
Dead space
Encyclopedia
In physiology
, dead space is air that is inhaled by the body in breathing, but does not take part in gas exchange. Not all the air in each breath is able to be used for the exchange of oxygen
and carbon dioxide
. About a third of every resting breath has no change in O2 and CO2 levels. In adults, it is usually in the range of 150 mL.
Because of dead space, taking deep breaths more slowly (e.g. ten 500 mL breaths per minute) is more effective than taking shallow breaths quickly (e.g. twenty 250 mL breaths per minute). Although the amount of gas per minute is the same (5 L/min), a large proportion of the shallow breaths is dead space, and does not allow oxygen to get into the blood.
Dead space can be enlarged (and better envisaged) by breathing into a long tube. Even though one end of the tube is open to the air, when one inhales, it is mostly the carbon dioxide from expiration. Using a snorkel increases a diver's dead space in the airways.
and trachea
, where air does not come into contact with the alveoli of the lungs. Birds, which, relatively, have a far longer and wider trachea than mammals, have a higher proportion of dead space.
It is normally equal in milliliters to your body weight in pounds. A 150 lb (68 kg) male would have an anatomical dead space of about 150 mL. 1 mL per lb or 2.2 mL per kilogram of body weight. This is the same conversion of kilograms to pounds, except the final unit is in mL. This is about a third of the resting tidal volume
(450-500 mL).
Anatomic dead space is the volume of the conducting airways. It may be measured by Fowler's method, a nitrogen
washout technique.
. Formally, Bohr's method is used to calculate the former. In practice, it is more commonly used to calculate the latter.
The Bohr equation states that the dead space (Vd) is calculated as follows:
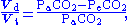
where Vd is dead space volume, Vt is tidal volume, PaCO2 is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood, and PeCO2 is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the expired air.
Depending on how the expired CO2 is measured, this equation gives the physiological or alveolar dead space. When calculating the:
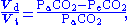
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
, dead space is air that is inhaled by the body in breathing, but does not take part in gas exchange. Not all the air in each breath is able to be used for the exchange of oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
. About a third of every resting breath has no change in O2 and CO2 levels. In adults, it is usually in the range of 150 mL.
Because of dead space, taking deep breaths more slowly (e.g. ten 500 mL breaths per minute) is more effective than taking shallow breaths quickly (e.g. twenty 250 mL breaths per minute). Although the amount of gas per minute is the same (5 L/min), a large proportion of the shallow breaths is dead space, and does not allow oxygen to get into the blood.
Dead space can be enlarged (and better envisaged) by breathing into a long tube. Even though one end of the tube is open to the air, when one inhales, it is mostly the carbon dioxide from expiration. Using a snorkel increases a diver's dead space in the airways.
Components
Total dead space (also known as "physiological" dead space) can be divided into anatomical dead space and alveolar dead space.Anatomical dead space
Anatomical dead space is the gas in the conducting areas of the respiratory system, such as the mouthMouth
The mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food andsaliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth....
and trachea
Vertebrate trachea
In tetrapod anatomy the trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the pharynx or larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air. It is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium cells with goblet cells that produce mucus...
, where air does not come into contact with the alveoli of the lungs. Birds, which, relatively, have a far longer and wider trachea than mammals, have a higher proportion of dead space.
It is normally equal in milliliters to your body weight in pounds. A 150 lb (68 kg) male would have an anatomical dead space of about 150 mL. 1 mL per lb or 2.2 mL per kilogram of body weight. This is the same conversion of kilograms to pounds, except the final unit is in mL. This is about a third of the resting tidal volume
Tidal volume
Tidal volume is the lung volume representing the normal volume of air displaced between normal inspiration and expiration when extra effort is not applied.Typical values are around 500ml or 7ml/kg bodyweight.-Mechanical Ventilation:...
(450-500 mL).
Anatomic dead space is the volume of the conducting airways. It may be measured by Fowler's method, a nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
washout technique.
Alveolar dead space
Alveolar dead space is caused by air contacting alveoli without bloodflow in their adjacent pulmonary capillaries, i.e. ventilation without perfusion. As a result, no gas exchange can occur. Alveolar dead space is negligible in healthy individuals, but can increase dramatically in some lung diseases.Overview
Anatomical and alveolar dead space can both be measured using the Bohr equationBohr equation
The Bohr equation, named after named after Danish physician Christian Bohr , describes the amount of physiological dead space in a person's lungs. This is given as a ratio of dead space to tidal volume...
. Formally, Bohr's method is used to calculate the former. In practice, it is more commonly used to calculate the latter.
The Bohr equation states that the dead space (Vd) is calculated as follows:
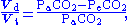
where Vd is dead space volume, Vt is tidal volume, PaCO2 is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood, and PeCO2 is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the expired air.
Depending on how the expired CO2 is measured, this equation gives the physiological or alveolar dead space. When calculating the:
- physiological dead space, a large plastic bag (that is, a Douglas bag) is used to collect all of the patients expired gas, and the total expired CO2 is measured as a fraction of total expired gas. This gives PeCO2, which is then substituted into the Bohr equation.
- alveolar dead space, the end-tidal CO2 in capnographyCapnographyCapnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the respiratory gases. Its main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anaesthesia and intensive care. It is usually presented as a graph of expiratory plotted against time, or, less...
is used as a surrogate for the expired CO2. PetCO2 is then used instead of PeCO2 in the Bohr equation.
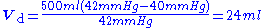
Example
If a patient's tidal volume is 500 mL, their arterial carbon dioxide (PaCO2) is 42 mmHg (5,599.5 Pa), and their end-expired carbon dioxide (ETCO2) on capnography is 40 mmHg (5,332.9 Pa), the alveolar dead space can be calculated as follows: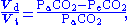

See also
- Bohr equationBohr equationThe Bohr equation, named after named after Danish physician Christian Bohr , describes the amount of physiological dead space in a person's lungs. This is given as a ratio of dead space to tidal volume...
- Christian BohrChristian BohrChristian Harald Lauritz Peter Emil Bohr was a Danish physician, father of the physicist and Nobel laureate Niels Bohr, as well as the mathematician Harald Bohr and grandfather of another physicist and nobel laureate Aage Bohr...
- Respiratory physiologyRespiratory physiologyRespiratory physiology is the branch of human physiology focusing upon respiration.Topics include:-Volumes:* lung volumes* vital capacity* functional residual capacity* dead space* spirometry* body plethysmography* peak flow meter-Mechanics:...
- Ventilation (physiology)Ventilation (physiology)In respiratory physiology, ventilation is the rate at which gas enters or leaves the lung. It is categorized under the following definitions:-Sample values:...

