
EIF2
Encyclopedia
Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 (eIF2) is a eukaryotic initiation factor
. It is required in the initiation of translation. In this fundamental process of life, the ribosome
builds protein
s according to the information encoded on the mRNA
. eIF2 mediates the binding of tRNAmet to the ribosome in a GTP
-dependent manner. eIF2 is a heterotrimer consisting of an alpha
(also called subunit 1), a beta
(subunit 2), and a gamma
(subunit 3) subunit.
Once the initiation is completed, eIF2 is released from the ribosome bound to GDP
as an inactive binary complex. To participate in another round of translation initiation, this GDP must be exchanged for GTP.
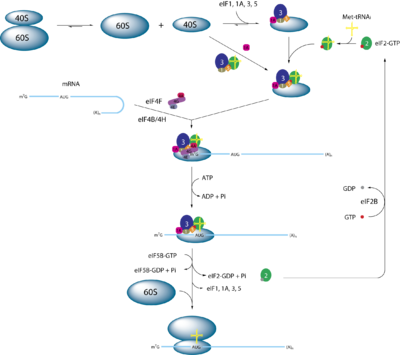 eIF2 is an essential factor for protein synthesis that forms a ternary complex (TC) with GTP
eIF2 is an essential factor for protein synthesis that forms a ternary complex (TC) with GTP
and the initiator Met
-tRNA. After its formation the TC binds the 40S ribosomal subunit to form the 43S preinitiation complex (PIC). PIC-assembly is believed to be stimulated by the initiation factors
eIF1, eIF2A and the eIF3 complex according to in vitro experiments. The 43S PIC then binds mRNA
that has previously been unwound by the eIF4s. The 43S PIC and the eIF4 proteins form a new 48S complex on the mRNA which starts searching along the mRNA for the start codon
(AUG). Upon base pairing of the AUG-codon with the Met-tRNA, eIF5 (which is a GTPase activating protein
) is recruited to the complex and induces eIF2 to hydrolyse its GTP. This causes eIF2-GDP to be released from this 48S complex and translation begins after recruitment of the 60S ribosomal subunit and formation of the 80S initiation complex. Finally, with the help of the Guanine nucleotide exchange factor
eIF2B, the GDP in eIF2 is exchanged for a GTP and the ternary complex reforms for a new round of translation initiation.
that is composed of the three subunits α
(subunit 1), β
(subunit 2), and γ
(subunit 3).
The sequences of all three subunits are highly conserved (pairwise amino acid identities for each subunit range from 47 – 72 % when comparing the proteins of Homo sapiens and Saccharomyces cerevisiae
).
The α-subunit contains the main target for phosphorylation
, a serine
at position 51. It also contains a S1
motif domain, which is a potential RNA binding-site. Therefore the α-subunit can be considered the
regulatory subunit of the trimer.
The β-subunit contains multiple phosphorylation sites (residues 2, 13, 67, 218). More importantly there
are also three lysine
clusters in the N-terminal domain (NTD) which are important for the interaction
with eIF2B. Moreover the sequence of the protein comprises a zinc finger motif which was shown to play a role in both ternary complex and 43S preinitiation complex formation. There are also two guanine nucleotide binding
sequences which have not been shown to be involved in the regulation of eIF2 activity. The β-subunit is also believed to interact with both tRNA and mRNA.
The γ-subunit comprises three guanine nucleotide binding sites and is known to be the main docking
site for GTP/GDP. It also contains a tRNA binding cavity which has been shown by X-ray crystallography
. A zinc knuckle motif is able to bind one Zn2+ cation.
 eIF2 activity is regulated by a mechanism involving both guanine nucleotide exchange and
eIF2 activity is regulated by a mechanism involving both guanine nucleotide exchange and
phosphorylation
. Phosphorylation takes place at the α-subunit which is a target for a number of serine kinases
that phosphorylate serine
51. Those kinases act as a result of stress such as
amino acid deprivation (GCN2
), ER stress (PERK
), the presence of dsRNA (PKR
) or Heme deficiency (HRI). Once phosphorylated, eIF2 shows increased affinity for its
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor
eIF2B. However, eIF2B is only able to exchange GDP for GTP if eIF2 is in its unphosphorylated
state. Phosphorylated eIF2, though, due to its stronger binding acts as an inhibitor of its own GEF (eIF2B).
Since the cellular concentration of eIF2B is much lower than that of eIF2, even a small amount of
phosphorylated eIF2 can completely abolish eIF2B activity by sequestration. Without the GEF, eIF2
can no longer be returned to its active (GTP-bound) state. Consequently translation comes to a halt since
initiation is no longer possible without any available ternary complex.
viability. Therefore no diseases directly related to mutations in eIF2 can be observed.
