
Davey–Stewartson equation
Encyclopedia
In fluid dynamics
, the Davey–Stewartson equation (DSE) was introduced in a paper by to describe the evolution of a three-dimensional wave-packet
on water of finite depth.
It is a system of partial differential equations for a complex (wave-amplitude
) field
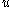 and a real (mean-flow
and a real (mean-flow
) field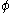 :
:
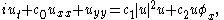
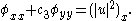
The DSE is an example of a soliton
equation in 2+1 dimensions. The corresponding Lax representation for it is given in .
In 1+1 dimensions the DSE reduces to the nonlinear Schrödinger equation
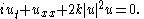
Itself, the DSE is the particular reduction of the Zakharov–Schulman system
. On the other hand, the equivalent counterpart of the DSE is the Ishimori equation
.
The DSE is the result of a multiple-scale analysis
of modulated
nonlinear surface gravity waves, propagating over a horizontal sea bed.
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
, the Davey–Stewartson equation (DSE) was introduced in a paper by to describe the evolution of a three-dimensional wave-packet
Wave packet
In physics, a wave packet is a short "burst" or "envelope" of wave action that travels as a unit. A wave packet can be analyzed into, or can be synthesized from, an infinite set of component sinusoidal waves of different wavenumbers, with phases and amplitudes such that they interfere...
on water of finite depth.
It is a system of partial differential equations for a complex (wave-amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
) field
Field (physics)
In physics, a field is a physical quantity associated with each point of spacetime. A field can be classified as a scalar field, a vector field, a spinor field, or a tensor field according to whether the value of the field at each point is a scalar, a vector, a spinor or, more generally, a tensor,...
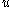 and a real (mean-flow
and a real (mean-flowMean flow
In fluid dynamics, the fluid flow is often decomposed into a mean flow – and deviations from the mean. The averaging can be done either in space or in time....
) field
 :
: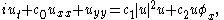
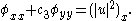
The DSE is an example of a soliton
Soliton
In mathematics and physics, a soliton is a self-reinforcing solitary wave that maintains its shape while it travels at constant speed. Solitons are caused by a cancellation of nonlinear and dispersive effects in the medium...
equation in 2+1 dimensions. The corresponding Lax representation for it is given in .
In 1+1 dimensions the DSE reduces to the nonlinear Schrödinger equation
Nonlinear Schrödinger equation
In theoretical physics, the nonlinear Schrödinger equation is a nonlinear version of Schrödinger's equation. It is a classical field equation with applications to optics and water waves. Unlike the Schrödinger equation, it never describes the time evolution of a quantum state...
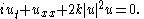
Itself, the DSE is the particular reduction of the Zakharov–Schulman system
Zakharov–Schulman system
In mathematics, the Zakharov–Schulman system is a system of nonlinear partial differential equations introduced in to describe the interactions of small amplitude, high frequency waves with acoustic waves....
. On the other hand, the equivalent counterpart of the DSE is the Ishimori equation
Ishimori equation
The Ishimori equation is a partial differential equation proposed by the Japanese mathematician . Its interest is as the first example of a nonlinear spin-one field model in the plane that is integrable .-Equation:The IE has the form...
.
The DSE is the result of a multiple-scale analysis
Multiple-scale analysis
In mathematics and physics, multiple-scale analysis comprises techniques used to construct uniformly valid approximations to the solutions of perturbation problems, both for small as well as large values of the independent variables...
of modulated
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
nonlinear surface gravity waves, propagating over a horizontal sea bed.
External links
- Davey-Stewartson_system at the dispersive equations wiki.

