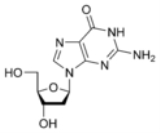
Deoxyguanosine
Encyclopedia
Deoxyguanosine is composed of the purine
nucleoside
guanine
linked by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of deoxyribose. It is similar to guanosine
, but with one hydroxyl group removed from the 2' position of the ribose
sugar (making it deoxyribose
). If a phosphate group is attached at the 5' position, it becomes deoxyguanosine monophosphate
.
Purine
A purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, consisting of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring. Purines, including substituted purines and their tautomers, are the most widely distributed kind of nitrogen-containing heterocycle in nature....
nucleoside
Nucleoside
Nucleosides are glycosylamines consisting of a nucleobase bound to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar via a beta-glycosidic linkage...
guanine
Guanine
Guanine is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine . In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with...
linked by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of deoxyribose. It is similar to guanosine
Guanosine
Guanosine is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose ring via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate , cyclic guanosine monophosphate , guanosine diphosphate , and guanosine triphosphate...
, but with one hydroxyl group removed from the 2' position of the ribose
Ribose
Ribose is an organic compound with the formula C5H10O5; specifically, a monosaccharide with linear form H––4–H, which has all the hydroxyl groups on the same side in the Fischer projection....
sugar (making it deoxyribose
Deoxyribose
Deoxyribose, more, precisely 2-deoxyribose, is a monosaccharide with idealized formula H---3-H. Its name indicates that it is a deoxy sugar, meaning that it is derived from the sugar ribose by loss of an oxygen atom...
). If a phosphate group is attached at the 5' position, it becomes deoxyguanosine monophosphate
Deoxyguanosine monophosphate
Deoxyguanosine monophosphate, also known as deoxyguanylate, or dGMP, is a derivative of the common nucleic acid guanosine triphosphate , in which the –OH group on the 2' carbon on the nucleotide's pentose has been reduced to just a hydrogen atom...
.

