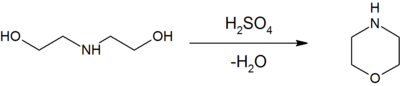Diethanolamine
Encyclopedia
Diethanolamine, often abbreviated as DEA, is an organic compound
with the formula HN(CH2CH2OH)2. This colorless liquid is polyfunctional, being a secondary amine
and a diol
. Like other organic amines, diethanolamine acts as a weak base
. Reflecting the hydrophilic character of the alcohol groups, DEA is soluble in water, and is even hygroscopic. Amides prepared from DEA are often also hydrophilic.
with aqueous ammonia
first produces ethanolamine
:
which reacts with a second and third equivalent of ethylene oxide to give DEA and triethanolamine
:
About 300M kg are produced annually in this way. The ratio of the products can be controlled by changing the stoichiometry
of the reactants.
DEA is used as a surfactant and a corrosion inhibitor
. It is used to remove hydrogen sulfide
and carbon dioxide
from natural gas.
In oil refineries, a DEA in water solution is commonly used to remove hydrogen sulfide
from various process gases. It has an advantage over a similar amine ethanolamine
in that a higher concentration may be used for the same corrosion potential. This allows refiners to scrub hydrogen sulfide
at a lower circulating amine rate with less overall energy usage.
DEA is a versatile chemical intermediate, principal derivatives include ethyleneimine and ethylenediamine. Dehydration of DEA with sulfuric acid
gives morpholine
:
Amides derived from DEA and fatty acid
s, known as diethanolamide
s, are amphiphilic.
s, which are common ingredients in cosmetics
and shampoo
s added to confer a creamy texture and foaming action. Consequently, some cosmetics that include diethanolamides as ingredients may contain traces of DEA. Some of the most commonly used diethanolamides include:
, which is necessary for brain development and maintenance; however, a study in humans determined that dermal treatment for 1 month with a commercially available skin lotion containing DEA resulted in DEA levels that were "far below those concentrations associated with perturbed brain development in the mouse". In a mouse study of chronic exposure to inhaled DEA at high concentrations (above 150 mg/m3), DEA was found to induce body and organ weight changes, clinical and histopathological changes, indicative of mild blood, liver, kidney and testicular systemic toxicity. A 2009 study found that DEA has potential acute, chronic and subchronic toxicity properties for aquatic species.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the formula HN(CH2CH2OH)2. This colorless liquid is polyfunctional, being a secondary amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
and a diol
Diol
A diol or glycol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups A geminal diol has two hydroxyl groups bonded to the same atom...
. Like other organic amines, diethanolamine acts as a weak base
Weak base
In chemistry, a weak base is a chemical base that does not ionize fully in an aqueous solution. As Brønsted–Lowry bases are proton acceptors, a weak base may also be defined as a chemical base in which protonation is incomplete. This results in a relatively low pH compared to strong bases...
. Reflecting the hydrophilic character of the alcohol groups, DEA is soluble in water, and is even hygroscopic. Amides prepared from DEA are often also hydrophilic.
Production and uses
The reaction of ethylene oxideEthylene oxide
Ethylene oxide, also called oxirane, is the organic compound with the formula . It is a cyclic ether. This means that it is composed of two alkyl groups attached to an oxygen atom in a cyclic shape . This colorless flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor is the simplest epoxide, a three-membered...
with aqueous ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
first produces ethanolamine
Ethanolamine
Ethanolamine, also called 2-aminoethanol or monoethanolamine , is an organic chemical compound that is both a primary amine and a primary alcohol . Like other amines, monoethanolamine acts as a weak base...
:
- C2H4O + NH3 → H2NCH2CH2OH
which reacts with a second and third equivalent of ethylene oxide to give DEA and triethanolamine
Triethanolamine
Triethanolamine, often abbreviated as TEA, is an organic chemical compound which is both a tertiary amine and a triol. A triol is a molecule with three alcohol groups. Like other amines, triethanolamine is a strong base due to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. Triethanolamine can...
:
- C2H4O + H2NCH2CH2OH → HN(CH2CH2OH)2
- C2H4O + HN(CH2CH2OH)2 → N(CH2CH2OH)3
About 300M kg are produced annually in this way. The ratio of the products can be controlled by changing the stoichiometry
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. In a balanced chemical reaction, the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of whole numbers...
of the reactants.
