
Dopaminergic pathways
Encyclopedia
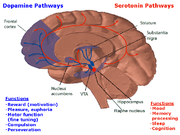
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
which transmit the neurotransmitter dopamine
Dopamine
Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter present in a wide variety of animals, including both vertebrates and invertebrates. In the brain, this substituted phenethylamine functions as a neurotransmitter, activating the five known types of dopamine receptors—D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5—and their...
from one region of the brain to another.
The neurons of the dopaminergic pathways have axon
Axon
An axon is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma....
s which run the entire length of the pathway. The neurons' soma produces the enzymes that synthesize dopamine, and they are then transmitted via the projecting axons to their synaptic destinations, where most of the dopamine is produced. Dopaminergic nerve cell bodies in such areas as the substantia nigra
Substantia nigra
The substantia nigra is a brain structure located in the mesencephalon that plays an important role in reward, addiction, and movement. Substantia nigra is Latin for "black substance", as parts of the substantia nigra appear darker than neighboring areas due to high levels of melanin in...
tend to be pigmented due to the presence of the black pigment melanin
Melanin
Melanin is a pigment that is ubiquitous in nature, being found in most organisms . In animals melanin pigments are derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine. The most common form of biological melanin is eumelanin, a brown-black polymer of dihydroxyindole carboxylic acids, and their reduced forms...
.
Examples
There are eight dopaminergic pathwaysNeural pathway
A neural pathway, neural tract, or neural face, connects one part of the nervous system with another and usually consists of bundles of elongated, myelin-insulated neurons, known collectively as white matter...
, but the four major ones are:
| Name | Description | Disorders >- | mesolimbic pathway Mesolimbic pathway The mesolimbic pathway is one of the dopaminergic pathways in the brain. The pathway begins in the ventral tegmental area of the midbrain and connects to the limbic system via the nucleus accumbens, the amygdala, and the hippocampus as well as to the medial prefrontal cortex... |
The mesolimbic pathway transmits dopamine from the ventral tegmental area (VTA) to the nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens The nucleus accumbens , also known as the accumbens nucleus or as the nucleus accumbens septi , is a collection of neurons and forms the main part of the ventral striatum... . The VTA is located in the midbrain, and the nucleus accumbens is in the limbic system Limbic system The limbic system is a set of brain structures including the hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, septum, limbic cortex and fornix, which seemingly support a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long term memory, and olfaction. The term "limbic" comes from the Latin... . The "meso-" prefix in the word "mesolimbic" refers to the midbrain, or "middle brain", since "meso" means "middle" in Greek Greek language Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;... . |
schizophrenia Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social... >- | mesocortical pathway Mesocortical pathway The mesocortical pathway is a neural pathway that connects the ventral tegmentum to the cerebral cortex, particularly the frontal lobes. It is one of the four major dopamine pathways in the brain... |
The mesocortical pathway transmits dopamine from the VTA to the frontal cortex. The "meso-" prefix in "mesocortical" refers to the VTA which is located in the midbrain, and "cortical" refers to the cortex. | schizophrenia Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social... >- | nigrostriatal pathway Nigrostriatal pathway The nigrostriatal pathway is a neural pathway that connects the substantia nigra with the striatum. It is one of the four major dopamine pathways in the brain, and is particularly involved in the production of movement, as part of a system called the basal ganglia motor loop.Loss of dopamine... |
The nigrostriatal pathway transmits dopamine from the substantia nigra Substantia nigra The substantia nigra is a brain structure located in the mesencephalon that plays an important role in reward, addiction, and movement. Substantia nigra is Latin for "black substance", as parts of the substantia nigra appear darker than neighboring areas due to high levels of melanin in... to the striatum Striatum The striatum, also known as the neostriatum or striate nucleus, is a subcortical part of the forebrain. It is the major input station of the basal ganglia system. The striatum, in turn, gets input from the cerebral cortex... . This pathway is associated with motor control. |
Parkinson's disease Parkinson's disease Parkinson's disease is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system... , chorea >- | tuberoinfundibular pathway Tuberoinfundibular pathway The tuberoinfundibular pathway refers to a population of dopamine neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the mediobasal hypothalamus that project to the median eminence . It is one of the four major dopamine pathways in the brain... |
The tuberoinfundibular pathway transmits dopamine from the hypothalamus Hypothalamus The Hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions... to the pituitary gland Pituitary gland In vertebrate anatomy the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland about the size of a pea and weighing 0.5 g , in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain, and rests in a small, bony cavity covered by a dural fold... . This pathway influences the secretion of certain hormone Hormone A hormone is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. In essence, it is a chemical messenger that transports a signal from one... s, including prolactin Prolactin Prolactin also known as luteotropic hormone is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRL gene.Prolactin is a peptide hormone discovered by Henry Friesen... . "Infundibular" in the word "tuberoinfundibular" refers to the infundibulum Infundibulum An infundibulum is a funnel-shaped cavity or organ.* Lungs: The alveolar sacs of the lungs from which the air chambers open are called infundibula... out of which the pituitary gland develops. |
hyperprolactinaemia Hyperprolactinaemia Hyperprolactinaemia or hyperprolactinemia is the presence of abnormally-high levels of prolactin in the blood. Normal levels are less than 500 mIU/L for women, and less than 450 mIU/L for men.... |
Minor ones include the incertohypothalamic pathway
Incertohypothalamic pathway
The incertohypothalamic pathway is a short dopaminergic pathway in the hypothalamus of the brain. It has a role in sexual behaviour....
within the hypothalamus, which has a role in sexual behaviour.

