
Supply shock
Encyclopedia
Commodity
In economics, a commodity is the generic term for any marketable item produced to satisfy wants or needs. Economic commodities comprise goods and services....
or service. It may be caused by a sudden increase or decrease in the supply
Supply (economics)
In economics, supply is the amount of some product producers are willing and able to sell at a given price all other factors being held constant. Usually, supply is plotted as a supply curve showing the relationship of price to the amount of product businesses are willing to sell.In economics the...
of a particular good. This sudden change affects the equilibrium price.
A negative supply shock (sudden supply decrease) will raise prices and shift the aggregate supply
Aggregate supply
In economics, aggregate supply is the total supply of goods and services that firms in a national economy plan on selling during a specific time period...
curve to the left. A negative supply shock can cause stagflation
Stagflation
In economics, stagflation is a situation in which the inflation rate is high and the economic growth rate slows down and unemployment remains steadily high...
due to a combination of raising prices and falling output.
A positive supply shock (an increase in supply) will lower the price of said good and shift the aggregate supply curve to the right. A positive supply shock could be an advance in technology (a technology shock
Technology shocks
Technology shocks are events in a macroeconomic model, that change the production function. Usually this is modelled with an aggregate production function that has a scaling factor....
) which makes production more efficient, thus increasing output.
An example of a negative supply shock is the increase in oil prices during the 1973 energy crisis.
Technical analysis
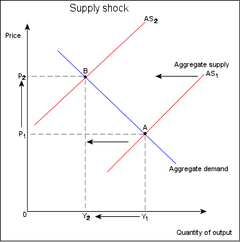
The diagram to the right demonstrates a negative supply shock; The initial position is at point A, producing Y1 quantity, at P1 prices. Then there is a supply shock, this has an adverse effect on aggregate supply, the supply curve shifts left (from AS1 to AS2), while the demand curve stays in the same position. The intersection of the supply and demand curves has now moved and the equilibrium is now point B, quantity has been reduced to Y2, while prices have been increased to P2.See also
- Demand shockDemand shockIn economics, a demand shock is a sudden event that increases or decreases demand for goods or services temporarily. A positive demand shock increases demand and a negative demand shock decreases demand. Prices of goods and services are affected in both cases. When demand for a good or service...
- MacroeconomicsMacroeconomicsMacroeconomics is a branch of economics dealing with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of the whole economy. This includes a national, regional, or global economy...
- StagflationStagflationIn economics, stagflation is a situation in which the inflation rate is high and the economic growth rate slows down and unemployment remains steadily high...
- Supply and demandSupply and demandSupply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded by consumers will equal the quantity supplied by producers , resulting in an...

