
Data Matrix
Encyclopedia

Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
barcode
Barcode
A barcode is an optical machine-readable representation of data, which shows data about the object to which it attaches. Originally barcodes represented data by varying the widths and spacings of parallel lines, and may be referred to as linear or 1 dimensional . Later they evolved into rectangles,...
consisting of black and white "cells" or modules arranged in either a square
Square (geometry)
In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. This means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles...
or rectangular
Rectangle
In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is any quadrilateral with four right angles. The term "oblong" is occasionally used to refer to a non-square rectangle...
pattern. The information to be encoded can be text or raw data. Usual data size is from a few bytes up to 1556 byte
Byte
The byte is a unit of digital information in computing and telecommunications that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, a byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the basic addressable element in many computer...
s. The length of the encoded data depends on the symbol dimension used. Error correction codes are added to increase symbol strength: even if they are partially damaged, they can still be read. A Data Matrix symbol can store up to 2,335 alphanumeric
Alphanumeric
Alphanumeric is a combination of alphabetic and numeric characters, and is used to describe the collection of Latin letters and Arabic digits or a text constructed from this collection. There are either 36 or 62 alphanumeric characters. The alphanumeric character set consists of the numbers 0 to...
characters.
Data Matrix symbols are rectangular in shape and usually square, they are made of cells: little elements that represent bits. Depending on the situation a "light" module is a 0 and a "dark" module is a 1, or vice versa. Every Data Matrix is composed of two solid adjacent borders in an "L" shape (called the "finder pattern") and two other borders consisting of alternating dark and light "cells" or modules (called the "timing pattern"). Within these borders are rows and columns of cells encoding information. The finder pattern is used to locate and orient the symbol while the timing pattern provides a count of the number of rows and columns in the symbol. As more data is encoded in the symbol, the number of cells (rows and columns) increases. Symbol sizes vary from 8×8 to 144×144.
Applications
The most popular application for Data Matrix is marking small items, due to the code’s ability to encode fifty characters in a symbol that is readable at 2 or 3 mm2 and the fact that the code can be read with only a 20% contrast ratio.The Data Matrix is scalable, with commercial applications as small as 300 micrometres (laser etched on a 600 micrometre silicon device) and as large as a 1 metre (3 ft) square (painted on the roof of a boxcar). Fidelity of the marking and reading systems are the only limitation.
The United States of America's Electronic Industries Alliance
Electronic Industries Alliance
The Electronic Industries Alliance was a standards and trade organization composed as an alliance of trade associations for electronics manufacturers in the United States. They developed standards to ensure the equipment of different manufacturers was compatible and interchangeable...
(EIA) recommends using Data Matrix for labeling small electronic components.
Data Matrix codes are part of a new traceability drive in many industries in the United States of America, particularly aerospace where quality control is tight and a black market exists for counterfeit or non-serviceable parts. Data Matrix codes (and accompanying alpha-numeric data) identify details of the component, including manufacturer ID, part number and a unique serial number. The US Department of Defense
United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
has selected Data Matrix for the mandatory unique identification of certain assets it procures for all of the services. Items from individual weapons to critical components of major systems must be permanently marked with a unique data matrix code in accordance with standards in Military Standard 130. Much of the Aerospace Industry, especially members of the Air Transport Association (ATA), aims to have all components of every new aircraft identified by Data Matrix codes within a tight deadline.
The Data Matrix format is used by Semacode
Semacode
Semacode is a software company based in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. It is also this company's trade name for machine-readable ISO/IEC 16022 data matrix symbols, a type of barcode resembling a crossword puzzle, which encode Internet URLs....
to encode 4096 bits RSA private keys that can be read by cameras or scanners.
Technical specifications

ASCII
The American Standard Code for Information Interchange is a character-encoding scheme based on the ordering of the English alphabet. ASCII codes represent text in computers, communications equipment, and other devices that use text...
character set (with extensions). The symbol consists of data regions which contain modules set out in a regular array. Large symbols contain several regions. Each data region is delimited by a finder pattern, and this is surrounded on all four sides by a quiet zone border (margin). (Note: The modules may be round or square- no specific shape is defined in the standard. For example, dot-peened cells are generally round.)
