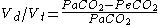Bohr equation
Encyclopedia
The Bohr equation, named after named after Danish
physician Christian Bohr
(1855–1911), describes the amount of physiological dead space in a person's lungs. This is given as a ratio
of dead space to tidal volume
. It differs from anatomical dead space as measured by Fowler's method as it includes alveolar
dead space.
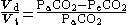
 ) will produce CO2
) will produce CO2
. Because the Total tidal volume ( ) is made up of
) is made up of 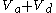 (alveolar volume + dead space volume), we can substitute
(alveolar volume + dead space volume), we can substitute 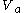 for
for 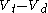 .
.
Initially, Bohr tells us Vt = Vd + Va. The Bohr equation helps us find the amount of any expired gas, , N2, O2, etc. In this case we will focus on . Defining Fe as the fraction of expired and Fa as the fraction of expired alveolar , and Fd as fraction of expired dead space volume , we can say
Vt x Fe = ( Vd x Fd ) + (Va x Fa ). This merely means all the expired comes from two parts, the dead space volume and the alveolar volume.
If we suppose that Fd = 0 (since carbon dioxide concentration in air is normally negligible), then we can say that:
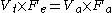 Where Fe = Fraction expired CO2, and Fa = Alveolar fraction of CO2.
Where Fe = Fraction expired CO2, and Fa = Alveolar fraction of CO2.
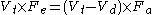 Substituted as above.
Substituted as above.
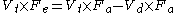 Multiply out of the brackets.
Multiply out of the brackets.
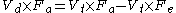 Rearrange.
Rearrange.
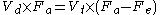
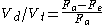 Divide by Vt and by Fa.
Divide by Vt and by Fa.
The above equation makes sense because it describes the total being measured by the spirometer. The only source of the we are assuming to measure is from the alveolar space where and O2 exchange takes place. Thus alveolar's fractional component, Fa, will always be higher than the total content of the expired air, Fe, thus we will be always yielding a positive number.
Where Ptot is the total pressure, we obtain:
Therefore:
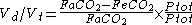
This is simplified as:
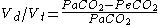
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
physician Christian Bohr
Christian Bohr
Christian Harald Lauritz Peter Emil Bohr was a Danish physician, father of the physicist and Nobel laureate Niels Bohr, as well as the mathematician Harald Bohr and grandfather of another physicist and nobel laureate Aage Bohr...
(1855–1911), describes the amount of physiological dead space in a person's lungs. This is given as a ratio
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
of dead space to tidal volume
Tidal volume
Tidal volume is the lung volume representing the normal volume of air displaced between normal inspiration and expiration when extra effort is not applied.Typical values are around 500ml or 7ml/kg bodyweight.-Mechanical Ventilation:...
. It differs from anatomical dead space as measured by Fowler's method as it includes alveolar
Pulmonary alveolus
An alveolus is an anatomical structure that has the form of a hollow cavity. Found in the lung parenchyma, the pulmonary alveoli are the dead ends of the respiratory tree, which outcrop from either alveolar sacs or alveolar ducts, which are both sites of gas exchange with the blood as well...
dead space.
Description
The Bohr equation is used to quantify the ratio of physiological dead space to the total tidal volume, and gives an indication of the extent of wasted ventilation. It is stated as follows: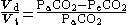
Derivation
Its derivation is based on the fact that only the ventilated gases involved in gas exchange (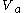 ) will produce CO2
) will produce CO2Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
. Because the Total tidal volume (
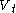 ) is made up of
) is made up of 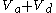 (alveolar volume + dead space volume), we can substitute
(alveolar volume + dead space volume), we can substitute 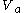 for
for 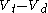 .
.Initially, Bohr tells us Vt = Vd + Va. The Bohr equation helps us find the amount of any expired gas, , N2, O2, etc. In this case we will focus on . Defining Fe as the fraction of expired and Fa as the fraction of expired alveolar , and Fd as fraction of expired dead space volume , we can say
Vt x Fe = ( Vd x Fd ) + (Va x Fa ). This merely means all the expired comes from two parts, the dead space volume and the alveolar volume.
If we suppose that Fd = 0 (since carbon dioxide concentration in air is normally negligible), then we can say that:
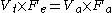 Where Fe = Fraction expired CO2, and Fa = Alveolar fraction of CO2.
Where Fe = Fraction expired CO2, and Fa = Alveolar fraction of CO2.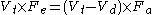 Substituted as above.
Substituted as above.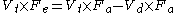 Multiply out of the brackets.
Multiply out of the brackets.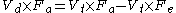 Rearrange.
Rearrange.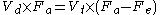
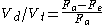 Divide by Vt and by Fa.
Divide by Vt and by Fa.The above equation makes sense because it describes the total being measured by the spirometer. The only source of the we are assuming to measure is from the alveolar space where and O2 exchange takes place. Thus alveolar's fractional component, Fa, will always be higher than the total content of the expired air, Fe, thus we will be always yielding a positive number.
Where Ptot is the total pressure, we obtain:
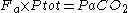 and
and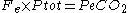
Therefore:
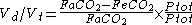
This is simplified as: