
Doppler imaging
Encyclopedia
Inhomogeneous structures on stellar surfaces, i.e. temperature differences, chemical composition or magnetic field
s, create characteristic distortions in the spectral lines due to the Doppler effect
. These distortions will move across spectral line
profiles due to the stellar rotation. The technique to reconstruct these structures on the stellar surface is called Doppler-imaging, often based on the Maximum Entropy image reconstruction to find the stellar image. This technique gives the smoothest and simplest image that is consistent with observations.
To understand the magnetic field and activity on stars studies of the Sun
is not sufficient, therefore studies of other stars are necessary. Periodic changes in brightness have long been observed in stars which indicate cooler or brighter starspot
s on the surface. These spots are larger than the ones on the Sun, covering up to 20% of the star. Spots with similar size as the ones on the Sun would hardly give rise to changes in intensity. In order to understand the magnetic field structure of a star it is not enough to know that spots exist, their location and extent are also important.
. For mapping starspots it was first used by Steven Vogt and Penrod in 1983, when they demonstrated that signatures of starspots were observable in the line profiles of the active binary star
HR 1099 (V711 Tau); from this they could derive an image of the stellar surface.
side when it becomes visible towards the observer. Then it will move across the line profile and increase in angular size since the spot is seen more face-on, the maximum is when the spot passes the star’s meridian
. The opposite happens when the spot moves over to the other side of the star. The spot has its maximum Doppler shift for;
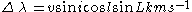
Where l is the latitude and L is the longitude.
Thus signatures from spots at higher latitudes will be restricted to spectral line centers, which will also occurring when the rotation axis is not perpendicular to the line of sight. If the spot is located at high latitude it is possible that it will always be seen, in which case the distortion in the line profile will move back and forth and only the amount of distortion will change.
Doppler imaging can also be made for changing chemical abundances across the stellar surface; these may not give rise to notches in the line profile since they can be brighter then the rest of the surface, instead producing a dip in the line profile.
is a variant of the Doppler imaging technique, by using circular and linear polarization information to see the small shifts in wavelength and profile shapes that occur when a magnetic field is present.
. Then the problem with i =90° is reduced and the mapping of the stellar surface can be improved. When one of the stars passes in front of the other there will be an eclipse
, and starspots on the eclipsed hemisphere will cause a distortion in the eclipse curve, revealing the location and size of the spots. This technique can be used for finding both dark (cool) and bright (hot) spots.
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
s, create characteristic distortions in the spectral lines due to the Doppler effect
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
. These distortions will move across spectral line
Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from a deficiency or excess of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies.- Types of line spectra :...
profiles due to the stellar rotation. The technique to reconstruct these structures on the stellar surface is called Doppler-imaging, often based on the Maximum Entropy image reconstruction to find the stellar image. This technique gives the smoothest and simplest image that is consistent with observations.
To understand the magnetic field and activity on stars studies of the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
is not sufficient, therefore studies of other stars are necessary. Periodic changes in brightness have long been observed in stars which indicate cooler or brighter starspot
Starspot
Starspots are equivalent to sunspots but located on other stars. Spots the size of sunspots are very hard to detect since they are too small to cause fluctuations in brightness...
s on the surface. These spots are larger than the ones on the Sun, covering up to 20% of the star. Spots with similar size as the ones on the Sun would hardly give rise to changes in intensity. In order to understand the magnetic field structure of a star it is not enough to know that spots exist, their location and extent are also important.
History
Doppler imaging was first used to map chemical peculiarities on the surface of Ap starsAp and Bp star
Ap and Bp stars are peculiar stars of types A and B which show overabundances of some metals, such as strontium, chromium and europium; in addition, larger overabundances are often seen in praseodymium and neodymium...
. For mapping starspots it was first used by Steven Vogt and Penrod in 1983, when they demonstrated that signatures of starspots were observable in the line profiles of the active binary star
Binary star
A binary star is a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass. The brighter star is called the primary and the other is its companion star, comes, or secondary...
HR 1099 (V711 Tau); from this they could derive an image of the stellar surface.
Criteria for Doppler Imaging
In order to be able to use the Doppler imaging technique the star needs to fulfill some specific criteria.- The stellar rotationStellar rotationStellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface....
needs to be the dominating effect broadening spectral lines,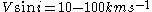 .
.
- The projected equatorial rotational velocity should be at least ,
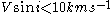 . If the velocity in lower, spatial resolution is degraded, but variations in the line profile can still give information of areas with higher velocities. For very high velocities ,
. If the velocity in lower, spatial resolution is degraded, but variations in the line profile can still give information of areas with higher velocities. For very high velocities , 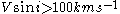 ., lines become too shallow for recognizing spots.
., lines become too shallow for recognizing spots.
- The inclinationInclinationInclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit...
angle, i, should preferably be between 20˚-70˚.
- The inclination
- When i =0˚ the star is seen from the pole and therefore there is no line-of-sight component of the rotational velocity, i.e. no Doppler effect. When seen equator-on, i =90˚ the Doppler image will get a mirror-image symmetry, since it is impossible to distinguish if a spot is on the northern or southern hemisphere. This problem will always occur when i ≥70˚; Doppler images are still possible to get but harder to interpret.
How does it work?
In the simplest case, dark starspots decrease the amount of light coming from one specific region; this causes a dip or notch in the spectral line. As the star rotates the notch will first appear on the short wavelengthWavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
side when it becomes visible towards the observer. Then it will move across the line profile and increase in angular size since the spot is seen more face-on, the maximum is when the spot passes the star’s meridian
Meridian (astronomy)
This article is about the astronomical concept. For other uses of the word, see Meridian.In the sky, a meridian is an imaginary great circle on the celestial sphere. It passes through the north point on the horizon, through the celestial pole, up to the zenith, through the south point on the...
. The opposite happens when the spot moves over to the other side of the star. The spot has its maximum Doppler shift for;
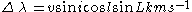
Where l is the latitude and L is the longitude.
Thus signatures from spots at higher latitudes will be restricted to spectral line centers, which will also occurring when the rotation axis is not perpendicular to the line of sight. If the spot is located at high latitude it is possible that it will always be seen, in which case the distortion in the line profile will move back and forth and only the amount of distortion will change.
Doppler imaging can also be made for changing chemical abundances across the stellar surface; these may not give rise to notches in the line profile since they can be brighter then the rest of the surface, instead producing a dip in the line profile.
Zeeman-Doppler imaging
The Zeeman-Doppler imagingZeeman-Doppler imaging
In astrophysics, Zeeman–Doppler imaging is a tomographic technique dedicated to the cartography of stellar magnetic fields.This method makes use of the ability of magnetic fields to polarize the light emitted in spectral lines formed in the stellar atmosphere...
is a variant of the Doppler imaging technique, by using circular and linear polarization information to see the small shifts in wavelength and profile shapes that occur when a magnetic field is present.
Binary stars
Another way to determine and see the extent of starspots is to study stars that are binariesBinary star
A binary star is a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass. The brighter star is called the primary and the other is its companion star, comes, or secondary...
. Then the problem with i =90° is reduced and the mapping of the stellar surface can be improved. When one of the stars passes in front of the other there will be an eclipse
Eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when an astronomical object is temporarily obscured, either by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer...
, and starspots on the eclipsed hemisphere will cause a distortion in the eclipse curve, revealing the location and size of the spots. This technique can be used for finding both dark (cool) and bright (hot) spots.