However there are many illnesses caused by down-regulation of eIF2 through its upstream kinases. For
example, increased concentrations of active PKR and inactive (phosphorylated) eIF2 were found in
patients suffering from neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s
, Parkinson’s
and Huntington’s
disease. There is also one proven example of a disease related to the GEF eIF2B. Mutations in all of the
five subunits of eIF2B could be linked with leukoencephalopathy
, an illness that causes the brain’s
white matter to disappear. It is still not fully understood why only brain cells seem to be affected by
these defects. Potentially reduced levels of unstable regulatory proteins might play a role in the
development of the diseases mentioned.
Eukaryotic initiation factor
Eukaryotic initiation factors are proteins involved in the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. They function in forming a complex with the 40S ribosomal subunit and Met-tRNAi called the 43S preinitation complex , recognizing the 5' cap structure of mRNA and recruiting the 43S PIC to mRNA,...
. It is required in the initiation of translation. In this fundamental process of life, the ribosome
Ribosome
A ribosome is a component of cells that assembles the twenty specific amino acid molecules to form the particular protein molecule determined by the nucleotide sequence of an RNA molecule....
builds protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s according to the information encoded on the mRNA
Messenger RNA
Messenger RNA is a molecule of RNA encoding a chemical "blueprint" for a protein product. mRNA is transcribed from a DNA template, and carries coding information to the sites of protein synthesis: the ribosomes. Here, the nucleic acid polymer is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein...
. eIF2 mediates the binding of tRNAmet to the ribosome in a GTP
Guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It can act as a substrate for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process...
-dependent manner. eIF2 is a heterotrimer consisting of an alpha
EIF2S1
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2S1 gene.-Function:The protein encoded by this gene is the alpha subunit of the translation initiation factor eIF2 complex which catalyzes the first regulated step of protein synthesis initiation,...
(also called subunit 1), a beta
EIF2S2
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2S2 gene.-Function:Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 functions in the early steps of protein synthesis by forming a ternary complex with GTP and initiator tRNA and binding to a 40S...
(subunit 2), and a gamma
EIF2S3
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2S3 gene.-Function:Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 functions in the early steps of protein synthesis by forming a ternary complex with GTP and initiator tRNA and binding to a 40S...
(subunit 3) subunit.
Once the initiation is completed, eIF2 is released from the ribosome bound to GDP
Guanosine diphosphate
Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine....
as an inactive binary complex. To participate in another round of translation initiation, this GDP must be exchanged for GTP.
Function

Guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It can act as a substrate for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process...
and the initiator Met
Methionine
Methionine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2SCH3. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. This amino-acid is coded by the codon AUG, also known as the initiation codon, since it indicates mRNA's coding region where translation into protein...
-tRNA. After its formation the TC binds the 40S ribosomal subunit to form the 43S preinitiation complex (PIC). PIC-assembly is believed to be stimulated by the initiation factors
Eukaryotic initiation factor
Eukaryotic initiation factors are proteins involved in the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. They function in forming a complex with the 40S ribosomal subunit and Met-tRNAi called the 43S preinitation complex , recognizing the 5' cap structure of mRNA and recruiting the 43S PIC to mRNA,...
eIF1, eIF2A and the eIF3 complex according to in vitro experiments. The 43S PIC then binds mRNA
Messenger RNA
Messenger RNA is a molecule of RNA encoding a chemical "blueprint" for a protein product. mRNA is transcribed from a DNA template, and carries coding information to the sites of protein synthesis: the ribosomes. Here, the nucleic acid polymer is translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein...
that has previously been unwound by the eIF4s. The 43S PIC and the eIF4 proteins form a new 48S complex on the mRNA which starts searching along the mRNA for the start codon
Start codon
The start codon is generally defined as the point, sequence, at which a ribosome begins to translate a sequence of RNA into amino acids.When an RNA transcript is "read" from the 5' carbon to the 3' carbon by the ribosome the start codon is the first codon on which the tRNA bound to Met,...
(AUG). Upon base pairing of the AUG-codon with the Met-tRNA, eIF5 (which is a GTPase activating protein
GTPase activating protein
GTPase-Activating Proteins, or GAPs, or GTPase-Accelerating Proteins are a family of regulatory proteins whose members can bind to activated G proteins and stimulate their GTPase activity, with the result of terminating the signaling event...
