Contrast effect
Encyclopedia
A contrast effect is the enhancement or diminishment, relative to normal, of perception
, cognition
and related performance as a result of immediately previous or simultaneous exposure to a stimulus
of lesser or greater value in the same dimension. (Here, normal perception or performance is that which would be obtained in the absence of the comparison stimulus—i.e., one based on all previous experience.)
Contrast
effects are ubiquitous throughout human and non-human animal perception, cognition, and resultant performance. A hefted weight is perceived as heavier than normal when "contrasted" with a lighter weight. It is perceived as lighter than normal when contrasted with a heavier weight. An animal works harder than normal for a given amount of reward when that amount is contrasted with a lesser amount and works less energetically for that given amount when it is contrasted with a greater amount. A person appears more appealing than normal when contrasted with a person of less appeal
and less appealing than normal when contrasted with one of greater appeal.
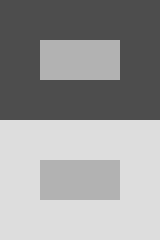
 Simultaneous contrast identified by Michel Eugène Chevreul
Simultaneous contrast identified by Michel Eugène Chevreul
refers to the manner in which the color
s of two different objects affect each other. The effect is more noticeable when shared between objects of complementary color
.
In the image here, the two inner rectangles are exactly the same shade of grey, but the upper one appears to be a lighter grey than the lower one due to the background provided by the outer rectangles.
This is a different concept from contrast
, which by itself refers to one object's difference in color and luminance
compared to its surroundings or background.
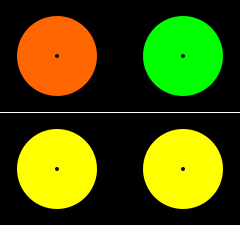 Successive contrast occurs when the perception of currently viewed stimuli is modulated by previously viewed stimuli.
Successive contrast occurs when the perception of currently viewed stimuli is modulated by previously viewed stimuli.
For example, when one stares at the dot in the center of one of the two colored disks on the top row for a few seconds and then looks at the dot in the center of the disk on the same side in the bottom row, the two lower disks, though identically colored, appear to have different colors for a few moments.
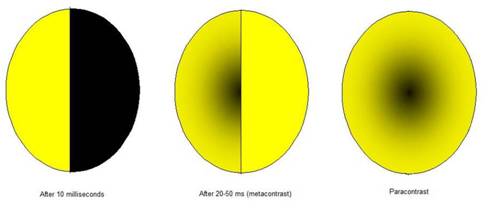
One type of contrast that involves both time and space is metacontrast and paracontrast. When one half of a circle is lit for 10 milliseconds, it is at its maximum intensity. If the other half is displayed at the same time (but 20-50 ms later), there is a mutual inhibition: the left side is darkened by the right half (metacontrast), and the center may be completely obliterated. At the same time, there is a slight darkening of the right side due to the first stimulus; this is paracontrast.
, who observed that lukewarm water can feel hot or cold, depending on whether the hand touching it was previously in hot or cold water. In the early 20th Century, Wilhelm Wundt
identified contrast as a fundamental principle of perception, and since then the effect has been confirmed in many different areas. Contrast effects shape not only visual qualities like color and brightness, but other kinds of perception, including the perception of weight. One experiment found that thinking of the name "Hitler" led to subjects rating a person as more friendly. Whether a piece of music is perceived as good or bad can depend on whether the music heard before it was unpleasant or pleasant. For the effect to work, the objects being compared need to be similar to each other: a television reporter can seem to shrink when interviewing a tall basketball player, but not when standing next to a tall building.
Perception
Perception is the process of attaining awareness or understanding of the environment by organizing and interpreting sensory information. All perception involves signals in the nervous system, which in turn result from physical stimulation of the sense organs...
, cognition
Cognition
In science, cognition refers to mental processes. These processes include attention, remembering, producing and understanding language, solving problems, and making decisions. Cognition is studied in various disciplines such as psychology, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science...
and related performance as a result of immediately previous or simultaneous exposure to a stimulus
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity....
of lesser or greater value in the same dimension. (Here, normal perception or performance is that which would be obtained in the absence of the comparison stimulus—i.e., one based on all previous experience.)
Contrast
Contrast
Contrast may refer to:* Contrast , the difference in color and light between parts of an image* Contrast , expressing distinctions between words...
effects are ubiquitous throughout human and non-human animal perception, cognition, and resultant performance. A hefted weight is perceived as heavier than normal when "contrasted" with a lighter weight. It is perceived as lighter than normal when contrasted with a heavier weight. An animal works harder than normal for a given amount of reward when that amount is contrasted with a lesser amount and works less energetically for that given amount when it is contrasted with a greater amount. A person appears more appealing than normal when contrasted with a person of less appeal
Appeal
An appeal is a petition for review of a case that has been decided by a court of law. The petition is made to a higher court for the purpose of overturning the lower court's decision....
and less appealing than normal when contrasted with one of greater appeal.
Types

