
Direct Shear Test
Encyclopedia
A direct shear test also known as shearbox test is a laboratory or field test used by geotechnical engineers
to measure the shear strength
properties of soil
or rock
material, or of discontinuties
in soil or rock masses.
the U.S. and U.K. standards defining how the test should be performed are ASTM D 3080 and BS
1377-7:1990 respectively to establish the shear strength
properties of soil
. It is also possible to estimate typical values of the shear strength parameters based on the type and classification of the soils.
with (very) low (shear) strength. The test is, however, standard practice to establish the shear strength properties of discontinuties
in rock.
. The load applied and the strain induced is recorded at frequent intervals to determine a stress-strain curve
for the confining stress.
Direct Shear tests can be performed under several conditions. The sample is normally saturated before the test is run, but can be run at the in-situ moisture content. The rate of strain can be varied to create a test of undrained or drained conditions, depending whether the strain is applied slowly enough for water in the sample to prevent pore-water pressure buildup.
Several specimens are tested at varying confining stresses to determine the shear strength parameters, the soil cohesion (c) and the angle of internal friction (commonly friction angle) (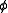 ). The results of the tests on each specimen are plotted on a graph with the peak (or residual) stress on the x-axis and the confining stress on the y-axis. The y-intercept of the curve which fits the test results is the cohesion, and the slope of the line or curve is the friction angle.
). The results of the tests on each specimen are plotted on a graph with the peak (or residual) stress on the x-axis and the confining stress on the y-axis. The y-intercept of the curve which fits the test results is the cohesion, and the slope of the line or curve is the friction angle.
.
Geotechnical engineering
Geotechnical engineering is the branch of civil engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of earth materials. Geotechnical engineering is important in civil engineering, but is also used by military, mining, petroleum, or any other engineering concerned with construction on or in the ground...
to measure the shear strength
Shear strength
Shear strength in engineering is a term used to describe the strength of a material or component against the type of yield or structural failure where the material or component fails in shear. A shear load is a force that tends to produce a sliding failure on a material along a plane that is...
properties of soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
or rock
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock or stone is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids.The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock. In general rocks are of three types, namely, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic...
material, or of discontinuties
Discontinuity
Discontinuity may refer to:*Discontinuity , a harmless irregularity in a casting*Discontinuity in geotechnics is a plane or surface marking a change in physical or chemical properties in a soil or rock mass...
in soil or rock masses.
Soil
For soilSoil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
the U.S. and U.K. standards defining how the test should be performed are ASTM D 3080 and BS
British Standards
British Standards are the standards produced by BSI Group which is incorporated under a Royal Charter...
1377-7:1990 respectively to establish the shear strength
Shear strength (soil)
Shear strength is a term used in soil mechanics to describe the magnitude of the shear stress that a soil can sustain. The shear resistance of soil is a result of friction and interlocking of particles, and possibly cementation or bonding at particle contacts. Due to interlocking, particulate...
properties of soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
. It is also possible to estimate typical values of the shear strength parameters based on the type and classification of the soils.
Rock
For rock the test is generally restricted to rockRock (geology)
In geology, rock or stone is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids.The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock. In general rocks are of three types, namely, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic...
with (very) low (shear) strength. The test is, however, standard practice to establish the shear strength properties of discontinuties
Shear strength (discontinuity)
The shear strength of a discontinuity in a soil or rock mass may have a strong impact on the mechanical behavior of a soil or rock mass. The shear strength of a discontinuity is often considerably lower than the shear strength of the blocks of intact material in between the discontinuities, and...
in rock.
Soil or rock material
The test is performed on three or four specimens from a relatively undisturbed soil sample. A specimen is placed in a shear box which has two stacked rings to hold the sample; the contact between the two rings is at approximately the mid-height of the sample. A confining stress is applied vertically to the specimen, and the upper ring is pulled laterally until the sample fails, or through a specified strainStrain (materials science)
In continuum mechanics, the infinitesimal strain theory, sometimes called small deformation theory, small displacement theory, or small displacement-gradient theory, deals with infinitesimal deformations of a continuum body...
. The load applied and the strain induced is recorded at frequent intervals to determine a stress-strain curve
Stress-strain curve
During tensile testing of a material sample, the stress–strain curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between stress, derived from measuring the load applied on the sample, and strain, derived from measuring the deformation of the sample, i.e. elongation, compression, or distortion...
for the confining stress.
Direct Shear tests can be performed under several conditions. The sample is normally saturated before the test is run, but can be run at the in-situ moisture content. The rate of strain can be varied to create a test of undrained or drained conditions, depending whether the strain is applied slowly enough for water in the sample to prevent pore-water pressure buildup.
Several specimens are tested at varying confining stresses to determine the shear strength parameters, the soil cohesion (c) and the angle of internal friction (commonly friction angle) (
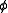 ). The results of the tests on each specimen are plotted on a graph with the peak (or residual) stress on the x-axis and the confining stress on the y-axis. The y-intercept of the curve which fits the test results is the cohesion, and the slope of the line or curve is the friction angle.
). The results of the tests on each specimen are plotted on a graph with the peak (or residual) stress on the x-axis and the confining stress on the y-axis. The y-intercept of the curve which fits the test results is the cohesion, and the slope of the line or curve is the friction angle.Test on discontinuities
The test equipment and procedures are slightly different for test on discontinutiesDiscontinuity
Discontinuity may refer to:*Discontinuity , a harmless irregularity in a casting*Discontinuity in geotechnics is a plane or surface marking a change in physical or chemical properties in a soil or rock mass...
.
See also
- Geotechnical investigationGeotechnical investigationGeotechnical investigations are performed by geotechnical engineers or engineering geologists to obtain information on the physical properties of soil and rock around a site to design earthworks and foundations for proposed structures and for repair of distress to earthworks and structures caused...
- Shear strength (Discontinuity)Shear strength (discontinuity)The shear strength of a discontinuity in a soil or rock mass may have a strong impact on the mechanical behavior of a soil or rock mass. The shear strength of a discontinuity is often considerably lower than the shear strength of the blocks of intact material in between the discontinuities, and...
- Tilt test (Geotechnical engineering)Tilt test (geotechnical engineering)In geomechanics a tilt test is a simple test to estimate the shear strength parameters of a discontinuity. Two pieces of rock containing a discontinuity are held in hand or mounted in test equipment with the discontinuity horizontal. The sample is slowly tilted until the top block moves...
- Triaxial shear test