) is recruited to the complex and induces eIF2 to hydrolyse its GTP. This causes eIF2-GDP to be released from this 48S complex and translation begins after recruitment of the 60S ribosomal subunit and formation of the 80S initiation complex. Finally, with the help of the Guanine nucleotide exchange factor
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate . A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity...
eIF2B, the GDP in eIF2 is exchanged for a GTP and the ternary complex reforms for a new round of translation initiation.
Structure
eIF2 is a heterotrimer of a total molar mass of 126 kDaDalton
Dalton may refer to:-In Canada:* Dalton, Algoma District, Ontario* Dalton Armoury, a Canadian Forces facility primarily used by the Queen's Own Rifles of Canada- In the United Kingdom :* Dalton, Cumbria, England* Dalton, Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland...
that is composed of the three subunits α
EIF2S1
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2S1 gene.-Function:The protein encoded by this gene is the alpha subunit of the translation initiation factor eIF2 complex which catalyzes the first regulated step of protein synthesis initiation,...
(subunit 1), β
EIF2S2
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2S2 gene.-Function:Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 functions in the early steps of protein synthesis by forming a ternary complex with GTP and initiator tRNA and binding to a 40S...
(subunit 2), and γ
EIF2S3
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2S3 gene.-Function:Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 functions in the early steps of protein synthesis by forming a ternary complex with GTP and initiator tRNA and binding to a 40S...
(subunit 3).
The sequences of all three subunits are highly conserved (pairwise amino acid identities for each subunit range from 47 – 72 % when comparing the proteins of Homo sapiens and Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
).
| Subunit | Alpha | Beta | Gamma |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight / kDa | 36 | 38 | 52 |
| Similarity | eIF2-alpha family | GTP-binding elongation factor family | eIF2-beta / eIF5 family |
| Interactions | Binding of eIF5, eIF2B and RNA | Binding of GTP and RNA |
The α-subunit contains the main target for phosphorylation
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation activates or deactivates many protein enzymes....
, a serine
Serine
Serine is an amino acid with the formula HO2CCHCH2OH. It is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. By virtue of the hydroxyl group, serine is classified as a polar amino acid.-Occurrence and biosynthesis:...
at position 51. It also contains a S1
motif domain, which is a potential RNA binding-site. Therefore the α-subunit can be considered the
regulatory subunit of the trimer.
The β-subunit contains multiple phosphorylation sites (residues 2, 13, 67, 218). More importantly there
are also three lysine
Lysine
Lysine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH4NH2. It is an essential amino acid, which means that the human body cannot synthesize it. Its codons are AAA and AAG....
clusters in the N-terminal domain (NTD) which are important for the interaction
with eIF2B. Moreover the sequence of the protein comprises a zinc finger motif which was shown to play a role in both ternary complex and 43S preinitiation complex formation. There are also two guanine nucleotide binding
sequences which have not been shown to be involved in the regulation of eIF2 activity. The β-subunit is also believed to interact with both tRNA and mRNA.
The γ-subunit comprises three guanine nucleotide binding sites and is known to be the main docking
site for GTP/GDP. It also contains a tRNA binding cavity which has been shown by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a...
. A zinc knuckle motif is able to bind one Zn2+ cation.
Regulation

phosphorylation
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation activates or deactivates many protein enzymes....
. Phosphorylation takes place at the α-subunit which is a target for a number of serine kinases
Serine/threonine-specific protein kinase
Serine/threonine protein kinases phosphorylate the OH group of serine or threonine .At least 125 of the 500+ human protein kinases are serine/threonine kinases .-Regulation:...
that phosphorylate serine
Serine
Serine is an amino acid with the formula HO2CCHCH2OH. It is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. By virtue of the hydroxyl group, serine is classified as a polar amino acid.-Occurrence and biosynthesis:...
51. Those kinases act as a result of stress such as
amino acid deprivation (GCN2
EIF2AK4
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the EIF2AK4 gene.-Further reading:...
), ER stress (PERK
EIF2AK3
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the EIF2AK3 gene. Patients with mutations in this gene develop Wolcott-Rallison syndrome.-Interactions:...
), the presence of dsRNA (PKR
Protein kinase R
Protein kinase RNA-activated also known as protein kinase R , interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase, or eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the EIF2AK2 gene.PKR protects against viral...
) or Heme deficiency (HRI). Once phosphorylated, eIF2 shows increased affinity for its
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate . A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity...
eIF2B. However, eIF2B is only able to exchange GDP for GTP if eIF2 is in its unphosphorylated
state. Phosphorylated eIF2, though, due to its stronger binding acts as an inhibitor of its own GEF (eIF2B).