Michel Eugène Chevreul
Michel Eugène Chevreul was a French chemist whose work with fatty acids led to early applications in the fields of art and science. He is credited with the discovery of margaric acid and designing an early form of soap made from animal fats and salt...
refers to the manner in which the color
Color
Color or colour is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue and others. Color derives from the spectrum of light interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors...
s of two different objects affect each other. The effect is more noticeable when shared between objects of complementary color
Complementary color
Complementary colors are pairs of colors that are of “opposite” hue in some color model. The exact hue “complementary” to a given hue depends on the model in question, and perceptually uniform, additive, and subtractive color models, for example, have differing complements for any given color.-...
.
In the image here, the two inner rectangles are exactly the same shade of grey, but the upper one appears to be a lighter grey than the lower one due to the background provided by the outer rectangles.
This is a different concept from contrast
Contrast (vision)
Contrast is the difference in visual properties that makes an object distinguishable from other objects and the background. In visual perception of the real world, contrast is determined by the difference in the color and brightness of the object and other objects within the same field of view...
, which by itself refers to one object's difference in color and luminance
Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square...
compared to its surroundings or background.

For example, when one stares at the dot in the center of one of the two colored disks on the top row for a few seconds and then looks at the dot in the center of the disk on the same side in the bottom row, the two lower disks, though identically colored, appear to have different colors for a few moments.
One type of contrast that involves both time and space is metacontrast and paracontrast. When one half of a circle is lit for 10 milliseconds, it is at its maximum intensity. If the other half is displayed at the same time (but 20-50 ms later), there is a mutual inhibition: the left side is darkened by the right half (metacontrast), and the center may be completely obliterated. At the same time, there is a slight darkening of the right side due to the first stimulus; this is paracontrast.

Domains
The contrast effect was noted by the 17th Century philosopher John LockeJohn Locke
John Locke FRS , widely known as the Father of Liberalism, was an English philosopher and physician regarded as one of the most influential of Enlightenment thinkers. Considered one of the first of the British empiricists, following the tradition of Francis Bacon, he is equally important to social...
, who observed that lukewarm water can feel hot or cold, depending on whether the hand touching it was previously in hot or cold water. In the early 20th Century, Wilhelm Wundt
Wilhelm Wundt
Wilhelm Maximilian Wundt was a German physician, psychologist, physiologist, philosopher, and professor, known today as one of the founding figures of modern psychology. He is widely regarded as the "father of experimental psychology"...
identified contrast as a fundamental principle of perception, and since then the effect has been confirmed in many different areas. Contrast effects shape not only visual qualities like color and brightness, but other kinds of perception, including the perception of weight. One experiment found that thinking of the name "Hitler" led to subjects rating a person as more friendly. Whether a piece of music is perceived as good or bad can depend on whether the music heard before it was unpleasant or pleasant. For the effect to work, the objects being compared need to be similar to each other: a television reporter can seem to shrink when interviewing a tall basketball player, but not when standing next to a tall building.
See also
- Chubb illusionChubb illusionThe Chubb illusion is an optical illusion wherein the apparent contrast of an object varies dramatically, depending on the context of the presentation. Low-contrast texture surrounded by a uniform field appears to have higher contrast than when it is surrounded by high-contrast texture...
- Negative (Positive) contrast effectNegative (positive) contrast effect-Negative contrast effect in operant conditioning:In the behavioral theory of operant conditioning, the negative contrast effect is evident when an attempt to reinforce a particular behavior through reward; when the rewards are finally withdrawn or reduced the subject is even less likely to...
- List of cognitive biases

