
Discrete Morse theory
Encyclopedia
Discrete Morse theory is a combinatorial adaptation of Morse theory
defined on finite CW complex
es.
 be a CW complex
be a CW complex
. Define the incidence function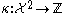 in the following way: given two cells
in the following way: given two cells  and
and  in
in 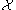 ,
,  equals the degree
equals the degree
of the attaching map from the boundary of to
to  . The boundary operator
. The boundary operator 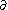 on
on  is defined by
is defined by

It is a defining property of boundary operators that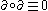 .
.
-valued function is a discrete Morse function if it satisfies the following two properties:
is a discrete Morse function if it satisfies the following two properties:
It can be shown that both conditions can not hold simultaneously for a fixed cell provided that
provided that 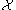 is a regular CW complex. In this case, each cell
is a regular CW complex. In this case, each cell  can be paired with at most one exceptional cell
can be paired with at most one exceptional cell 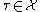 : either a boundary cell with larger
: either a boundary cell with larger 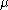 value, or a co-boundary cell with smaller
value, or a co-boundary cell with smaller 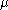 value. The cells which have no pairs, i.e., their function values are strictly higher than their boundary cells and strictly lower than their co-boundary cells are called critical cells. Thus, a discrete Morse function partitions the CW complex into three distinct cell collections:
value. The cells which have no pairs, i.e., their function values are strictly higher than their boundary cells and strictly lower than their co-boundary cells are called critical cells. Thus, a discrete Morse function partitions the CW complex into three distinct cell collections:  , where:
, where:
By construction, there is a bijection
of sets between -dimensional cells in
-dimensional cells in  and the
and the  -dimensional cells in
-dimensional cells in  , which can be denoted by
, which can be denoted by  for each natural number
for each natural number
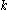 . It is an additional technical requirement that for each
. It is an additional technical requirement that for each  , the degree of the attaching map from the boundary of
, the degree of the attaching map from the boundary of  to its paired cell
to its paired cell 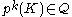 is a unit
is a unit
in the underlying ring
of . For instance, over the integers
. For instance, over the integers
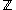 , the only allowed values are
, the only allowed values are  . This technical requirement is guaranteed when one assumes that
. This technical requirement is guaranteed when one assumes that 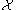 is a regular CW complex over
is a regular CW complex over  .
.
The fundamental result of discrete Morse theory establishes that the CW complex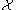 is isomorphic
is isomorphic
on the level of homology
to a new complex consisting of only the critical cells. The paired cells in
consisting of only the critical cells. The paired cells in  and
and  describe gradient paths between adjacent critical cells which can be used to obtain the boundary operator on
describe gradient paths between adjacent critical cells which can be used to obtain the boundary operator on 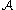 . Some details of this construction are provided in the next section.
. Some details of this construction are provided in the next section.
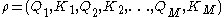 is a sequence of cell pairs
is a sequence of cell pairs  so that
so that 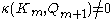 . The index of this gradient path is defined to be the integer
. The index of this gradient path is defined to be the integer  . The division here makes sense because the incidence between paired cells must be
. The division here makes sense because the incidence between paired cells must be 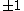 . Note that by construction, the values of the discrete Morse function
. Note that by construction, the values of the discrete Morse function  must decrease across
must decrease across  . The path
. The path 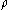 is said to connect two critical cells
is said to connect two critical cells 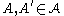 if
if  . This relationship may be expressed as
. This relationship may be expressed as 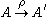 . The multiplicity of this connection is defined to be the integer
. The multiplicity of this connection is defined to be the integer 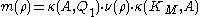 . Finally, the Morse boundary operator on the critical cells
. Finally, the Morse boundary operator on the critical cells 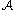 is defined by
is defined by

where the sum is taken over all gradient path connections from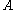 to
to 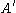 .
.
Morse theory
In differential topology, the techniques of Morse theory give a very direct way of analyzing the topology of a manifold by studying differentiable functions on that manifold. According to the basic insights of Marston Morse, a differentiable function on a manifold will, in a typical case, reflect...
defined on finite CW complex
CW complex
In topology, a CW complex is a type of topological space introduced by J. H. C. Whitehead to meet the needs of homotopy theory. This class of spaces is broader and has some better categorical properties than simplicial complexes, but still retains a combinatorial naturethat allows for...
es.
Notation regarding CW complexes
Let be a CW complex
be a CW complexCW complex
In topology, a CW complex is a type of topological space introduced by J. H. C. Whitehead to meet the needs of homotopy theory. This class of spaces is broader and has some better categorical properties than simplicial complexes, but still retains a combinatorial naturethat allows for...
. Define the incidence function
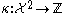 in the following way: given two cells
in the following way: given two cells  and
and  in
in 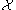 ,
,  equals the degree
equals the degreeTopological degree theory
In mathematics, topological degree theory is a generalization of the winding number of a curve in the complex plane. It can be used to estimate the number of solutions of an equation, and is closely connected to fixed-point theory. When one solution of an equation is easily found, degree theory can...
of the attaching map from the boundary of
 to
to  . The boundary operator
. The boundary operator 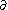 on
on  is defined by
is defined by
It is a defining property of boundary operators that
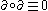 .
.Discrete Morse functions
A RealReal number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
-valued function
 is a discrete Morse function if it satisfies the following two properties:
is a discrete Morse function if it satisfies the following two properties:- For any cell
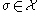 , the number of cells
, the number of cells 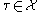 in the boundary of
in the boundary of  which satisfy
which satisfy  is at most one.
is at most one. - For any cell
 , the number of cells
, the number of cells  containing
containing  in their boundary which satisfy
in their boundary which satisfy  is at most one.
is at most one.
