
Cranial vault
Encyclopedia
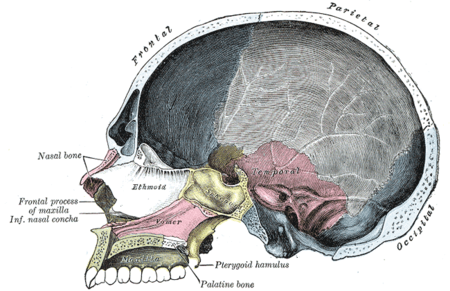
Skull
The skull is a bony structure in the head of many animals that supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. A skull without a mandible is only a cranium. Animals that have skulls are called craniates...
within the neurocranium, occupied by the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
. In human
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
s, the size and shape of the brain, may be affected by the size of the vault as shown in craniometry, but studies relating it to intelligence have been ambivalent. The vault is alternatively called "skullcap" or even calvaria
Calvaria (skull)
The calvaria is the upper part of the cranium and surrounds the cranial cavity containing the brain.The calvaria is made up of the frontal, occipital and right and left parietals....
, though these properly refer to the upper portion of the skull only.
Development
In humans, the cranial vault is imperfectly composed in newborns, to allow the large human head to pass through the birth canal. During birth, the various bones connected by cartilageCartilage
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in many areas in the bodies of humans and other animals, including the joints between bones, the rib cage, the ear, the nose, the elbow, the knee, the ankle, the bronchial tubes and the intervertebral discs...
and ligament
Ligament
In anatomy, the term ligament is used to denote any of three types of structures. Most commonly, it refers to fibrous tissue that connects bones to other bones and is also known as articular ligament, articular larua, fibrous ligament, or true ligament.Ligament can also refer to:* Peritoneal...
s only will move relatively to each other. The open portion between the major bones of the upper part of the vault, called fontanelle
Fontanelle
A fontanelle is an anatomical feature on an infant's skull.-Anatomy:Fontanelles are soft spots on a baby's head which, during birth, enable the bony plates of the skull to flex, allowing the child's head to pass through the birth canal. The ossification of the bones of the skull causes the...
s, normally remain soft up to two years after birth.
As the fontanelles close, the vault loses some of its plasticity. The sutures between the bones remain until 30 to 40 years of age, allowing for growth of the brain. Cranial vault size is directly proportional to skull size and is developed early.
The size and shape of the brain and the surrounding vault remain quite plastic as the brain grows in childhood. In several ancient societies, head shape was altered for aesthetic or religious reasons by binding cloth or boards tightly around the head during infancy. It is not known whether such artificial cranial deformation
Artificial cranial deformation
Artificial cranial deformation, head flattening, or head binding is a form of permanent body alteration in which the skull of a human being is intentionally deformed. It is done by distorting the normal growth of a child's skull by applying force...
has an effect in mental capacity.
Evolution
The cranial vault is composed of the endocraniumEndocranium
For internal cast of the cranium, see Endocast.The endocranium in comparative anatomy is a part of the skull base in vertebrates and represent the basal, inner part of the cranium. The term is also applied to the outer layer of the dura mater in human anatomy.-Basic structure:Structurally, the...
forming the basal parts, topped by the skull roof
Skull roof
The skull roof , or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes and all land living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone, hence the alternative name dermatocranium...
in land vertebrates
Tetrapod
Tetrapods are vertebrate animals having four limbs. Amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals are all tetrapods; even snakes and other limbless reptiles and amphibians are tetrapods by descent. The earliest tetrapods evolved from the lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian...
.
In fishes no distinct cranial vault as such exists, the skull being composed of loosely jointed bones. The cranial vault as a distinct unit arose with the fusion of the skull roof
Skull roof
The skull roof , or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes and all land living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone, hence the alternative name dermatocranium...
and the endocranium
Endocranium
For internal cast of the cranium, see Endocast.The endocranium in comparative anatomy is a part of the skull base in vertebrates and represent the basal, inner part of the cranium. The term is also applied to the outer layer of the dura mater in human anatomy.-Basic structure:Structurally, the...
on the early Labyrinthodonts. In amphibians and reptiles the vault is rather small and inconspicuous, only forming proper vaults in mammals and birds.