Symbols have an even number of rows and an even number of columns. Most of the symbols are square with sizes from 10×10 to 144×144. Some symbols however are rectangular with sizes from 8×18 to 16×48. All symbols utilizing the ECC200 error correction can be recognized by the upper right corner module being the same as the background color. (binary 0).
ECC200 is the newest version of Data Matrix and supports advanced encoding error checking and correction algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
s (such as Reed-Solomon). ECC200 allows the routine reconstruction of the entire encoded data string when the symbol has sustained 30% damage, assuming the matrix can still be accurately located. Data Matrix has an error rate of less than 1 in 10 million characters scanned.
Data Matrix applications

Barcode reader
A barcode reader is an electronic device for reading printed barcodes. Like a flatbed scanner, it consists of a light source, a lens and a light sensor translating optical impulses into electrical ones...
which allows the media to be tracked, for example when a parcel has been dispatched to the recipient.
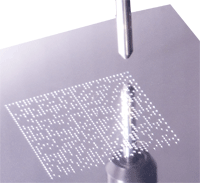
For industrial engineering purposes, Data Matrix codes can be marked directly onto components, ensuring that only the intended component is identified with the Data Matrix encoded data. The codes can be marked onto components with various methods, but within the aerospace industry these are commonly industrial ink-jet, dot-peen marking, laser marking, and electrolytic chemical etching (ECE). These methods give a permanent mark which should last the lifetime of the component.
After creation of the Data Matrix code, the code is usually verified using specialist camera equipment and software. This verification ensures the code conforms to the relevant standards, and ensures it will be readable for the lifetime of the component. After the component enters service, the Data Matrix code can then be read by a reader camera, which decodes the Data Matrix data which can then be used for a number of purposes, such as movement tracking or inventory stock checks.
Data Matrix codes, along with other Open Source codes such as 1D Barcodes can also now be read with mobile phones, simply by downloading the application to compatible mobile phones. Although the majority of these mobile readers are capable of reading Data Matrix, only a few can extend the decoding to enable mobile access and interaction, whereupon the codes can be used securely and across media; for example, in track and trace, anti-counterfeit, e.govt, and banking solutions.
Standards
Data Matrix was invented by International Data Matrix, Inc. (ID Matrix) which was merged into RVSI/Acuity CiMatrix, who were acquired by SiemensSiemens
Siemens may refer toSiemens, a German family name carried by generations of telecommunications industrialists, including:* Werner von Siemens , inventor, founder of Siemens AG...
AG in October, 2005 and Microscan Systems
Microscan Systems
Microscan Systems, Inc. is a manufacturer of precision data acquisition and control solutions for automation and OEM applications. Founded in 1982, Microscan provides systems for ID tracking, traceability and inspection...
in September 2008. Data Matrix is covered today by several ISO/IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission is a non-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology"...
standards and is in the public domain for many applications, which means it can be used free of any licensing or royalties.
- ISO/IEC 16022:2006—Data Matrix bar code symbology specification
- ISO/IEC 15415—2-D Print Quality Standard
- ISO/IEC 15418:2009—Symbol Data Format Semantics (GS1GS1Founded in 1977, GS1 is an international not-for-profit association dedicated to the development and implementation of global standards and solutions to improve the efficiency and visibility of supply and demand chains globally and across multiple sectors...
Application Identifiers and ASC MH10 Data Identifiers and maintenance) - ISO/IEC 15424:2008—Data Carrier Identifiers (including Symbology Identifiers) [IDs for distinguishing different bar code types]
- ISO/IEC 15434:2009—Syntax for high-capacity ADC media (format of data transferred from scanner to software, etc.)
- ISO/IEC 15459—Unique Identifiers
Encoding
Although this is a free standard, there are no free documents that explain the encoding process.Documentation in PDF or paper
Paper
Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
format can be purchased from the ISO web site
The diagram below illustrates the placement of the message data within a Data Matrix symbol. The message is "Wikipedia", and it is arranged in a somewhat complicated diagonal pattern starting near the upper-left corner. Some characters are split in two pieces, such as the initial W. Also shown are the end-of-message code (marked End), the padding (P) and error correction (E) bytes, and four modules of unused space (X).
