranged from 10 to 67% (see payout ratio).
Other related measures
It is sometimes recommended that revenue growthRevenue
In business, revenue is income that a company receives from its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and services to customers. In many countries, such as the United Kingdom, revenue is referred to as turnover....
should be checked to ensure that earnings growth is not coming from special situations like sale of assets.
When the earnings acceleration (rate of change of earnings growth) is positive, it ensures that earnings growth is likely to continue.
Historical growth rates
According to Economics Robert Shiller, earnings per share on the S&P 500 grew at a 3.8% annualized rate between 1874 and 2004 (inflation-adjusted growth rate was 1.7%). Since 1980, the most bullish period in U.S. stock market history, real earnings growth according to Shiller, has been 2.6%.The table below gives recent values of earnings growth for S&P 500.
| Date | Index | P/E | EPS growth (%) | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12/31/2007 | 1468.36 | 17.58 | 1.4 | |
| 12/31/2006 | 1418.30 | 17.40 | 14.7 | |
| 12/31/2005 | 1248.29 | 17.85 | 13.0 | |
| 12/31/2004 | 1211.92 | 20.70 | 23.8 | |
| 12/31/2003 | 1111.92 | 22.81 | 18.8 | |
| 12/31/2002 | 879.82 | 31.89 | 18.5 | |
| 12/31/2001 | 1148.08 | 46.50 | ||
| 2001 contraction Early 2000s recession The early 2000s recession was a decline in economic activity which occurred mainly in developed countries. The recession affected the European Union mostly during 2000 and 2001 and the United States mostly in 2002 and 2003. The UK, Canada and Australia avoided the recession for the most part, while... resulting in P/E Peak |
||||
| 12/31/2000 | 1320.28 | 26.41 | 8.6 | Dot-com bubble Dot-com bubble The dot-com bubble was a speculative bubble covering roughly 1995–2000 during which stock markets in industrialized nations saw their equity value rise rapidly from growth in the more... burst: March 10, 2000 |
| 12/31/1999 | 1469.25 | 30.50 | 16.7 | |
| 12/31/1998 | 1229.23 | 32.60 | 0.6 | |
| 12/31/1997 | 970.43 | 24.43 | 8.3 | |
| 12/31/1996 | 740.74 | 19.13 | 7.3 | |
| 12/31/1995 | 615.93 | 18.14 | 18.7 | |
| 12/31/1994 | 459.27 | 15.01 | 18.0 | |
| 12/31/1993 | 466.45 | 21.31 | 28.9 | |
| 12/31/1992 | 435.71 | 22.82 | 8.1 | |
| 12/31/1991 | 417.09 | 26.12 | ||
| 12/31/1990 | 330.22 | 15.47 | ||
| July 1990-March 1991 contraction. | ||||
| 12/31/1989 | 353.40 | 15.45 | . | |
| 12/31/1988 | 277.72 | 11.69 | . | Bottom (Black Monday Black Monday Black Monday is a term used to refer to certain events which occur on a Monday. It has been used in the following cases:* Black Monday, Dublin, 1209 – when a group of 500 recently arrived settlers from Bristol were massacred by warriors of the Gaelic O'Byrne clan... was October 19, 1987) |
The Federal Reserve responded to decline in earnings growth by cutting the Intended federal funds rate
Federal funds rate
In the United States, the federal funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions actively trade balances held at the Federal Reserve, called federal funds, with each other, usually overnight, on an uncollateralized basis. Institutions with surplus balances in their accounts lend...
(from 6.00 to 1.75% in 2001) and raising them when the growth rates are high(from 3.25 to 5.50 in 1994, 2.50 to 4.25 in 2005).
P/E ratio and growth rate
The growth stockGrowth stock
In finance, a growth stock is a stockof a company that generates substantial and sustainable positive cash flow and whose revenues and earnings are expected to increase at a faster rate than the average company within the same industry...
s generally command a higher P/E ratio because their future earnings are expected to be greater. In Stocks for the Long Run
Stocks for the Long Run
Stocks for the Long Run is a book on investing by Jeremy Siegel. Its first edition was released in 1994. Its fourth edition was released on November 27, 2007...
, Jeremy Siegel examines the P/E ratios of growth and technology stocks. He examined Nifty Fifty
Nifty Fifty
Nifty Fifty was an informal term used to refer to 50 popular large cap stocks on the New York Stock Exchange in the 1960s and 1970s that were widely regarded as solid buy and hold growth stocks....
stocks for the duration December 1972 to Nov 2001. He found that
| Portfolio | Annualized Returns | 1972 P/E | Warranted P/E | EPS Earnings per share Earnings per share is the amount of earnings per each outstanding share of a company's stock.In the United States, the Financial Accounting Standards Board requires companies' income statements to report EPS for each of the major categories of the income statement: continuing operations,... Growth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nifty Fifty average | 11.62% | 41.9 | 38.7 | 10.14% |
| S&P 500 | 12.14% | 18.9 | 18.9 | 6.98% |
This suggests that the significantly P/E ratio for the Nifty Fifty as a group in 1972 was actually justified by the returns during the next three decades. However, he found that some individual stocks within the Nifty Fifty were overvalued while others were undervalued.
Sustainability of high growth rates
High growth rates cannot be sustained indefinitely. Ben McClure suggests that period for which such rates can be sustained can be estimated using the following:| Competitive Situation | Sustainable period |
|---|---|
| Not very competitive | 1 year |
| Solid company with recognizable brand name | 5 years |
| Company with very high barriers to entry | 10 years |
Relationship with GDP growth
It has been suggested that the earnings growth depends on the nominal GDP, since the earnings form a part of the GDP. It has been argued that the earnings growth must grow slower than GDP by approximately two percent.On-line valuation calculators
- http://www.moneychimp.com/articles/valuation/dcf.htm: Discounted Cash Flows Calculator that assumes that a higher growth can be sustained for a limited number of years.
- http://intelligentinvesting.googlepages.com/DCF.xls: A DCF spreadsheet that allows different growth rates to be specified for years 1, 2 to 4, 5 to 7 and 8 to 10.

