Erectile tissue
Encyclopedia
Erectile tissue is tissue in the body that can become erect, usually by becoming engorged with blood
.
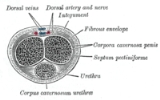
 Erectile tissue exists in places such as the corpora cavernosa of the penis
Erectile tissue exists in places such as the corpora cavernosa of the penis
, and in the clitoris
or in the bulbs of vestibule. During erection
, the corpora cavernosa will become engorged with venous blood, a process called tumescence. This may result from any of various physiological stimuli, also known as sexual arousal
. The corpus spongiosum is a single tubular structure located just below the corpora cavernosa. This may also become slightly engorged with blood, but less so than the corpora cavernosa.
, perineal sponge
, and vestibular bulbs
. The erection
of nipples is not due to erectile tissue, but rather due to the contraction of smooth muscle
under the control of the autonomic nervous system
.
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
.
Erectile tissue in the clitoris and penis

Penis
The penis is a biological feature of male animals including both vertebrates and invertebrates...
, and in the clitoris
Clitoris
The clitoris is a sexual organ that is present only in female mammals. In humans, the visible button-like portion is located near the anterior junction of the labia minora, above the opening of the urethra and vagina. Unlike the penis, which is homologous to the clitoris, the clitoris does not...
or in the bulbs of vestibule. During erection
Erection
Penile erection is a physiological phenomenon where the penis becomes enlarged and firm. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular and endocrine factors, and is usually, though not exclusively, associated with sexual arousal...
, the corpora cavernosa will become engorged with venous blood, a process called tumescence. This may result from any of various physiological stimuli, also known as sexual arousal
Sexual arousal
Sexual arousal, or sexual excitement, is the arousal of sexual desire, during or in anticipation of sexual activity. Things that precipitate human sexual arousal are called erotic stimuli, or colloquially known as turn-ons. There are many potential stimuli, both physical or mental, which can cause...
. The corpus spongiosum is a single tubular structure located just below the corpora cavernosa. This may also become slightly engorged with blood, but less so than the corpora cavernosa.
Other erectile tissue
Erectile tissue is also found in the nose, ear, urethral spongeUrethral sponge
The urethral sponge is a spongy cushion of tissue, found in the lower genital area of women, that sits against both the pubic bone and vaginal wall, and surrounds the urethra.-Functions:...
, perineal sponge
Perineal sponge
The perineal sponge is a spongy cushion of tissue and blood vessels, found in the lower genital area of women. It sits between the vagina and rectum and is internal to the perineum and perineal body.-Functions:...
, and vestibular bulbs
Vestibular bulbs
The vestibular bulbs, also known as the clitoral bulbs, are aggregations of erectile tissue that are an internal part of the clitoris. They can also be found throughout the vestibule: next to the clitoral body, clitoral crura, urethra, urethral sponge, and vagina.They are to the left and right of...
. The erection
Erection
Penile erection is a physiological phenomenon where the penis becomes enlarged and firm. Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular and endocrine factors, and is usually, though not exclusively, associated with sexual arousal...
of nipples is not due to erectile tissue, but rather due to the contraction of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle. It is divided into two sub-groups; the single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit smooth muscle tissues, the autonomic nervous system innervates a single cell within a sheet or bundle and the action potential is propagated by...
under the control of the autonomic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
.