There are multiple encoding modes used to store different kinds of messages. The default mode stores one ASCII
ASCII
The American Standard Code for Information Interchange is a character-encoding scheme based on the ordering of the English alphabet. ASCII codes represent text in computers, communications equipment, and other devices that use text...
character per 8-bit codeword. Control codes are provided to switch between modes, as shown below.
| Codeword | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 0 | Not used |
| 1 – 128 | ASCII data (ASCII value + 1) |
| 129 | End of message |
| 130 – 229 | Digit pairs 00 – 99 |
| 230 | Begin C40 encoding |
| 231 | Begin Base 256 encoding |
| 232 | FNC1 |
| 233 | Structured append. Allows a message to be split across multiple symbols. |
| 234 | Reader programming |
| 235 | Set high bit of the following character |
| 236 | 05 Macro |
| 237 | 06 Macro |
| 238 | Begin ANSI X12 encoding |
| 239 | Begin Text encoding |
| 240 | Begin EDIFACT encoding |
| 241 | Extended Channel Interpretation code |
| 242 – 255 | Not used |
Text modes
The C40, Text and X12 modes are potentially more compact for storing text messages. They use character codes in the range 0–39, and three of these codes are packed into two bytes as follows.- V = C1*1600 + C2*40 + C3
- B1 = floor(V/256)
- B2 = V mod 256
The resulting value of B1 is in the range 0–249. The special value 254 is used to return to ASCII encoding mode.
Character code interpretations are shown in the table below. The C40 and Text modes have four separate sets. Set 0 is the default, and contains codes that temporarily select a different set for the next character. Set 1 contains ASCII control codes, while set 2 contains punctuation symbols; these sets are identical in C40 and Text mode.
| Code | | C40 | | Text | X12 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| set 0 | set 1 | set 2 | set 3 | set 0 | set 3 | ||
| 0 | set 1 | NUL | ! | ' | set 1 | ' | CR |
| 1 | set 2 | SOH | " | a | set 2 | A | * |
| 2 | set 3 | STX | # | b | set 3 | B | > |
| 3 | space | ETX | $ | c | space | C | space |
| 4 | 0 | EOT | % | d | 0 | D | 0 |
| 5 | 1 | ENQ | & | e | 1 | E | 1 |
| 6 | 2 | ACK | ‘ | f | 2 | F | 2 |
| 7 | 3 | BEL | ( | g | 3 | G | 3 |
| 8 | 4 | BS | ) | h | 4 | H | 4 |
| 9 | 5 | HT | * | i | 5 | I | 5 |
| 10 | 6 | LF | + | j | 6 | J | 6 |
| 11 | 7 | VT | , | k | 7 | K | 7 |
| 12 | 8 | FF | - | l | 8 | L | 8 |
| 13 | 9 | CR | . | m | 9 | M | 9 |
| 14 | A | SO | / | n | a | N | A |
| 15 | B | SI | : | o | b | O | B |
| 16 | C | DLE | ; | p | c | P | C |
| 17 | D | DC1 | < | q | d | Q | D |
| 18 | E | DC2 | = | r | e | R | E |
| 19 | F | DC3 | > | s | f | S | F |
| 20 | G | DC4 | ? | t | g | T | G |
| 21 | H | NAK | @ | u | h | U | H |
| 22 | I | SYN | [ | v | i | V | I |
| 23 | J | ETB | \ | w | j | W | J |
| 24 | K | CAN | ] | x | k | X | K |
| 25 | L | EM | ^ | y | l | Y | L |
| 26 | M | SUB | _ | z | m | Z | M |
| 27 | N | ESC | FNC1 | { | n | { | N |
| 28 | O | FS | | | o | | | O | |
| 29 | P | GS | } | p | } | P | |
| 30 | Q | RS | hibit | ~ | q | ~ | Q |
| 31 | R | US | DEL | r | DEL | R | |
| 32 | S | s | S | ||||
| 33 | T | t | T | ||||
| 34 | U | u | U | ||||
| 35 | V | v | V | ||||
| 36 | W | w | W | ||||
| 37 | X | x | X | ||||
| 38 | Y | y | Y | ||||
| 39 | Z | z | Z | ||||
EDIFACT mode
EDIFACT mode uses six bits per character, with four characters packed into three bytes. It can store digits, upper-case letters, and many punctuation marks, but has no support for lower-case letters.| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 – 30 | ASCII codes 64 – 94 |
| 31 | Return to ASCII mode |
| 32 – 63 | ASCII codes 32 – 63 |
Base 256 mode
Base 256 mode data starts with a length indicator, followed by a number of data bytes. A length of 1 to 249 is encoded as a single byte,and longer lengths are stored as two bytes.
