
Digital frequency
Encyclopedia
Digital frequency is the analogue for discrete signal
s as frequency
is to continuous signal
s.
Since a discrete signal is a sequence
(merely a series of symbols; typically, numbers) it contains no direct information as to determine the frequency of the corresponding continuous signal.
Just like in frequency
, a digital frequency can have values in degree
s or radian
s.
However, it is common to represent a digital frequency that has been normalized to either the Nyquist frequency
or the sampling frequency.
It is therefore very important to specify the frequency range.
The following frequency ranges assume a signal has been properly sampled by satisfying the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem.
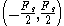 hertz.
hertz.
Likewise for radians, values of digital frequency are in the range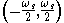 radians.
radians.
A valid signal is on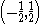 cycles per sample.
cycles per sample.
Instead, the normalizing frequency could be the nyquist frequency, which puts a valid signal on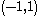 cycles per sample.
cycles per sample.
For radians, normalized frequencies are in the range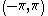 , equivalent to half a cycle per sample.
, equivalent to half a cycle per sample.
Clearly a frequency of just "0.1" is insufficient to describe the true frequency of the discrete signal
.
To remove the ambiguity, it is necessary to specify the range and what normalization frequency was used (if applicable).
Discrete signal
A discrete signal or discrete-time signal is a time series consisting of a sequence of qualities...
s as frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
is to continuous signal
Continuous signal
A continuous signal or a continuous-time signal is a varying quantity whose domain, which is often time, is a continuum . That is, the function's domain is an uncountable set. The function itself need not be continuous...
s.
Since a discrete signal is a sequence
Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an ordered list of objects . Like a set, it contains members , and the number of terms is called the length of the sequence. Unlike a set, order matters, and exactly the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in the sequence...
(merely a series of symbols; typically, numbers) it contains no direct information as to determine the frequency of the corresponding continuous signal.
Just like in frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, a digital frequency can have values in degree
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
s or radian
Radian
Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
s.
However, it is common to represent a digital frequency that has been normalized to either the Nyquist frequency
Nyquist frequency
The Nyquist frequency, named after the Swedish-American engineer Harry Nyquist or the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, is half the sampling frequency of a discrete signal processing system...
or the sampling frequency.
It is therefore very important to specify the frequency range.
The following frequency ranges assume a signal has been properly sampled by satisfying the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem.
Standard ranges
The values of a valid signal is in the range of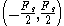 hertz.
hertz.Likewise for radians, values of digital frequency are in the range
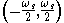 radians.
radians.Normalized ranges
The normalized hertz range is the hertz range divided by the sampling frequency.A valid signal is on
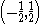 cycles per sample.
cycles per sample.Instead, the normalizing frequency could be the nyquist frequency, which puts a valid signal on
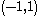 cycles per sample.
cycles per sample.For radians, normalized frequencies are in the range
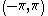 , equivalent to half a cycle per sample.
, equivalent to half a cycle per sample.Clearly a frequency of just "0.1" is insufficient to describe the true frequency of the discrete signal
Discrete signal
A discrete signal or discrete-time signal is a time series consisting of a sequence of qualities...
.
To remove the ambiguity, it is necessary to specify the range and what normalization frequency was used (if applicable).
See also
- Continuous signalContinuous signalA continuous signal or a continuous-time signal is a varying quantity whose domain, which is often time, is a continuum . That is, the function's domain is an uncountable set. The function itself need not be continuous...
vs. Discrete signalDiscrete signalA discrete signal or discrete-time signal is a time series consisting of a sequence of qualities... - FrequencyFrequencyFrequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
- Nyquist–Shannon sampling theoremNyquist–Shannon sampling theoremThe Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, after Harry Nyquist and Claude Shannon, is a fundamental result in the field of information theory, in particular telecommunications and signal processing. Sampling is the process of converting a signal into a numeric sequence...
- Whittaker–Shannon interpolation formulaWhittaker–Shannon interpolation formulaThe Whittaker–Shannon interpolation formula or sinc interpolation is a method to reconstruct a continuous-time bandlimited signal from a set of equally spaced samples.-Definition:...
- Sample (signal)
- Sampling (signal processing)Sampling (signal processing)In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous signal to a discrete signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of samples ....
- Sampling frequency
- Nyquist frequencyNyquist frequencyThe Nyquist frequency, named after the Swedish-American engineer Harry Nyquist or the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, is half the sampling frequency of a discrete signal processing system...

