
Duality gap
Encyclopedia
In optimization
problems in applied mathematics, the duality gap is the difference between the primal and dual solutions
. If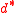 is the optimal dual value and
is the optimal dual value and 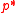 is the optimal primal value then the duality gap is equal to
is the optimal primal value then the duality gap is equal to 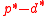 . This value is always greater than or equal to 0. The duality gap is zero if and only if strong duality holds. Otherwise the gap is strictly positive and weak duality holds.
. This value is always greater than or equal to 0. The duality gap is zero if and only if strong duality holds. Otherwise the gap is strictly positive and weak duality holds.
In general given two dual pair
s separated locally convex spaces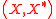 and
and 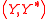 . Then given the function
. Then given the function 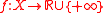 , we can define the primal problem by
, we can define the primal problem by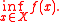
If there are constraint conditions, these can be built in to the function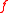 by letting
by letting  where
where 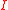 is the indicator function
is the indicator function
. Then let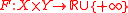 be a perturbation function
be a perturbation function
such that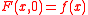 . The duality gap is the difference given by
. The duality gap is the difference given by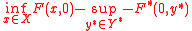
where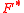 is the convex conjugate
is the convex conjugate
in both variables.
The duality gap is used in certain optimization methods to determine how far off from optimality the current solution is.
Optimization
Optimization or optimality may refer to:* Mathematical optimization, the theory and computation of extrema or stationary points of functionsEconomics and business* Optimality, in economics; see utility and economic efficiency...
problems in applied mathematics, the duality gap is the difference between the primal and dual solutions
Dual problem
In constrained optimization, it is often possible to convert the primal problem to a dual form, which is termed a dual problem. Usually dual problem refers to the Lagrangian dual problem but other dual problems are used, for example, the Wolfe dual problem and the Fenchel dual problem...
. If
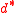 is the optimal dual value and
is the optimal dual value and 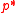 is the optimal primal value then the duality gap is equal to
is the optimal primal value then the duality gap is equal to 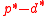 . This value is always greater than or equal to 0. The duality gap is zero if and only if strong duality holds. Otherwise the gap is strictly positive and weak duality holds.
. This value is always greater than or equal to 0. The duality gap is zero if and only if strong duality holds. Otherwise the gap is strictly positive and weak duality holds.In general given two dual pair
Dual pair
In functional analysis and related areas of mathematics a dual pair or dual system is a pair of vector spaces with an associated bilinear form....
s separated locally convex spaces
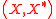 and
and 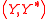 . Then given the function
. Then given the function 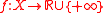 , we can define the primal problem by
, we can define the primal problem by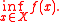
If there are constraint conditions, these can be built in to the function
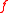 by letting
by letting  where
where 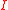 is the indicator function
is the indicator functionCharacteristic function (convex analysis)
In the field of mathematics known as convex analysis, the characteristic function of a set is a convex function that indicates the membership of a given element in that set...
. Then let
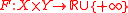 be a perturbation function
be a perturbation functionPerturbation function
In mathematical optimization, the perturbation function is any function which relates to primal and dual problems. The name comes from the fact that any such function defines a perturbation of the initial problem...
such that
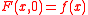 . The duality gap is the difference given by
. The duality gap is the difference given by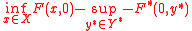
where
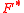 is the convex conjugate
is the convex conjugateConvex conjugate
In mathematics, convex conjugation is a generalization of the Legendre transformation. It is also known as Legendre–Fenchel transformation or Fenchel transformation .- Definition :...
in both variables.
The duality gap is used in certain optimization methods to determine how far off from optimality the current solution is.