- L1 = floor(length / 250) + 249, L2 = length mod 250
It is desirable to avoid long strings of zeros in the coded message, because they become large blank areas in the Data Matrix symbol, which may
cause a scanner to lose synchronization. (The default ASCII encoding does not use zero for this reason.) In order to make that less likely, the
length and data bytes are obscured by adding a pseudorandom value R(n), where n is the position in the byte stream.
- R(n) = (149 × n) mod 255 + 1
Patent issues
Prior to the expiration of , intellectual property company Acacia Technologies claimed that Data Matrix was partially covered by its contents. As the patent owner, Acacia allegedly contacted Data Matrix users demanding license fees related to the patent.Cognex Corporation
Cognex Corporation
Cognex Corporation is a manufacturer of machine vision systems, software and sensors used in automated manufacturing to inspect and identify parts, detect defects, verify product assembly, and guide assembly robots. Cognex is headquartered in Natick, Massachusetts, USA...
, a large manufacturer of 2D barcode devices, filed a declaratory judgment complaint on March 13, 2006 after receiving information that Acacia had contacted its customers demanding licensing fees. On May 19, 2008 Judge Joan N. Ericksen of the U.S. District Court in Minnesota ruled in favor of Cognex. The ruling held that the '524 patent, which claimed to cover a system for capturing and reading 2D symbology codes, is both invalid and unenforceable due to inequitable conduct by the defendants during the procurement of the patent.
Notably, since the '524 patent expired in November 2007, a ruling against Cognex wouldn't have affected current use of Data Matrix codes. However, it would have established that use of Data Matrix prior to November 2007 could potentially be covered by the '524 patent.
A German Patent Application DE 4107020 was filed in 1991, and published in 1992. This patent is not cited in the above US patent applications and might invalidate them.
Crop circle
In May 2006 a German computer programmer, Bernd Hopfengärtner, created a large data matrix in a wheat field (in a fashion similar to crop circleCrop circle
A crop circle is a sizable pattern created by the flattening of a crop such as wheat, barley, rye, maize, or rapeseed. Crop circles are also referred to as crop formations, because they are not always circular in shape. While the exact date crop circles began to appear is unknown, the documented...
s). The message read "Hello, World!".
See also
- Aztec CodeAztec CodeAztec Code is a type of 2D barcode invented by Andrew Longacre, Jr. and Robert Hussey in 1995. The code was published by AIM, Inc. in 1997. Although the Aztec code is patented, it has been released to the public domain.- Encoding :...
- High Capacity Color BarcodeHigh Capacity Color BarcodeHigh Capacity Color Barcode is the name coined by Microsoft for its technology of encoding data in a 2D "barcode" using clusters of colored triangles instead of the square pixels traditionally associated with 2D barcodes. Data density is increased by using a palette of 4 or 8 colors for the...
- MaxiCodeMaxiCodeMaxiCode is a public domain, machine-readable symbol system originally created and used by United Parcel Service. Suitable for tracking and managing the shipment of packages, it resembles a barcode, but uses dots arranged in a hexagonal grid instead of bars...
- Nintendo e-Reader
- QR CodeQR CodeA QR code is a type of matrix barcode first designed for the automotive industry. More recently, the system has become popular outside of the industry due to its fast readability and comparatively large storage capacity. The code consists of black modules arranged in a square pattern on a white...
- SemacodeSemacodeSemacode is a software company based in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. It is also this company's trade name for machine-readable ISO/IEC 16022 data matrix symbols, a type of barcode resembling a crossword puzzle, which encode Internet URLs....
- SPARQCodeSPARQCodeA SPARQCode is a matrix code encoding standard that is based on the physical QR Code definition created by Japanese corporation Denso-Wave.- Overview :...
- Trusted paper keyTrusted paper keyA paper key is a machine-readable print of a cryptographic key. The printed key can be used to decrypt data, e.g. archives or backup data. A paper key can be the result of an offline private key protocol...

