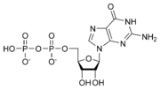
Guanosine diphosphate
Encyclopedia
Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester
of pyrophosphoric acid
with the nucleoside
guanosine
. GDP consists of the pyrophosphate
group
, the pentose
sugar
ribose
, and the nucleobase
guanine
.
GDP is the product of GTP
dephosphorylation
by GTPase
s, e.g., the G-proteins that are involved in signal transduction
.
GDP is converted into GTP with the help of pyruvate kinase and phosphoenolpyruvate.
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
of pyrophosphoric acid
Pyrophosphoric acid
Pyrophosphoric acid, also known under the name diphosphoric acid, is colorless, odorless, hygroscopic and is soluble in water, diethyl ether, and ethyl alcohol. It is produced from phosphoric acid by dehydration. Pyrophosphoric acid slowly hydrolyzes in the presence of water into phosphoric...
with the nucleoside
Nucleoside
Nucleosides are glycosylamines consisting of a nucleobase bound to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar via a beta-glycosidic linkage...
guanosine
Guanosine
Guanosine is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose ring via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate , cyclic guanosine monophosphate , guanosine diphosphate , and guanosine triphosphate...
. GDP consists of the pyrophosphate
Pyrophosphate
In chemistry, the anion, the salts, and the esters of pyrophosphoric acid are called pyrophosphates. Any salt or ester containing two phosphate groups is called a diphosphate. As a food additive, diphosphates are known as E450.- Chemistry :...
group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
, the pentose
Pentose
A pentose is a monosaccharide with five carbon atoms. Pentoses are organized into two groups. Aldopentoses have an aldehyde functional group at position 1...
sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
ribose
Ribose
Ribose is an organic compound with the formula C5H10O5; specifically, a monosaccharide with linear form H––4–H, which has all the hydroxyl groups on the same side in the Fischer projection....
, and the nucleobase
Nucleobase
Nucleobases are a group of nitrogen-based molecules that are required to form nucleotides, the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. Nucleobases provide the molecular structure necessary for the hydrogen bonding of complementary DNA and RNA strands, and are key components in the formation of stable...
guanine
Guanine
Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine . In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with...
.
GDP is the product of GTP
Guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It can act as a substrate for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process...
dephosphorylation
Dephosphorylation
Dephosphorylation is the essential process of removing phosphate groups from an organic compound by hydrolysis. Its opposite is phosphorylation...
by GTPase
GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate . The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved G domain common to all GTPases.-Functions:...
s, e.g., the G-proteins that are involved in signal transduction
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
.
GDP is converted into GTP with the help of pyruvate kinase and phosphoenolpyruvate.
See also
- NucleosideNucleosideNucleosides are glycosylamines consisting of a nucleobase bound to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar via a beta-glycosidic linkage...
- NucleotideNucleotideNucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
- DNADNADeoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
- RNARNARibonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
- OligonucleotideOligonucleotideAn oligonucleotide is a short nucleic acid polymer, typically with fifty or fewer bases. Although they can be formed by bond cleavage of longer segments, they are now more commonly synthesized, in a sequence-specific manner, from individual nucleoside phosphoramidites...
- Guanosine triphosphateGuanosine triphosphateGuanosine-5'-triphosphate is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It can act as a substrate for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process...

