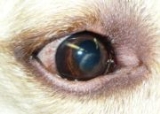
Corneal dystrophy
Encyclopedia
Corneal dystrophy is a group of disorders, characterised by a noninflammatory, inherited, bilateral opacity of the transparent front part of the eye
called the cornea
.
The distrophies could be subdivided based on specie affected:
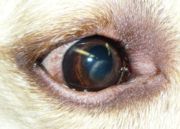
. Corneal dystrophy can also have a crystalline appearance.
s or cholesterol
crystals.
With penetrating keratoplasty (corneal transplant), the long term results are good-excellent. Recent surgical improvements have been made which have increased the success rate for this procedure. However, recurrence of the disease in the donor graft is not ruled out.
.
Corneal endothelial dystrophy is an age-related change that affects the inner layer of the cornea, the endothelium.
Eye
Eyes are organs that detect light and convert it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons. The simplest photoreceptors in conscious vision connect light to movement...
called the cornea
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Together with the lens, the cornea refracts light, with the cornea accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is...
.
The distrophies could be subdivided based on specie affected:
- Corneal dystrophies in human
- Corneal dystrophies in dogsCorneal dystrophies in dogsCorneal dystrophy is not uncommon in some canine breeds.-Treatment:Suboptimal vision caused by corneal dystrophy usually requires surgical intervention in the form of corneal transplantation. Penetrating keratoplasty is commonly performed for extensive corneal dystrophy...
- Corneal dystrophies in cats

Signs and symptoms
Corneal dystrophy may not significantly affect vision in the early stages. However, it does require proper evaluation and treatment for restoration of optimal vision. It can, however, rarely cause corneal ulceration, especially with epithelial dystrophy. It appears as grayish white lines, circles, or clouding of the corneaCornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Together with the lens, the cornea refracts light, with the cornea accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is...
. Corneal dystrophy can also have a crystalline appearance.
Pathophysiology
A corneal dystrophy can be caused by an accumulation of extraneous material in the cornea - it can be in the form of lipidLipid
Lipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
s or cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
crystals.
Classification
Corneal dystrophies are commonly subdivided depending on its specific location within the cornea. It can be basically divided into anterior, stromal, or posterior according to the layer of the cornea affected by the dystrophy. http://www.eyeworld.org/article.php?sid=3199 http://www.bchealthguide.org/kbase/nord/nord455.htmTreatment
Suboptimal vision caused by corneal dystrophy usually requires surgical intervention in the form of corneal transplantation. Penetrating keratoplasty is commonly performed for extensive corneal dystrophy.Prognosis
Early stages may be asymptomatic and may not require any intervention. Initial treatment may include hypertonic eyedrops and/or ointment to reduce the corneal edema and may offer symptomatic improvement prior to surgical intervention.With penetrating keratoplasty (corneal transplant), the long term results are good-excellent. Recent surgical improvements have been made which have increased the success rate for this procedure. However, recurrence of the disease in the donor graft is not ruled out.
Corneal endothelial dystrophy
Corneal endothelial dystrophy is an age-related change that affects the inner layer of the corneal, the endotheliumCorneal endothelium
The corneal endothelium is a single layer of cells on the inner surface of the cornea. It faces the chamber formed between the cornea and the iris....
.
See also
- Recurrent corneal erosionRecurrent corneal erosionRecurrent corneal erosion is a disorder of the eyes characterized by the failure of the cornea's outermost layer of epithelial cells to attach to the underlying basement membrane...
- KeratoconusKeratoconusKeratoconus , is a degenerative disorder of the eye in which structural changes within the cornea cause it to thin and change to a more conical shape than its normal gradual curve....
- KeratoglobusKeratoglobusKeratoglobus , is a degenerative non-inflammatory disorder of the eye in which structural changes within the cornea cause it to become extremely thin and change to a more globular shape than its normal gradual curve...
- Macular corneal dystrophyMacular corneal dystrophyMacular corneal dystrophy is a rare pathological condition affecting the stroma of cornea. The first signs are usually noticed in the first decade of life, and progress afterwards, with opacities developing in the cornea and attacks of pain...
- Reis-Bucklers corneal dystrophy
Corneal endothelial dystrophy is an age-related change that affects the inner layer of the cornea, the endothelium.
External links
- Facts About the Cornea and Corneal Disease The National Eye Institute (NEI)

