
Diet and obesity
Encyclopedia
 |
 |
Diet
Diet (nutrition)
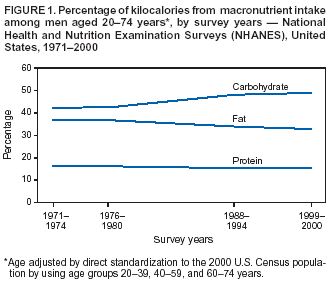
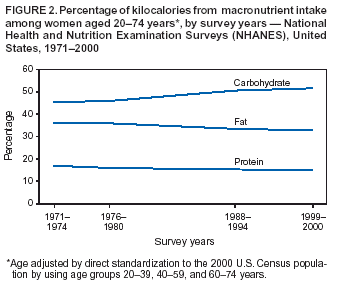
In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism. Dietary habits are the habitual decisions an individual or culture makes when choosing what foods to eat. With the word diet, it is often implied the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management...
plays an important role in the genesis of obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
. Personal choices, advertising, social customs and cultural influences, as well as food availability and pricing all play a role in determining what and how much an individual eats.
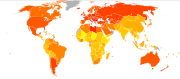
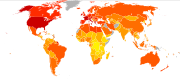
Dietary energy supply
The dietary energy supplyDietary energy supply
The dietary energy supply is the food available for human consumption, usually expressed in kilocalories per person per day. It gives an overestimate of the total amount of food consumed as it reflects both food consumed and food wasted. It varies markedly between different regions and countries...
is the food available for human consumption, usually expressed in kilocalories per person per day. It gives an overestimate of the total amount of food consumed as it reflects both food consumed and food wasted. The per capita dietary energy supply
Dietary energy supply
The dietary energy supply is the food available for human consumption, usually expressed in kilocalories per person per day. It gives an overestimate of the total amount of food consumed as it reflects both food consumed and food wasted. It varies markedly between different regions and countries...
varies markedly between different regions and countries. It has also changed significantly over time. From the early 1970s to the late 1990s, the average calories available per person per day (the amount of food bought) has increased in all part of the world except Eastern Europe and parts of Africa. The United States had the highest availability with 3654 calories per person in 1996. This increased further in 2002 to 3770. During the late 1990s, Europeans had 3394 calories per person, in the developing areas of Asia there were 2648 calories per person, and in sub-Sahara Africa people had 2176 calories per person.
Average calorie consumption
 |
 |
Fast food
As societies become increasingly reliant on energy-denseFood energy
Food energy is the amount of energy obtained from food that is available through cellular respiration.Food energy is expressed in food calories or kilojoules...
fast-food meals, the association between fast food
Fast food
Fast food is the term given to food that can be prepared and served very quickly. While any meal with low preparation time can be considered to be fast food, typically the term refers to food sold in a restaurant or store with preheated or precooked ingredients, and served to the customer in a...
consumption and obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
becomes more concerning. In the United States consumption of fast food meal has tripled and calorie intake from fast food has quadrupled between 1977 and 1995. Consumption of sweetened drinks is also believed to be a major contributor to the rising rates of obesity.
Portion size

Fast food serving for example 2 to 5 times larger than they were in the 1980s. Evidence has shown that larger portions of energy-dense foods lead to greater energy intake and thus to greater rates of obesity.
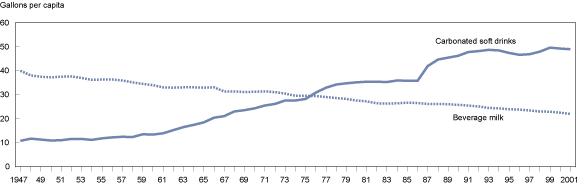
Sugar consumption
Sweetened drinks containing either sucroseSucrose
Sucrose is the organic compound commonly known as table sugar and sometimes called saccharose. A white, odorless, crystalline powder with a sweet taste, it is best known for its role in human nutrition. The molecule is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose with the molecular formula...
alone or sucrose in combination with fructose
Fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a simple monosaccharide found in many plants. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed directly into the bloodstream during digestion. Fructose was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1847...
appear to lead to weight gain due to increase energy intake.
Social policy and change
Agricultural policy and techniques in the United States and Europe have led to lower food prices. In the United States, subsidization of cornMaize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
, soy, wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
, and rice
Rice
Rice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
through the U.S. farm bill
U.S. farm bill
In the United States, the farm bill is the primary agricultural and food policy tool of the federal government. The comprehensive omnibus bill is passed every 5 years or so by the United States Congress and deals with both agriculture and all other affairs under the purview of the United States...
has made the main sources of processed food cheap compared to fruits and vegetables.
Metabolism
Evidence does not support the commonly expressed view that some obese people eat little yet gain weight due to a slow metabolismMetabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
. On average obese people have a greater energy expenditure than normal weight or thin people. This is because it takes more energy to maintain an increased body mass. Obese people also underreport how much food they consume compared to those of normal weight. Tests of human subjects carried out in a calorimeter
Calorimeter
A calorimeter is a device used for calorimetry, the science of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal microcalorimeters, titration calorimeters and accelerated rate calorimeters are among the most common...
support this conclusion.

