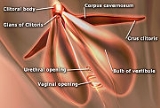
Corpus cavernosum clitoridis
Encyclopedia
The corpus cavernosum clitoridis is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue
which contain most of the blood
in the clitoris
during clitoral erection
. This is homologous
to the corpus cavernosum penis
in the male; the body of the clitoris
contains erectile tissue
in a pair of corpora cavernosa (literally "cave-like bodies"), with a recognisably similar structure.
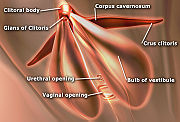 The two corpora cavernosa are expandable erectile tissues which fill with blood
The two corpora cavernosa are expandable erectile tissues which fill with blood
during clitoral erection
. These formations are made of a sponge-like tissue containing irregular blood-filled spaces lined by endothelium
and separated by connective tissue
septa
. United together along their medial surfaces by an incomplete fibrous pectiniform septum; each corpus is connected to the rami
of the pubis
and ischium by a clitoral crus
.
The female anatomy has two vestibular bulbs
beneath the skin
of the labia minora
(at the entrance to the vagina
), which expand at the same time as the glans clitoris to cap the ends of the corpora cavernosa. This is homologous with the corpus spongiosum
of the male anatomy.
precedes relaxation of the clitoral cavernosal artery and nearby muscle
, in a process similar to male arousal. More blood flows in through the clitoral cavernosal artery
, the pressure
in the corpora cavernosa clitoridis rises, and the clitoris is engorged with blood
. This leads to extrusion of the glans clitoridis and enhanced sensitivity
to physical contact.
Erectile tissue
Erectile tissue is tissue in the body that can become erect, usually by becoming engorged with blood.-Erectile tissue in the clitoris and penis:...
which contain most of the blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
in the clitoris
Clitoris
The clitoris is a sexual organ that is present only in female mammals. In humans, the visible button-like portion is located near the anterior junction of the labia minora, above the opening of the urethra and vagina. Unlike the penis, which is homologous to the clitoris, the clitoris does not...
during clitoral erection
Clitoral erection
Clitoral erection is a physiological phenomenon where the clitoris becomes enlarged and firm. Clitoral erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular and endocrine factors, and is usually, though not exclusively, associated with sexual...
. This is homologous
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
to the corpus cavernosum penis
Corpus cavernosum penis
The corpus cavernosum penis is one of a pair of sponge-like regions of erectile tissue which contain most of the blood in the penis during penile erection...
in the male; the body of the clitoris
Clitoris
The clitoris is a sexual organ that is present only in female mammals. In humans, the visible button-like portion is located near the anterior junction of the labia minora, above the opening of the urethra and vagina. Unlike the penis, which is homologous to the clitoris, the clitoris does not...
contains erectile tissue
Erectile tissue
Erectile tissue is tissue in the body that can become erect, usually by becoming engorged with blood.-Erectile tissue in the clitoris and penis:...
in a pair of corpora cavernosa (literally "cave-like bodies"), with a recognisably similar structure.
Anatomy

Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
during clitoral erection
Clitoral erection
Clitoral erection is a physiological phenomenon where the clitoris becomes enlarged and firm. Clitoral erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular and endocrine factors, and is usually, though not exclusively, associated with sexual...
. These formations are made of a sponge-like tissue containing irregular blood-filled spaces lined by endothelium
Endothelium
The endothelium is the thin layer of cells that lines the interior surface of blood vessels, forming an interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. These cells are called endothelial cells. Endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart...
and separated by connective tissue
Connective tissue
"Connective tissue" is a fibrous tissue. It is one of the four traditional classes of tissues . Connective Tissue is found throughout the body.In fact the whole framework of the skeleton and the different specialized connective tissues from the crown of the head to the toes determine the form of...
septa
Septum
In anatomy, a septum is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones.-In human anatomy:...
. United together along their medial surfaces by an incomplete fibrous pectiniform septum; each corpus is connected to the rami
Rami
Rami or RAMI can refer to:*Rami, the plural of ramus, literally a branch, as of a plant, nerve, or blood vessel*Specifically, rami are upward portions on both sides of the mandible...
of the pubis
Pubis
Pubis may refer to:* Pubis * Mons pubis, a padding of fat that protects the pubis bone...
and ischium by a clitoral crus
Clitoral crura
- Anatomy :The clitoral crura are an internal portion of the clitoris. A single one is called a clitoral crus. They are shaped like an inverted "V" with the vertex of the "V" connecting to the clitoral body....
.
The female anatomy has two vestibular bulbs
Vestibular bulbs
The vestibular bulbs, also known as the clitoral bulbs, are aggregations of erectile tissue that are an internal part of the clitoris. They can also be found throughout the vestibule: next to the clitoral body, clitoral crura, urethra, urethral sponge, and vagina.They are to the left and right of...
beneath the skin
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
of the labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
(at the entrance to the vagina
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
), which expand at the same time as the glans clitoris to cap the ends of the corpora cavernosa. This is homologous with the corpus spongiosum
Corpus spongiosum
Corpus spongiosum is the mass of spongy tissue surrounding the male urethra within the penis...
of the male anatomy.
Physiology
In some circumstances, release of nitric oxideNitric oxide
Nitric oxide, also known as nitrogen monoxide, is a diatomic molecule with chemical formula NO. It is a free radical and is an important intermediate in the chemical industry...
precedes relaxation of the clitoral cavernosal artery and nearby muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
, in a process similar to male arousal. More blood flows in through the clitoral cavernosal artery
Artery
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. This blood is normally oxygenated, exceptions made for the pulmonary and umbilical arteries....
, the pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
in the corpora cavernosa clitoridis rises, and the clitoris is engorged with blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
. This leads to extrusion of the glans clitoridis and enhanced sensitivity
Sensitivity
Stimulus|Sensitivity may refer to:* Sensitivity , the ability to react to a stimulus* Sensitivity , the strength of physical or emotional reaction in people* Sensitivity , variations in process dynamics and control systems...
to physical contact.

