
Diseconomies of scale
Encyclopedia
Diseconomies of scale are the forces that cause larger firm
s and governments to produce goods
and services at increased per-unit cost
s. The concept is less well known than economies of scale
.
with each other so they know exactly what the other workers are doing. A firm with a single worker does not require any communication between employees. A firm with two workers requires one communication channel, directly between those two workers. A firm with three workers requires three communication channels (between employees A & B, B & C, and A & C). Here is a chart of one-on-one communication channels required:
The one-on-one channels of communication grow more rapidly than the number of workers, thus increasing the time, and therefore costs, of communication. At some point one-on-one communications between all workers becomes impractical; therefore only certain groups of employees will communicate with one another (salespeople with salespeople, production workers with production workers, etc.). This reduced communication slows, but doesn't stop, the increase in time and money with firm growth, but also costs additional money, due to duplication of effort, owing to this reduced level of communication.
, UNIGRAPHICS, CATIA
and other off-the-shelf CAD/CAM systems, thus increasing the cost of translating designs from one system to another. This endeavor eventually became so unmanageable that they acquired (and then eventually sold off) Electronic Data Systems
(EDS) in an effort to control the situation. Smaller firms typically choose a single off-the shelf CAD/CAM system, with no need to combine or translate between systems.
Business
A business is an organization engaged in the trade of goods, services, or both to consumers. Businesses are predominant in capitalist economies, where most of them are privately owned and administered to earn profit to increase the wealth of their owners. Businesses may also be not-for-profit...
s and governments to produce goods
Product (business)
In general, the product is defined as a "thing produced by labor or effort" or the "result of an act or a process", and stems from the verb produce, from the Latin prōdūce ' lead or bring forth'. Since 1575, the word "product" has referred to anything produced...
and services at increased per-unit cost
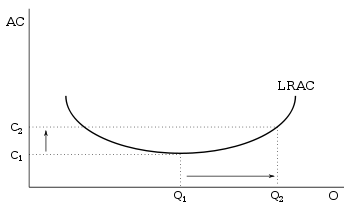
Average cost
In economics, average cost or unit cost is equal to total cost divided by the number of goods produced . It is also equal to the sum of average variable costs plus average fixed costs...
s. The concept is less well known than economies of scale
Economies of scale
Economies of scale, in microeconomics, refers to the cost advantages that an enterprise obtains due to expansion. There are factors that cause a producer’s average cost per unit to fall as the scale of output is increased. "Economies of scale" is a long run concept and refers to reductions in unit...
.

Communication costs
Ideally, all employees of a firm would have one-on-one communicationCommunication
Communication is the activity of conveying meaningful information. Communication requires a sender, a message, and an intended recipient, although the receiver need not be present or aware of the sender's intent to communicate at the time of communication; thus communication can occur across vast...
with each other so they know exactly what the other workers are doing. A firm with a single worker does not require any communication between employees. A firm with two workers requires one communication channel, directly between those two workers. A firm with three workers requires three communication channels (between employees A & B, B & C, and A & C). Here is a chart of one-on-one communication channels required:
| Workers | Communication Channels |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 6 |
| 5 | 10 |
| n |  |
The one-on-one channels of communication grow more rapidly than the number of workers, thus increasing the time, and therefore costs, of communication. At some point one-on-one communications between all workers becomes impractical; therefore only certain groups of employees will communicate with one another (salespeople with salespeople, production workers with production workers, etc.). This reduced communication slows, but doesn't stop, the increase in time and money with firm growth, but also costs additional money, due to duplication of effort, owing to this reduced level of communication.
Duplication of effort
A firm with only one employee can't have any duplication of effort between employees. A firm with two employees could have duplication of efforts, but this is improbable, as the two are likely to know what each other is working on at all times. When firms grow to thousands of workers, it is inevitable that someone, or even a team, will take on a project that is already being handled by another person or team. General Motors, for example, developed two in-house CAD/CAM systems: CADANCE was designed by the GM Design Staff, while Fisher Graphics was created by the former Fisher Body division. These similar systems later needed to be combined into a single Corporate Graphics System, CGS, at great expense. A smaller firm would neither have had the money to allow such expensive parallel developments, or the lack of communication and cooperation which precipitated this event. In addition to CGS, GM also used CADAMCADAM
CADAM History1977* IBM agrees to sell CADAM to aerospace companies1981* CADAM Release 18.3 Released.Provided support for IBM mainframes running VM/CMS.1983* CADAM INC is formed as a subsidiary of Lockheed Corp.1985* CADAM, Inc v. Adage, Inc....
, UNIGRAPHICS, CATIA
CATIA
CATIA is a multi-platform CAD/CAM/CAE commercial software suite developed by the French company Dassault Systemes...
and other off-the-shelf CAD/CAM systems, thus increasing the cost of translating designs from one system to another. This endeavor eventually became so unmanageable that they acquired (and then eventually sold off) Electronic Data Systems
Electronic Data Systems
HP Enterprise Services is the global business and technology services division of Hewlett Packard's HP Enterprise Business strategic business unit. It was formed by the combination of HP's legacy services consulting and outsourcing business and the integration of acquired Electronic Data Systems,...
(EDS) in an effort to control the situation. Smaller firms typically choose a single off-the shelf CAD/CAM system, with no need to combine or translate between systems.