DEA is used as a surfactant and a corrosion inhibitor
Corrosion inhibitor
A corrosion inhibitor is a chemical compound that, when added to a liquid or gas, decreases the corrosion rate of a material, typically a metal or an alloy. The effectiveness of a corrosion inhibitor depends on fluid composition, quantity of water, and flow regime...
. It is used to remove hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless, very poisonous, flammable gas with the characteristic foul odor of expired eggs perceptible at concentrations as low as 0.00047 parts per million...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
from natural gas.
In oil refineries, a DEA in water solution is commonly used to remove hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless, very poisonous, flammable gas with the characteristic foul odor of expired eggs perceptible at concentrations as low as 0.00047 parts per million...
from various process gases. It has an advantage over a similar amine ethanolamine
Ethanolamine
Ethanolamine, also called 2-aminoethanol or monoethanolamine , is an organic chemical compound that is both a primary amine and a primary alcohol . Like other amines, monoethanolamine acts as a weak base...
in that a higher concentration may be used for the same corrosion potential. This allows refiners to scrub hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless, very poisonous, flammable gas with the characteristic foul odor of expired eggs perceptible at concentrations as low as 0.00047 parts per million...
at a lower circulating amine rate with less overall energy usage.
DEA is a versatile chemical intermediate, principal derivatives include ethyleneimine and ethylenediamine. Dehydration of DEA with sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
gives morpholine
Morpholine
Morpholine is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula O2NH. This heterocycle, pictured at right, features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base; its conjugate acid is called morpholinium...
:
Amides derived from DEA and fatty acid
Fatty acid
In chemistry, especially biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long unbranched aliphatic tail , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have a chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are usually derived from...
s, known as diethanolamide
Diethanolamide
Diethanolamides are common ingredients used in cosmetics to act as a foaming agents or as emulsifiers. Chemically, they are amides formed from diethanolamine and carboxylic acids, typically fatty acids.Examples include:* Cocamide diethanolamine...
s, are amphiphilic.
Commonly used ingredients that may contain DEA
DEA is used in the production of diethanolamideDiethanolamide
Diethanolamides are common ingredients used in cosmetics to act as a foaming agents or as emulsifiers. Chemically, they are amides formed from diethanolamine and carboxylic acids, typically fatty acids.Examples include:* Cocamide diethanolamine...
s, which are common ingredients in cosmetics
Cosmetics
Cosmetics are substances used to enhance the appearance or odor of the human body. Cosmetics include skin-care creams, lotions, powders, perfumes, lipsticks, fingernail and toe nail polish, eye and facial makeup, towelettes, permanent waves, colored contact lenses, hair colors, hair sprays and...
and shampoo
Shampoo
Shampoo is a hair care product used for the removal of oils, dirt, skin particles, dandruff, environmental pollutants and other contaminant particles that gradually build up in hair...
s added to confer a creamy texture and foaming action. Consequently, some cosmetics that include diethanolamides as ingredients may contain traces of DEA. Some of the most commonly used diethanolamides include:
- Cocamide DEACocamide DEACocamide DEA, or cocamide diethanolamine, is a diethanolamide made by reacting the mixture of fatty acids from coconut oils with diethanolamine. It is a viscous liquid and is used as a foaming agent in bath products like shampoos and hand soaps, and in cosmetics as an emulsifying agent. See...
- DEA-Cetyl Phosphate
- DEA Oleth-3 Phosphate
- Lauramide DEA
- Myristamide DEA
- Oleamide DEA
- TriethanolamineTriethanolamineTriethanolamine, often abbreviated as TEA, is an organic chemical compound which is both a tertiary amine and a triol. A triol is a molecule with three alcohol groups. Like other amines, triethanolamine is a strong base due to the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. Triethanolamine can...
Safety
DEA is a potential skin irritant in workers sensitized by exposure to water-based metalworking fluids. One study showed that DEA inhibits in baby mice the absorption of cholineCholine
Choline is a water-soluble essential nutrient. It is usually grouped within the B-complex vitamins. Choline generally refers to the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the N,N,N-trimethylethanolammonium cation....
, which is necessary for brain development and maintenance; however, a study in humans determined that dermal treatment for 1 month with a commercially available skin lotion containing DEA resulted in DEA levels that were "far below those concentrations associated with perturbed brain development in the mouse". In a mouse study of chronic exposure to inhaled DEA at high concentrations (above 150 mg/m3), DEA was found to induce body and organ weight changes, clinical and histopathological changes, indicative of mild blood, liver, kidney and testicular systemic toxicity. A 2009 study found that DEA has potential acute, chronic and subchronic toxicity properties for aquatic species.