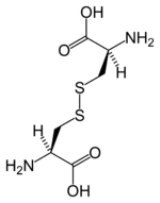
Cystine
Encyclopedia
Cystine is a dimeric amino acid
formed by the oxidation of two cysteine
residues that covalently link to make a disulfide
bond. This organosulfur compound has the formula
(SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H)2. It is a white solid, and melts at 247-249 °C. It was discovered in 1810 by William Hyde Wollaston
but was not recognized as being derived of proteins until it was isolated from the horn
of a cow in 1899. Through formation of disulfide bonds within and between protein molecules, cystine is a significant determinant of the tertiary structure
of most proteins. Disulfide bonding, along with hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions is partially responsible for the formation of the gluten matrix in bread. Human hair contains approximately 5% cystine by mass.
.CO2H)2 + 2 RSH
→ 2 HSCH2CH(NH2)CO2H + RSSR
For this reason, the nutritional benefits and sources of cystine are identical to those for the more-common cysteine. Disulfide bonds cleave more rapidly at higher temperatures.
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
formed by the oxidation of two cysteine
Cysteine
Cysteine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2SH. It is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans. Its codons are UGU and UGC. The side chain on cysteine is thiol, which is polar and thus cysteine is usually classified as a hydrophilic amino acid...
residues that covalently link to make a disulfide
Disulfide
In chemistry, a disulfide usually refers to the structural unit composed of a linked pair of sulfur atoms. Disulfide usually refer to a chemical compound that contains a disulfide bond, such as diphenyl disulfide, C6H5S-SC6H5....
bond. This organosulfur compound has the formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
(SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H)2. It is a white solid, and melts at 247-249 °C. It was discovered in 1810 by William Hyde Wollaston
William Hyde Wollaston
William Hyde Wollaston FRS was an English chemist and physicist who is famous for discovering two chemical elements and for developing a way to process platinum ore.-Biography:...
but was not recognized as being derived of proteins until it was isolated from the horn
Horn (anatomy)
A horn is a pointed projection of the skin on the head of various animals, consisting of a covering of horn surrounding a core of living bone. True horns are found mainly among the ruminant artiodactyls, in the families Antilocapridae and Bovidae...
of a cow in 1899. Through formation of disulfide bonds within and between protein molecules, cystine is a significant determinant of the tertiary structure
Tertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
of most proteins. Disulfide bonding, along with hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions is partially responsible for the formation of the gluten matrix in bread. Human hair contains approximately 5% cystine by mass.
Properties and nutritional aspects
The disulfide link is readily reduced to give the corresponding thiol cysteine. This reaction is typically effected with thiols such as mercaptoethanol or dithiothreitolDithiothreitol
Dithiothreitol is the common name for a small-molecule redox reagent known as Cleland's reagent. DTT's formula is C4H10O2S2 and the molecular structure of its reduced form is shown at the right; its oxidized form is a disulfide-bonded 6-membered ring . Its name derives from the four-carbon...
.CO2H)2 + 2 RSH
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol is an organosulfur compound that contains a carbon-bonded sulfhydryl group...
→ 2 HSCH2CH(NH2)CO2H + RSSR
For this reason, the nutritional benefits and sources of cystine are identical to those for the more-common cysteine. Disulfide bonds cleave more rapidly at higher temperatures.
See also
- CystinuriaCystinuriaCystinuria is an inherited autosomal recessive disease that is characterized by the formation of cystine stones in the kidneys, ureter, and bladder.-Signs and symptoms:Cystinuria is a cause of persistent kidney stones...
- CystinosisCystinosisCystinosis is a lysosomal storage disease characterized by the abnormal accumulation of the amino acid cystine. It is a genetic disorder that typically follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. Cystinosis is the most common cause of Fanconi syndrome in the pediatric age group...
- CysteineCysteineCysteine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2SH. It is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans. Its codons are UGU and UGC. The side chain on cysteine is thiol, which is polar and thus cysteine is usually classified as a hydrophilic amino acid...
- LanthionineLanthionineLanthionine is a nonproteinogenic amino acid with the chemical formula . As the monosulfide analog of cystine, lanthionine is composed of two alanine residues that are crosslinked on their β-carbon atoms by a thioether linkage...
, similar with mono-sulphide link

