Cost push inflation
Encyclopedia
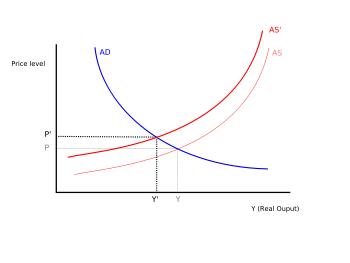
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
caused by substantial increases in the cost of important goods or services where no suitable alternative is available.Inflation originating from increase in cost is known as cost-push inflation or supply side inflation A situation that has been often cited of this was the oil crisis
1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis started in October 1973, when the members of Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries or the OAPEC proclaimed an oil embargo. This was "in response to the U.S. decision to re-supply the Israeli military" during the Yom Kippur war. It lasted until March 1974. With the...
of the 1970s, which some economists see as a major cause of the inflation experienced in the Western world
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West and the Occident , is a term referring to the countries of Western Europe , the countries of the Americas, as well all countries of Northern and Central Europe, Australia and New Zealand...
in that decade. It is argued that this inflation resulted from increases in the cost of petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
imposed by the member states of OPEC
OPEC
OPEC is an intergovernmental organization of twelve developing countries made up of Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela. OPEC has maintained its headquarters in Vienna since 1965, and hosts regular meetings...
. Since petroleum is so important to industrialised economies, a large increase in its price can lead to the increase in the price of most products, raising the inflation rate
Inflation rate
In economics, the inflation rate is a measure of inflation, the rate of increase of a price index . It is the percentage rate of change in price level over time. The rate of decrease in the purchasing power of money is approximately equal.The inflation rate is used to calculate the real interest...
. This can raise the normal or built-in inflation
Built-in inflation
Built-in inflation is a type of inflation that results from past events and persists in the present.Built-in inflation is one of three major determinants of the current inflation rate. In Robert J. Gordon's triangle model of inflation, the current inflation rate equals the sum of demand-pull...
rate, reflecting adaptive expectations
Adaptive expectations
In economics, adaptive expectations means that people form their expectations about what will happen in the future based on what has happened in the past...
and the price/wage spiral
Price/wage spiral
In macroeconomics, the price/wage spiral represents a vicious circle process in which different sides of the wage bargain try to keep up with inflation to protect real incomes. Thus, this process is one possible result of inflation...
, so that a supply shock
Supply shock
A supply shock is an event that suddenly changes the price of a commodity or service. It may be caused by a sudden increase or decrease in the supply of a particular good. This sudden change affects the equilibrium price....
can have persistent effects.
Keynesians argue that in a modern industrial economy, many prices are sticky downward or downward inflexible, so that instead of prices falling in this story, a supply shock would cause a recession
Recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction, a general slowdown in economic activity. During recessions, many macroeconomic indicators vary in a similar way...
, i.e., rising unemployment
Unemployment
Unemployment , as defined by the International Labour Organization, occurs when people are without jobs and they have actively sought work within the past four weeks...
and falling gross domestic product
Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
. It is the costs of such a recession that likely causes governments and central banks to allow a supply shock to result in inflation.
They also note that though there was no deflation in the 1980s, there was a definite fall in the inflation rate during this period. Actual deflation was prevented because supply shocks are not the only cause of inflation; in terms of the modern triangle model
Triangle model
In macroeconomics, the triangle model employed by new Keynesian economics is a model of inflation derived from the Phillips Curve and given its name by Robert J. Gordon. The model views inflation as having three root causes: built-in inflation, demand-pull inflation, and cost-push inflation...
of inflation, supply-driven deflation was counteracted by demand-pull inflation and built-in inflation resulting from adaptive expectations
Adaptive expectations
In economics, adaptive expectations means that people form their expectations about what will happen in the future based on what has happened in the past...
and the price/wage spiral.
Monetarist
Monetarism
Monetarism is a tendency in economic thought that emphasizes the role of governments in controlling the amount of money in circulation. It is the view within monetary economics that variation in the money supply has major influences on national output in the short run and the price level over...
economists such as Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman was an American economist, statistician, academic, and author who taught at the University of Chicago for more than three decades...
argue against the concept of cost-push inflation because increases in the cost of goods and services do not lead to inflation without the government and its central bank
Central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is a public institution that usually issues the currency, regulates the money supply, and controls the interest rates in a country. Central banks often also oversee the commercial banking system of their respective countries...
cooperating in increasing the money supply
Money supply
In economics, the money supply or money stock, is the total amount of money available in an economy at a specific time. There are several ways to define "money," but standard measures usually include currency in circulation and demand deposits .Money supply data are recorded and published, usually...
. The argument is that if the money supply is constant, increases in the cost of a good or service will decrease the money available for other goods and services, and therefore the price of some those goods will fall and offset the rise in price of those goods whose prices have increased. One consequence of this is that monetarist economists do not believe that the rise in the cost of oil was a direct cause of the inflation of the 1970s. They argue that although the price of oil went back down in the 1980s, there was no corresponding deflation
Deflation (economics)
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% . This should not be confused with disinflation, a slow-down in the inflation rate...
.