It can be shown that both conditions can not hold simultaneously for a fixed cell
 provided that
provided that 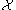 is a regular CW complex. In this case, each cell
is a regular CW complex. In this case, each cell  can be paired with at most one exceptional cell
can be paired with at most one exceptional cell 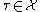 : either a boundary cell with larger
: either a boundary cell with larger 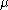 value, or a co-boundary cell with smaller
value, or a co-boundary cell with smaller 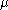 value. The cells which have no pairs, i.e., their function values are strictly higher than their boundary cells and strictly lower than their co-boundary cells are called critical cells. Thus, a discrete Morse function partitions the CW complex into three distinct cell collections:
value. The cells which have no pairs, i.e., their function values are strictly higher than their boundary cells and strictly lower than their co-boundary cells are called critical cells. Thus, a discrete Morse function partitions the CW complex into three distinct cell collections:  , where:
, where:-
 denotes the critical cells which are unpaired,
denotes the critical cells which are unpaired, -
 denotes cells which are paired with boundary cells, and
denotes cells which are paired with boundary cells, and -
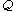 denotes cells which are paired with co-boundary cells.
denotes cells which are paired with co-boundary cells.
By construction, there is a bijection
Bijection
A bijection is a function giving an exact pairing of the elements of two sets. A bijection from the set X to the set Y has an inverse function from Y to X. If X and Y are finite sets, then the existence of a bijection means they have the same number of elements...
of sets between
 -dimensional cells in
-dimensional cells in  and the
and the  -dimensional cells in
-dimensional cells in  , which can be denoted by
, which can be denoted by  for each natural number
for each natural numberNatural number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the ordinary whole numbers used for counting and ordering . These purposes are related to the linguistic notions of cardinal and ordinal numbers, respectively...
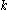 . It is an additional technical requirement that for each
. It is an additional technical requirement that for each  , the degree of the attaching map from the boundary of
, the degree of the attaching map from the boundary of  to its paired cell
to its paired cell 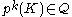 is a unit
is a unitUnit (ring theory)
In mathematics, an invertible element or a unit in a ring R refers to any element u that has an inverse element in the multiplicative monoid of R, i.e. such element v that...
in the underlying ring
Ring (mathematics)
In mathematics, a ring is an algebraic structure consisting of a set together with two binary operations usually called addition and multiplication, where the set is an abelian group under addition and a semigroup under multiplication such that multiplication distributes over addition...
of
 . For instance, over the integers
. For instance, over the integersInteger
The integers are formed by the natural numbers together with the negatives of the non-zero natural numbers .They are known as Positive and Negative Integers respectively...
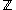 , the only allowed values are
, the only allowed values are  . This technical requirement is guaranteed when one assumes that
. This technical requirement is guaranteed when one assumes that 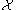 is a regular CW complex over
is a regular CW complex over  .
.The fundamental result of discrete Morse theory establishes that the CW complex
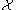 is isomorphic
is isomorphicIsomorphism
In abstract algebra, an isomorphism is a mapping between objects that shows a relationship between two properties or operations. If there exists an isomorphism between two structures, the two structures are said to be isomorphic. In a certain sense, isomorphic structures are...
on the level of homology
Homology
Homology may refer to:* Homology , analogy between human beliefs, practices or artifacts owing to genetic or historical connections* Homology , any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor....
to a new complex
 consisting of only the critical cells. The paired cells in
consisting of only the critical cells. The paired cells in  and
and  describe gradient paths between adjacent critical cells which can be used to obtain the boundary operator on
describe gradient paths between adjacent critical cells which can be used to obtain the boundary operator on 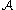 . Some details of this construction are provided in the next section.
. Some details of this construction are provided in the next section.The Morse complex
A gradient path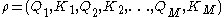 is a sequence of cell pairs
is a sequence of cell pairs  so that
so that 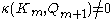 . The index of this gradient path is defined to be the integer
. The index of this gradient path is defined to be the integer  . The division here makes sense because the incidence between paired cells must be
. The division here makes sense because the incidence between paired cells must be 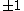 . Note that by construction, the values of the discrete Morse function
. Note that by construction, the values of the discrete Morse function  must decrease across
must decrease across  . The path
. The path 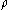 is said to connect two critical cells
is said to connect two critical cells 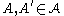 if
if  . This relationship may be expressed as
. This relationship may be expressed as 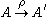 . The multiplicity of this connection is defined to be the integer
. The multiplicity of this connection is defined to be the integer 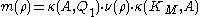 . Finally, the Morse boundary operator on the critical cells
. Finally, the Morse boundary operator on the critical cells 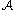 is defined by
is defined by
where the sum is taken over all gradient path connections from
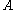 to
to 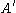 .
.See also
- Digital Morse theoryDigital Morse theoryIn mathematics, digital Morse theory is a digital adaptation of continuum Morse theory for scalar volume data.The main utility of a digital Morse theory is that it serves to provide a theoretical basis for isosurfaces, and perpendicular streamlines....
- Stratified Morse theory
- Piece-wise linear Morse theory
- Shape analysisShape analysisThis article describes shape analysis to analyze and process geometric shapes.The shape analysis described here is related to the statistical analysis of geometric shapes, to shape matching and shape recognition...
- Topological combinatoricsTopological combinatoricsThe discipline of combinatorial topology used combinatorial concepts in topology and in the early 20th century this gradually turned into the field of algebraic topology....
- Discrete differential geometryDiscrete differential geometryDiscrete differential geometry is the study of discrete counterparts of notions in differential geometry. Instead of smooth curves and surfaces, there are polygons, meshes, and simplicial complexes...