Since the cellular concentration of eIF2B is much lower than that of eIF2, even a small amount of
phosphorylated eIF2 can completely abolish eIF2B activity by sequestration. Without the GEF, eIF2
can no longer be returned to its active (GTP-bound) state. Consequently translation comes to a halt since
initiation is no longer possible without any available ternary complex.
Disease
Since eIF2 is essential for translation initiation and therefore protein synthesis, defects in eIF2 are lethal. The protein is highly conserved among evolutionary remote species - indicating a large impact of mutations on cellviability. Therefore no diseases directly related to mutations in eIF2 can be observed.
However there are many illnesses caused by down-regulation of eIF2 through its upstream kinases. For
example, increased concentrations of active PKR and inactive (phosphorylated) eIF2 were found in
patients suffering from neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease also known in medical literature as Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death...
, Parkinson’s
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system...
and Huntington’s
Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease, chorea, or disorder , is a neurodegenerative genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and dementia. It typically becomes noticeable in middle age. HD is the most common genetic cause of abnormal involuntary writhing movements called chorea...
disease. There is also one proven example of a disease related to the GEF eIF2B. Mutations in all of the
five subunits of eIF2B could be linked with leukoencephalopathy
Leukoencephalopathy
The term Leukoencephalopathy is a broad term for leukodystrophy-like diseases . It is applied to all brain white matter diseases, whether their molecular cause is known or not...
, an illness that causes the brain’s
white matter to disappear. It is still not fully understood why only brain cells seem to be affected by
these defects. Potentially reduced levels of unstable regulatory proteins might play a role in the
development of the diseases mentioned.
See also
- Eukaryotic initiation factors
- The three subunits of eIF2:
- α – EIF2S1EIF2S1Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2S1 gene.-Function:The protein encoded by this gene is the alpha subunit of the translation initiation factor eIF2 complex which catalyzes the first regulated step of protein synthesis initiation,...
- β – EIF2S2EIF2S2Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2S2 gene.-Function:Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 functions in the early steps of protein synthesis by forming a ternary complex with GTP and initiator tRNA and binding to a 40S...
- γ – EIF2S3EIF2S3Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2S3 gene.-Function:Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 functions in the early steps of protein synthesis by forming a ternary complex with GTP and initiator tRNA and binding to a 40S...
- α – EIF2S1
- Kinases of eIF2EIF-2 kinaseeIF-2 is a kinase enzyme that phosphorylates eIF-2.There are four forms in mammals:* EIF2AK1: heme-regulated inhibitor kinase * EIF2AK2: the double-stranded RNA-dependent kinase * EIF2AK3: PEK/PERK* EIF2AK4: GCN2...
- HRI (Heme-regulated inhibitor kinase) or EIF2AK1EIF2AK1Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the EIF2AK1 gene.-Further reading:...
- PKR (Protein kinase R)Protein kinase RProtein kinase RNA-activated also known as protein kinase R , interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase, or eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the EIF2AK2 gene.PKR protects against viral...
- PERK (PKR-like ER-localized eIF2α kinase)EIF2AK3Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the EIF2AK3 gene. Patients with mutations in this gene develop Wolcott-Rallison syndrome.-Interactions:...
- GCN2 (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha kinase 4)EIF2AK4Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the EIF2AK4 gene.-Further reading:...
- HRI (Heme-regulated inhibitor kinase) or EIF2AK1
- GEF EIF2BEIF2BeIF2B is a protein found in eukaryotes. It is the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 and therefore converts the inactive eIF2-GDP to the active eIF2-GTP...
(consists of the subunits EIF2B1EIF2B1Translation initiation factor eIF-2B subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2B1 gene.-Further reading:...
, EIF2B2EIF2B2Translation initiation factor eIF-2B subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2B2 gene.-Interactions:EIF2B2 has been shown to interact with EIF2B5 and NCK1.-Further reading:...
, EIF2B3EIF2B3Translation initiation factor eIF-2B subunit gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2B3 gene.-Further reading:...
, EIF2B4EIF2B4Translation initiation factor eIF-2B subunit delta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2B4 gene.-Further reading:...
, EIF2B5EIF2B5Translation initiation factor eIF-2B subunit epsilon is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2B5 gene.-Interactions:EIF2B5 has been shown to interact with EIF2B2 and EIF2B1.-Further reading:...
) - GAP EIF5EIF5Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF5 gene.EIF5 is a GTPase-activating protein.-External links:...
External links
- Cap-dependent translation initiation from Nature Reviews Microbiology. A good image and overview of the function of initiation factors

