
Curve number
Encyclopedia
The runoff curve number is an empirical
parameter used in hydrology
for predicting direct runoff
or infiltration
from rainfall
excess. The curve number method was developed by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service
, which was formerly called the Soil Conservation Service or SCS — the number is still popularly known as a "SCS runoff curve number" in the literature. The runoff curve number was developed from an empirical analysis
of runoff from small catchments and hillslope plots monitored by the USDA. It is widely used and is an efficient method for determining the approximate amount of direct runoff from a rainfall
event in a particular area.
The runoff curve number is based on the area's hydrologic soil group, land use
, treatment and hydrologic condition. References, such as from USDA indicate the runoff curve numbers for characteristic land cover descriptions and a hydrologic soil group.
The runoff equation is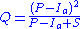
where is runoff
is runoff
([L]; in)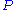 is rainfall
is rainfall
([L]; in)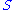 is the potential maximum soil moisture retention after runoff begins ([L]; in)
is the potential maximum soil moisture retention after runoff begins ([L]; in)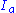 is the initial abstraction ([L]; in), or the amount of water before runoff, such as infiltration
is the initial abstraction ([L]; in), or the amount of water before runoff, such as infiltration
, or rainfall interception by vegetation; and it is generally assumed that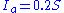
The runoff curve number, , is then related
, is then related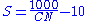
 has a range from 30 to 100; lower numbers indicate low runoff potential while larger numbers are for increasing runoff potential. The lower the curve number, the more permeable the soil is.
has a range from 30 to 100; lower numbers indicate low runoff potential while larger numbers are for increasing runoff potential. The lower the curve number, the more permeable the soil is.
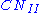 , or average soil moisture. The other moisture conditions are dry, AMC I or
, or average soil moisture. The other moisture conditions are dry, AMC I or 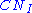 , and moist, AMC III or
, and moist, AMC III or 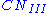 . The curve number can be adjusted by factors to
. The curve number can be adjusted by factors to 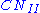 , where
, where 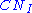 factors are less than 1 (reduce
factors are less than 1 (reduce  and potential runoff), while
and potential runoff), while 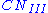 factor are greater than 1 (increase
factor are greater than 1 (increase  and potential runoff). The AMC factors can be looked up in a reference table.
and potential runoff). The AMC factors can be looked up in a reference table.
Empirical
The word empirical denotes information gained by means of observation or experimentation. Empirical data are data produced by an experiment or observation....
parameter used in hydrology
Hydrology
Hydrology is the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth and other planets, including the hydrologic cycle, water resources and environmental watershed sustainability...
for predicting direct runoff
Surface runoff
Surface runoff is the water flow that occurs when soil is infiltrated to full capacity and excess water from rain, meltwater, or other sources flows over the land. This is a major component of the water cycle. Runoff that occurs on surfaces before reaching a channel is also called a nonpoint source...
or infiltration
Infiltration (hydrology)
Infiltration is the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil. Infiltration rate in soil science is a measure of the rate at which soil is able to absorb rainfall or irrigation. It is measured in inches per hour or millimeters per hour. The rate decreases as the soil becomes...
from rainfall
Rain
Rain is liquid precipitation, as opposed to non-liquid kinds of precipitation such as snow, hail and sleet. Rain requires the presence of a thick layer of the atmosphere to have temperatures above the melting point of water near and above the Earth's surface...
excess. The curve number method was developed by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service
Natural Resources Conservation Service
The Natural Resources Conservation Service , formerly known as the Soil Conservation Service , is an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture that provides technical assistance to farmers and other private landowners and managers.Its name was changed in 1994 during the Presidency of...
, which was formerly called the Soil Conservation Service or SCS — the number is still popularly known as a "SCS runoff curve number" in the literature. The runoff curve number was developed from an empirical analysis
Empirical method
The empirical method is generally taken to mean the approach of using a collection of data to base a theory or derive a conclusion in science...
of runoff from small catchments and hillslope plots monitored by the USDA. It is widely used and is an efficient method for determining the approximate amount of direct runoff from a rainfall
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
event in a particular area.
The runoff curve number is based on the area's hydrologic soil group, land use
Land use
Land use is the human use of land. Land use involves the management and modification of natural environment or wilderness into built environment such as fields, pastures, and settlements. It has also been defined as "the arrangements, activities and inputs people undertake in a certain land cover...
, treatment and hydrologic condition. References, such as from USDA indicate the runoff curve numbers for characteristic land cover descriptions and a hydrologic soil group.
The runoff equation is
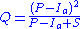
where
 is runoff
is runoffSurface runoff
Surface runoff is the water flow that occurs when soil is infiltrated to full capacity and excess water from rain, meltwater, or other sources flows over the land. This is a major component of the water cycle. Runoff that occurs on surfaces before reaching a channel is also called a nonpoint source...
([L]; in)
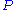 is rainfall
is rainfallRain
Rain is liquid precipitation, as opposed to non-liquid kinds of precipitation such as snow, hail and sleet. Rain requires the presence of a thick layer of the atmosphere to have temperatures above the melting point of water near and above the Earth's surface...
([L]; in)
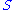 is the potential maximum soil moisture retention after runoff begins ([L]; in)
is the potential maximum soil moisture retention after runoff begins ([L]; in)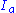 is the initial abstraction ([L]; in), or the amount of water before runoff, such as infiltration
is the initial abstraction ([L]; in), or the amount of water before runoff, such as infiltrationInfiltration (hydrology)
Infiltration is the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil. Infiltration rate in soil science is a measure of the rate at which soil is able to absorb rainfall or irrigation. It is measured in inches per hour or millimeters per hour. The rate decreases as the soil becomes...
, or rainfall interception by vegetation; and it is generally assumed that
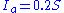
The runoff curve number,
 , is then related
, is then related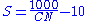
 has a range from 30 to 100; lower numbers indicate low runoff potential while larger numbers are for increasing runoff potential. The lower the curve number, the more permeable the soil is.
has a range from 30 to 100; lower numbers indicate low runoff potential while larger numbers are for increasing runoff potential. The lower the curve number, the more permeable the soil is.Antecedent moisture condition (AMC) adjustment
Runoff is affected by the soil moisture before a precipitation event, or the antecedent moisture condition (AMC). A curve number, as calculated above, may also be termed AMC II or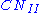 , or average soil moisture. The other moisture conditions are dry, AMC I or
, or average soil moisture. The other moisture conditions are dry, AMC I or 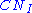 , and moist, AMC III or
, and moist, AMC III or 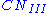 . The curve number can be adjusted by factors to
. The curve number can be adjusted by factors to 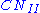 , where
, where 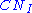 factors are less than 1 (reduce
factors are less than 1 (reduce  and potential runoff), while
and potential runoff), while 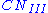 factor are greater than 1 (increase
factor are greater than 1 (increase  and potential runoff). The AMC factors can be looked up in a reference table.
and potential runoff). The AMC factors can be looked up in a reference table.External links
- SCS TR-55 Peak Discharge and Runoff Calculator
- Curve Number Calculator Online Free Curver Number Calculator
- Introduction to SCS Runoff Curve Number Method

